Servlet instance
Servlet is a Java class that serves HTTP requests and implements the javax.servlet.Servlet interface. Web application developers typically write servlets that extend javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet and implement abstract classes of the Servlet interface specifically to handle HTTP requests.
Hello World sample code
The following is the sample source code for Servlet to output Hello World:
// 导入必需的 java 库
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
// 扩展 HttpServlet 类
public class HelloWorld extends HttpServlet {
private String message;
public void init() throws ServletException
{
// 执行必需的初始化
message = "Hello World";
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
// 设置响应内容类型
response.setContentType("text/html");
// 实际的逻辑是在这里
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>" + message + "</h1>");
}
public void destroy()
{
// 什么也不做
}
}Compile Servlet
Let us write the above code in HelloWorld.java file, place this file in C:\ServletDevel (on Windows) or /usr/ServletDevel (on UNIX). You will also need to add these directories to the CLASSPATH.
Assuming your environment has been set up correctly, go to the ServletDevel directory and compile HelloWorld.java as follows:
$ javac HelloWorld.java
If the Servlet depends on any other libraries, You must include those JAR files in CLASSPATH. Here, I have only included the servlet-api.jar JAR file since I am not using any other library in the Hello World program.
This command line uses the javac compiler built into the Sun Microsystems Java Software Development Kit (JDK). For this command to work correctly, you must have the location of the Java SDK used in the PATH environment variable.
If everything goes well, the above compilation will generate the HelloWorld.class file in the same directory. The next section explains how the compiled servlet is deployed in production.
Servlet Deployment
By default, the Servlet application is located under the path <Tomcat-installation-directory>/webapps/ROOT, and the class files are placed in <Tomcat-installation-directory> /webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/classes.
If you have a fully qualified class name com.myorg.MyServlet, then this Servlet class must be located in WEB-INF/classes/com/myorg/MyServlet.class.
Now, let's copy HelloWorld.class to <Tomcat-installation-directory>/webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/classes and place it in <Tomcat-installation-directory>/webapps/ Create the following entries in the web.xml file of ROOT/WEB-INF/:
<servlet> <servlet-name>HelloWorld</servlet-name> <servlet-class>HelloWorld</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloWorld</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/HelloWorld</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
The above entries are to be created in the <web-app>.. .</web-app> tag. There may already be various entries available in this file, but don't worry about them.
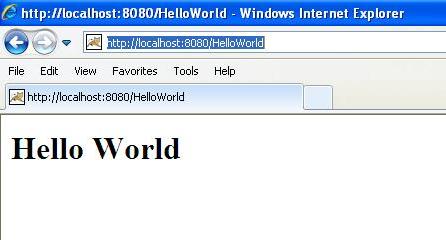
At this point, you're basically done, now let's use <Tomcat-installation-directory>\bin\startup.bat (on Windows) or <Tomcat-installation-directory>/bin /startup.sh (on Linux/Solaris, etc.) to start the tomcat server, and finally enter http://localhost:8080/HelloWorld in the browser's address bar. If all goes well, you will see the following results: