Scala loops
Sometimes, we may need to execute the same block of code multiple times. Normally, statements are executed sequentially: the first statement in the function is executed first, followed by the second statement, and so on.
Programming languages provide a variety of control structures for more complex execution paths.
Loop statements allow us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times. The following is a flow chart of loop statements in most programming languages:
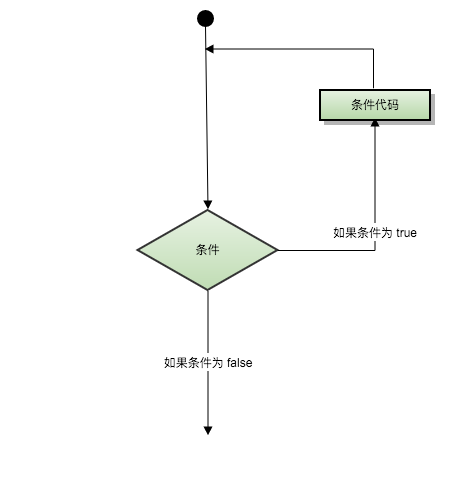
Loop types
Scala language provides the following loop types. Click on the links to view details on each type.
| Loop type | Description |
|---|---|
| while loop | Run a series of statements if If the condition is true, it will be run repeatedly until the condition becomes false. |
| do...while loop | Similar to the while statement, the difference is that the code block of the loop is executed once before the loop condition is judged. |
| for loop | is used to repeatedly execute a series of statements until a specific condition is reached, usually by increasing the value of the counter after each loop is completed. |
Loop control statement
Loop control statement changes the execution order of your code, through which you can realize code jumps. Scala has the following loop control statements:
Scala does not support break or continue statements, but it provides a way to interrupt the loop from version 2.8 onwards. Click the link below to view details.
| Control statement | Description |
|---|---|
| break statement | Break loop |
Infinite Loop
If the condition is always true, the loop will become an infinite loop. We can use the while statement to implement an infinite loop:
object Test {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
var a = 10;
// 无限循环
while( true ){
println( "a 的值为 : " + a );
}
}
}After the above code is executed, the loop will continue forever. You can use the Ctrl + C keys to interrupt the infinite loop.








