Introduction to Servlets
What is Servlet?
Java Servlet is a program that runs on a Web server or application server and acts as an intermediary layer between requests from a Web browser or other HTTP client and a database or application on the HTTP server.
Using Servlets, you can collect user input from web forms, render records from databases or other sources, and dynamically create web pages.
Java Servlet can usually achieve the same effect as a program implemented using CGI (Common Gateway Interface, public gateway interface). But compared to CGI, Servlet has the following advantages:
Performance is significantly better.
Servlet executes within the address space of the web server. This way it eliminates the need to create a separate process to handle each client request.
Servlets are platform independent because they are written in Java.
The Java Security Manager on the server enforces a series of restrictions to protect resources on the server computer. Therefore, the Servlet is trusted.
All functions of the Java class library are available to Servlets. It can interact with applets, databases, or other software through sockets and RMI mechanisms.
Servlet Architecture
The following diagram shows the location of Servlets in a web application.
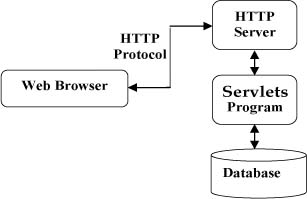
Servlet task
Servlet performs the following main tasks:
Read what the client (browser) sends of explicit data. This includes HTML forms on a web page, or it can be a form from an applet or custom HTTP client program.
Read the implicit HTTP request data sent by the client (browser). This includes things like cookies, media types and compression formats that the browser understands.
Process data and generate results. This process may require accessing a database, performing an RMI or CORBA call, calling a Web service, or directly calculating the corresponding response.
Send explicit data (i.e. document) to the client (browser). The document can be in a variety of formats, including text files (HTML or XML), binary files (GIF images), Excel, etc.
Send an implicit HTTP response to the client (browser). This includes telling the browser or other client what type of document to be returned (such as HTML), setting cookies and cache parameters, and other similar tasks.
Servlet Package
Java Servlet is a Java class that runs on a web server with an interpreter that supports the Java Servlet specification.
Servlet can be created using the javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages and is a standard part of Java Enterprise Edition, a version of Java that supports large development projects An extended version of the class library.
These classes implement the Java Servlet and JSP specifications. At the time of writing this tutorial, the corresponding versions are Java Servlet 2.5 and JSP 2.1.
Java Servlets are created and compiled just like any other Java class. After you install the Servlet packages and add them to the Classpath on your computer, you can compile the Servlet with the JDK's Java compiler or any other compiler.
What’s next?
Next, this tutorial will take you step by step to set up your Servlet environment in order to start subsequent Servlet use. So fasten your seatbelts and join us on our Servlet learning journey! I think you'll really enjoy this tutorial.








