Android file download (1)
Introduction to this section:
This is another deep pit, beginners should enter with caution... This section will be downloaded from ordinary single thread-> ordinary multi-threaded Download-> -> And a very practical example: using Android’s DownloadManager to update apk And overwrite the installation implementation code! Okay, it looks like this section is quite interesting. Let’s start this section! PS: We put the entire complete multi-threaded breakpoint resume transmission in the next section!
1. Ordinary single-threaded file download:
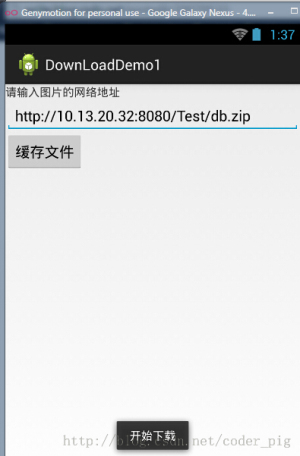
Directly use URLConnection.openStream() to open the network input stream, and then write the stream to the file!
Core method:
public static void downLoad(String path,Context context)throws Exception
{
URL url = new URL(path);
InputStream is = url.openStream();
//截取最后的文件名
String end = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("."));
//打开手机对应的输出流,输出到文件中
OutputStream os = context.openFileOutput("Cache_"+System.currentTimeMillis()+end, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//从输入六中读取数据,读到缓冲区中
while((len = is.read(buffer)) > 0)
{
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//关闭输入输出流
is.close();
os.close();
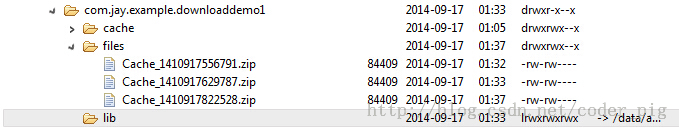
}Run result:
##2. Ordinary multi-thread download: We all know that using multi-thread to download files can complete the file download faster, but why?
Answer: Because there are many server resources preempted, assuming that the server can serve up to 100 users, one thread in the server Corresponding to one user, 100 threads are executed concurrently in the computer. The CPU divides the time slices and executes them in turns. After adding a, there are 99 threads. Downloading a file is equivalent to occupying 99 user resources, which naturally results in a faster download speed
PS: Of course, the more threads, the better. Open too many For threads, the app needs to maintain and synchronize the overhead of each thread. These overheads will lead to a reduction in download speed, and are also related to your network speed!
Multi-threaded download process:
PS: Create a Java project directly here, and then run the specified method in JUnit ,Get Network connectionCreate an empty file of the same size on the local diskCalculate which part of the file each thread needs to start downloading and end
- Create in sequence, start multiple Thread to download the specified part of the network resource
The core code is as follows:
public class Downloader {
//添加@Test标记是表示该方法是Junit测试的方法,就可以直接运行该方法了
@Test
public void download() throws Exception
{
//设置URL的地址和下载后的文件名
String filename = "meitu.exe";
String path = "http://10.13.20.32:8080/Test/XiuXiu_Green.exe";
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
//获得需要下载的文件的长度(大小)
int filelength = conn.getContentLength();
System.out.println("要下载的文件长度"+filelength);
//生成一个大小相同的本地文件
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(filename, "rwd");
file.setLength(filelength);
file.close();
conn.disconnect();
//设置有多少条线程下载
int threadsize = 3;
//计算每个线程下载的量
int threadlength = filelength % 3 == 0 ? filelength/3:filelength+1;
for(int i = 0;i < threadsize;i++)
{
//设置每条线程从哪个位置开始下载
int startposition = i * threadlength;
//从文件的什么位置开始写入数据
RandomAccessFile threadfile = new RandomAccessFile(filename, "rwd");
threadfile.seek(startposition);
//启动三条线程分别从startposition位置开始下载文件
new DownLoadThread(i,startposition,threadfile,threadlength,path).start();
}
int quit = System.in.read();
while('q' != quit)
{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
private class DownLoadThread extends Thread {
private int threadid;
private int startposition;
private RandomAccessFile threadfile;
private int threadlength;
private String path;
public DownLoadThread(int threadid, int startposition,
RandomAccessFile threadfile, int threadlength, String path) {
this.threadid = threadid;
this.startposition = startposition;
this.threadfile = threadfile;
this.threadlength = threadlength;
this.path = path;
}
public DownLoadThread() {}
@Override
public void run() {
try
{
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
//指定从什么位置开始下载
conn.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes="+startposition+"-");
//System.out.println(conn.getResponseCode());
if(conn.getResponseCode() == 206)
{
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
int length = 0;
while(length < threadlength && (len = is.read(buffer)) != -1)
{
threadfile.write(buffer,0,len);
//计算累计下载的长度
length += len;
}
threadfile.close();
is.close();
System.out.println("线程"+(threadid+1) + "已下载完成");
}
}catch(Exception ex){System.out.println("线程"+(threadid+1) + "下载出错"+ ex);}
}
}
}Running screenshot:
As shown in the figure, multi-threading is used to complete the file processing Download! Double-click the exe file to run, indicating that the file is not damaged!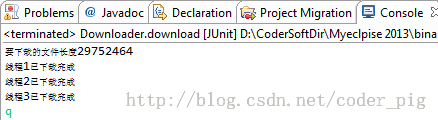
The following code can be used directly. After joining the project, remember to register a filter for this internal broadcast: AndroidManifest.xml Ordinary single-thread download file: DownLoadDemo1.zip Ordinary multi-thread download file: J2SEMulDownLoader.zip Okay, this section introduces you to ordinary single-threaded and multi-threaded file downloads, as well as using Android's own DownManager to download files.
Download the update APK and then overwrite the implementation! I believe it will bring convenience to everyone’s actual development. Okay, that’s all. Thank you~3. Use DownloadManager to update the application and overwrite it. Installation:
import android.app.DownloadManager;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/9 0009.
*/
public class UpdateAct extends AppCompatActivity {
//这个更新的APK的版本部分,我们是这样命名的:xxx_v1.0.0_xxxxxxxxx.apk
//这里我们用的是git提交版本的前九位作为表示
private static final String FILE_NAME = "ABCDEFGHI";
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
String endpoint = "";
try {
//这部分是获取AndroidManifest.xml里的配置信息的,包名,以及Meta_data里保存的东西
ApplicationInfo info = getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
//我们在meta_data保存了xxx.xxx这样一个数据,是https开头的一个链接,这里替换成http
endpoint = info.metaData.getString("xxxx.xxxx").replace("https",
"http");
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//下面的都是拼接apk更新下载url的,path是保存的文件夹路径
final String _Path = this.getIntent().getStringExtra("path");
final String _Url = endpoint + _Path;
final DownloadManager _DownloadManager = (DownloadManager) getSystemService(DOWNLOAD_SERVICE);
DownloadManager.Request _Request = new DownloadManager.Request(
Uri.parse(_Url));
_Request.setDestinationInExternalPublicDir(
Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS, FILE_NAME + ".apk");
_Request.setTitle(this.getString(R.string.app_name));
//是否显示下载对话框
_Request.setShowRunningNotification(true);
_Request.setMimeType("application/com.trinea.download.file");
//将下载请求放入队列
_DownloadManager.enqueue(_Request);
this.finish();
}
//注册一个广播接收器,当下载完毕后会收到一个android.intent.action.DOWNLOAD_COMPLETE
//的广播,在这里取出队列里下载任务,进行安装
public static class Receiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
final DownloadManager _DownloadManager = (DownloadManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.DOWNLOAD_SERVICE);
final long _DownloadId = intent.getLongExtra(
DownloadManager.EXTRA_DOWNLOAD_ID, 0);
final DownloadManager.Query _Query = new DownloadManager.Query();
_Query.setFilterById(_DownloadId);
final Cursor _Cursor = _DownloadManager.query(_Query);
if (_Cursor.moveToFirst()) {
final int _Status = _Cursor.getInt(_Cursor
.getColumnIndexOrThrow(DownloadManager.COLUMN_STATUS));
final String _Name = _Cursor.getString(_Cursor
.getColumnIndexOrThrow("local_filename"));
if (_Status == DownloadManager.STATUS_SUCCESSFUL
&& _Name.indexOf(FILE_NAME) != 0) {
Intent _Intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
_Intent.setDataAndType(
Uri.parse(_Cursor.getString(_Cursor
.getColumnIndexOrThrow(DownloadManager.COLUMN_LOCAL_URI))),
"application/vnd.android.package-archive");
_Intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
context.startActivity(_Intent);
}
}
_Cursor.close();
}
}
} 4. Reference code download:
Summary of this section:









