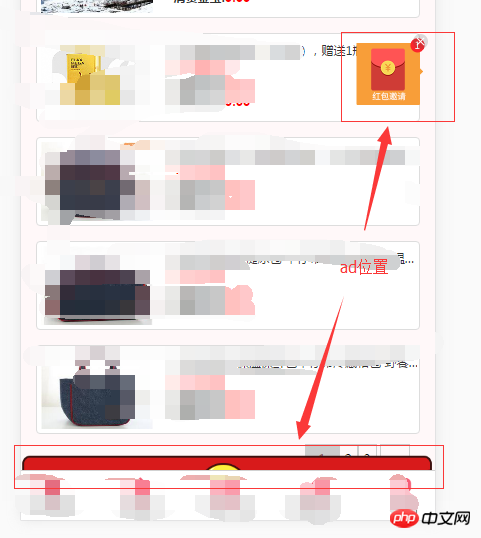
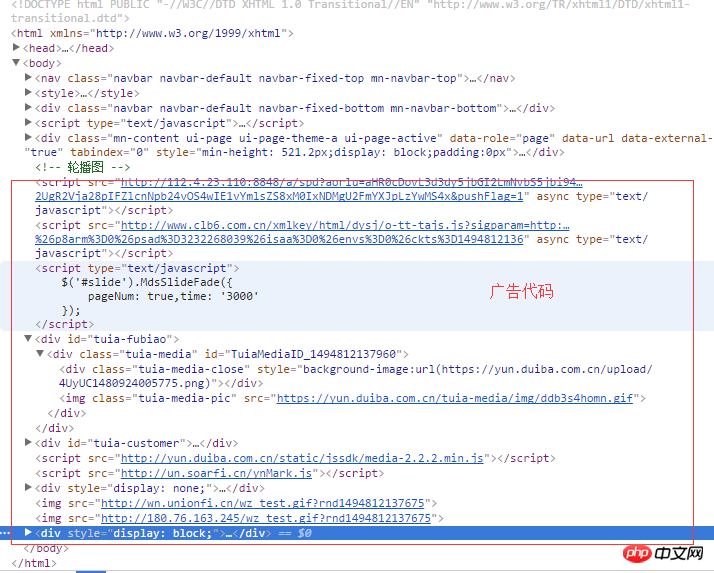
The frequency of occurrence is about 1%.
These are not in the source code of the website. I don’t know if there is a virus on the server or if there is a problem with the imported js file.
I would like to ask you why this situation occurs and possible solutions. Thank you all.
迷茫2017-05-16 12:04:10
If there is a problem with js, search for ads in the js source code域名或ip
The chance of server poisoning is generally low, you can leave it until the end
DNS hijacking, this is the most disgusting and the most frequent. No solution has been found except upgrading HTTPS
伊谢尔伦2017-05-16 12:04:10
Operator hijacking, common in certain country’s telecommunications, call to complain;
Router hijacking, please try again in a different network environment;
Server or DNS hijacking, agree to upgrade HTTPS upstairs;
仅有的幸福2017-05-16 12:04:10
There are two possibilities: 1. Your server’s DNS has been hijacked (including the URL of the js code you introduced may carry advertisements); 2. Your server has been poisoned.
漂亮男人2017-05-16 12:04:10
The content has been tampered with.
Confirm whether the source code on the server has been modified, or whether it has been tampered with during network transmission.
If it was modified during transmission, then try to use detection tools (17ce, webmaster tools, etc.) to see which regions/operators requested content that has been tampered with. You can try to contact your local operator to complain.
I saw a lot of people talking about "DNS hijacking". Are DNS hijacking and HTTP session hijacking (content tampering) confused?
DNS hijacking is a problem when the DNS server resolves the domain name (DNS returns a fake IP, and then the browser sends a request to the fake IP server). DNS resolution does not distinguish between HTTP/HTTPS;
HTTP session hijacking refers to tampering with the content during the transmission process, or forging a copy of the content and returning it to the requester without waiting for the origin server to respond (it will be discarded when the real origin server response content arrives);
There is another possibility that the content on the source server has been tampered with, and it is not a problem during the transmission process.
(However, the question says that it occurs with probability, so it should be a problem during the transmission process)
黄舟2017-05-16 12:04:10
You used a third-party plug-in script with ads embedded in it. Just delete it after you find it
给我你的怀抱2017-05-16 12:04:10
Check if you have ever used svg? Just remove the advertising links inside.
过去多啦不再A梦2017-05-16 12:04:10
DNS Hijacking You really have no choice, upgrade to HTTPS quickly!
仅有的幸福2017-05-16 12:04:10
Open your website and press F12 to open the developer tools.
Switch to the tab as shown below
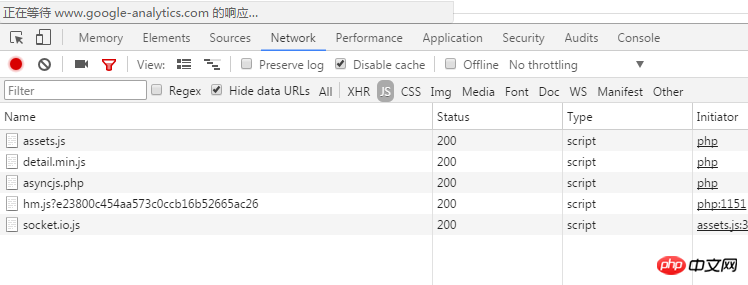
Then refresh your page, first select the tab to all, then switch to js after loading is complete, see which js is redundant, and then remove it.
PHP中文网2017-05-16 12:04:10
Since it is your own website, then upgrade to https, it is very simple.
Let’s Encrypt has long provided free SSL certificates for everyone to use, and the certificates it issues have been recognized by major browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari). The certificate it issues is valid for 90 days, and you need to renew it every 90 days. Updating is also easy, just execute a single command.
Let’s Encrypt official website: https://letsencrypt.org/
I wrote a tutorial on configuring Let’s Encrypt with Nginx on CentOS 7. The address is https://www.obneer.com/secure...