Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >C++ >Program C untuk penjadualan gelung
Program C untuk penjadualan gelung
- 王林ke hadapan
- 2023-09-25 17:09:02999semak imbas
Kami diberi n proses dengan masa pecah dan kuantum masa yang sepadan dan tugasnya adalah untuk mencari purata masa menunggu dan purata masa pusing ganti dan memaparkan hasilnya.
Apakah itu Round Robin Scheduling?
Round robin ialah algoritma penjadualan CPU yang direka khas untuk sistem perkongsian masa. Ia lebih seperti algoritma penjadualan FCFS dengan satu perubahan yang dalam proses Round Robin dibatasi dengan saiz masa kuantum. Unit kecil masa dikenali sebagai Time Quantum atau Time Slice. Kuantum masa boleh berkisar antara 10 hingga 100 milisaat. CPU menganggap baris gilir sedia sebagai baris gilir bulat untuk melaksanakan proses dengan kepingan masa yang diberikan. Ia mengikut pendekatan preemptive kerana masa tetap diperuntukkan kepada proses. Satu-satunya kelemahannya ialah overhed penukaran konteks.
Apa yang perlu kita kira?
Masa Siap#🎜🎜 # ialah masa yang diperlukan oleh proses untuk menyelesaikan pelaksanaannya
Masa Pusingan ialah selang masa antara penyerahan proses dan penyiapannya.#🎜 🎜#Masa Pusingan = selesai proses – penyerahan proses
Masa Menunggu ialah perbezaan antara masa pusing ganti dan masa pecah
Waiting Time = masa pusing ganti – masa pecah# 🎜🎜#
ContohKami diberikan 3 proses P1, P2 dan P3 dengan masa pecah yang sepadan sebagai 24, 3 dan 3#🎜🎜 Proses| #🎜🎜🎜##🎜🎜🎜##🎜🎜🎜##🎜🎜 🎜#24 | |
|---|---|
| 3 | #🎜🎜🎜# | P2
| #🎜#🎜#🎜🎜 | 3 |
| Oleh kerana kuantum masa ialah 4 milisaat, proses P1 mendapat 4 milisaat pertama tetapi memerlukan 20 milisaat lagi untuk melengkapkannya pelaksanaan tetapi CPU akan mendahuluinya selepas kuantum kali pertama dan CPU akan diperuntukkan kepada proses seterusnya P2. Seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam jadual, Proses P2 memerlukan hanya 3 milisaat untuk menyelesaikan pelaksanaannya supaya CPU akan diperuntukkan untuk kuantum masa 3 milisaat sahaja dan bukannya 4 milisaat. |
#🎜🎜🎜##🎜🎜🎜 #Algoritma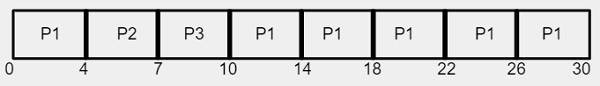
Start
Step 1-> In function int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i]
return 1
Step 2-> In function int waitingtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int quantum)
Declare rem_bt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rem_bt[i] = bt[i]
Set t = 0
Loop While (1)
Set done = true
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
If rem_bt[i] > 0 then,
Set done = false
If rem_bt[i] > quantum then,
Set t = t + quantum
Set rem_bt[i] = rem_bt[i] - quantum
Else
Set t = t + rem_bt[i]
Set wt[i] = t - bt[i]
Set rem_bt[i] = 0
If done == true then,
Break
Step 3->In function int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int quantum)
Declare and initialize wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call function waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum)
Call function turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat)
Print "Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time "
Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print the value i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]
Print "Average waiting time = total_wt / n
Print "Average turnaround time =total_tat / n
Step 4-> In function int main()
Delcare and initialize processes[] = { 1, 2, 3}
Declare and initialize n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0]
Declare and initialize burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12}
Set quantum = 2
Call function findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum)Contoh 实例演示#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time</p><p>");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d</p><p>",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("</p><p>Average turnaround time = %f</p><p>", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}输出#🎜##🎜##🎜 🎜🎜#Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Program C untuk penjadualan gelung. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

