MySQL creates data table
MySQL Create data table
Creating a MySQL data table requires the following information:
Table name Table field name Definition of each table field
Syntax
The following is the general SQL syntax for creating MySQL data tables:
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name column_type);
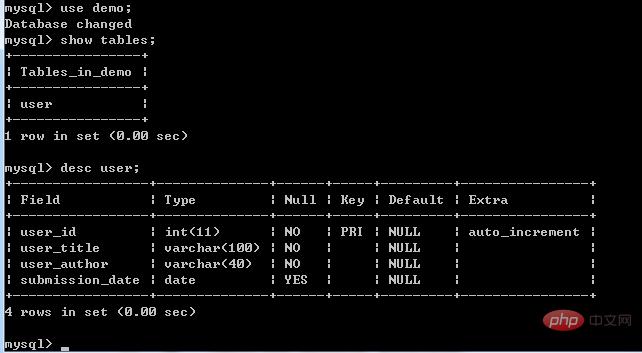
In the following examples we will create the data table user in the DEMO database:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user`( `user_id` INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `user_author` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, `submission_date` DATE, PRIMARY KEY ( `user_id` ))ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Example analysis:
#If you don’t want the field to be NULL, you can set the field’s attribute to NOT NULL. If you enter this field when operating the database If the data is NULL, an error will be reported. AUTO_INCREMENT is defined as an auto-incrementing attribute, generally used for primary keys, and the value will automatically increase by 1.
PRIMARY KEY keyword is used to define the column as the primary key. You can define a primary key using multiple columns, separated by commas.
ENGINE sets the storage engine and CHARSET sets the encoding.
#1. Create a table through the command prompt
MySQL data can be easily created through the mysql> command window surface. You can use the SQL statement CREATE TABLE to create a data table.
Example
The following is a user example to create a data table:
root@host# mysql -u root -pEnter password:*******mysql> use DEMO;Database changed mysql> CREATE TABLE user( -> user_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> user_title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, -> user_author VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, -> submission_date DATE, -> PRIMARY KEY ( user_id ) -> )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.16 sec)mysql>
Note: The MySQL command terminator is a semicolon;.
Note: -> is a newline identifier, do not copy it.
2. Use PHP script to create a data table
You can use PHP’s mysqli_query() function to create an existing database data sheet.
This function has two parameters and returns TRUE when executed successfully, otherwise it returns FALSE.
Syntax
mysqli_query(connection,query,resultmode);
| Description | |
| Required. Specifies the MySQL connection to use. | |
| Required, specifies the query string. | |
Optional. a constant. Can be any of the following values:
|
##Example
The following example uses a PHP script to create a data table:$ dbhost = 'localhost'; // mysql server host address
$dbuser = 'root'; ($dbhost, $dbuser, $dbpass);
if(! $conn )
{
die('Connection failed: ' . mysqli_error($conn));
}
echo 'Connection successful<br />';
$sql = "CREATE TABLE user( ".
"user_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, ".
"user_title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, ".
"user_author VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, ".
"submission_date DATE, ".
"PRIMARY KEY (user_id))ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; ";
mysqli_select_db( $conn , 'DEMO' );
$retval = mysqli_query( $conn, $sql );
if(! $retval )
{
die('Data table creation failed: ' . mysqli_error($ conn));
}
echo "Data table created successfully\n";
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
The results are as follows:
After successful execution, you can view the table structure through the command line: 
 Related video tutorials Recommended:
Related video tutorials Recommended:








