 hujung hadapan web
hujung hadapan web tutorial js
tutorial js JS melaksanakan kemahiran kesan menu teleskopik dinamik regangan mendatar code_javascript
JS melaksanakan kemahiran kesan menu teleskopik dinamik regangan mendatar code_javascriptJS melaksanakan kemahiran kesan menu teleskopik dinamik regangan mendatar code_javascript
Contoh dalam artikel ini menerangkan kod JS untuk melaksanakan kesan menu teleskopik dinamik regangan mendatar. Kongsikan dengan semua orang untuk rujukan anda. Butirannya adalah seperti berikut:
Ini adalah pelaksanaan JS regangan menegak ke regangan mendatar, menu teleskop dinamik, dan menu CSS yang disusun rapi Ia boleh digunakan sebagai menu dalam kedudukan penting seperti blog pembelajaran reka bentuk bahagian hadapan JavaScript.
Tangkapan skrin kesan berjalan adalah seperti berikut:
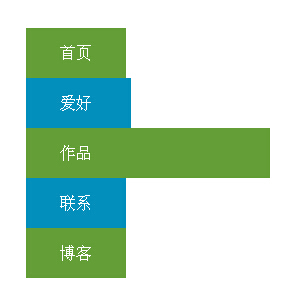
Alamat demo dalam talian adalah seperti berikut:
http://demo.jb51.net/js/2015/js-row-show-menu-style-codes/
Kod khusus adalah seperti berikut:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<title>有弹性的菜单</title>
<style>
*{ margin:0px; padding:0px;} body { background:#fff;} .naver{list-style-type:
none; width:700px; overflow:hidden; margin:100px auto 0;} .naver li{ width:100px;
height:50px; overflow:hidden; font-size:16px; text-align:center; cursor:
pointer; } .naver li a,.naver li a:hover{display: block;width:100px; height:50px;
line-height: 50px; color:#FFF; text-decoration: none; } .co1{ background:#649e37}
.co2{ background:#028fbc}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function() {
var oUl = document.getElementById("nav");
var aLi = oUl.getElementsByTagName("li");
var i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < aLi.length; i++) {
aLi[i].timer = null;
aLi[i].speed = 0;
aLi[i].onmouseover = function() {
startMove(this, 250);
};
aLi[i].onmouseout = function() {
startMove2(this, 100);
};
}
};
function startMove(obj, iTarget) {
if (obj.timer) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
obj.timer = setInterval(function() {
doMove(obj, iTarget);
}, 30)
};
function doMove(obj, iTarget) {
obj.speed += 3;
if (Math.abs(iTarget - obj.offsetWidth) < 1 && Math.abs(obj.speed) < 1) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer = null;
}
else {
if (obj.offsetWidth + obj.speed >= iTarget) {
obj.speed *= -0.7;
obj.style.width = iTarget + "px";
}
else {
obj.style.width = obj.offsetWidth + obj.speed + "px";
}
}
};
function startMove2(obj, iTarget) {
if (obj.timer) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
obj.timer = setInterval(function() {
doMove2(obj, iTarget);
}, 30)
};
function doMove2(obj, iTarget) {
obj.speed -= 3;
if (Math.abs(iTarget - obj.offsetWidth) < 1 && Math.abs(obj.speed) < 1) {
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer = null;
}
else {
if (obj.offsetWidth + obj.speed <= iTarget) {
obj.speed *= -0.7;
obj.style.width = iTarget + "px";
}
else {
obj.style.width = obj.offsetWidth + obj.speed + "px";
}
}
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="nav" class="naver">
<li class="co1">
<a href="#">首页</a>
</li>
<li class="co2">
<a href="#">爱好</a>
</li>
<li class="co1">
<a href="#">作品</a>
</li>
<li class="co2">
<a href="#">联系</a>
</li>
<li class="co1">
<a href="#">博客</a>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Saya harap artikel ini akan membantu reka bentuk pengaturcaraan JavaScript semua orang.
 Adakah JavaScript ditulis dalam C? Memeriksa buktiApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Adakah JavaScript ditulis dalam C? Memeriksa buktiApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AMYa, teras enjin JavaScript ditulis dalam C. 1) Bahasa C menyediakan prestasi yang efisien dan kawalan asas, yang sesuai untuk pembangunan enjin JavaScript. 2) Mengambil enjin V8 sebagai contoh, terasnya ditulis dalam C, menggabungkan kecekapan dan ciri-ciri berorientasikan objek C. 3) Prinsip kerja enjin JavaScript termasuk parsing, penyusun dan pelaksanaan, dan bahasa C memainkan peranan penting dalam proses ini.
 Peranan JavaScript: Membuat Web Interaktif dan DinamikApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Peranan JavaScript: Membuat Web Interaktif dan DinamikApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript adalah di tengah -tengah laman web moden kerana ia meningkatkan interaktiviti dan dinamik laman web. 1) Ia membolehkan untuk menukar kandungan tanpa menyegarkan halaman, 2) memanipulasi laman web melalui Domapi, 3) menyokong kesan interaktif kompleks seperti animasi dan drag-and-drop, 4) mengoptimumkan prestasi dan amalan terbaik untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna.
 C dan JavaScript: Sambungan dijelaskanApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C dan JavaScript: Sambungan dijelaskanApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC dan JavaScript mencapai interoperabilitas melalui webassembly. 1) Kod C disusun ke dalam modul WebAssembly dan diperkenalkan ke dalam persekitaran JavaScript untuk meningkatkan kuasa pengkomputeran. 2) Dalam pembangunan permainan, C mengendalikan enjin fizik dan rendering grafik, dan JavaScript bertanggungjawab untuk logik permainan dan antara muka pengguna.
 Dari laman web ke aplikasi: Aplikasi pelbagai JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Dari laman web ke aplikasi: Aplikasi pelbagai JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript digunakan secara meluas di laman web, aplikasi mudah alih, aplikasi desktop dan pengaturcaraan sisi pelayan. 1) Dalam pembangunan laman web, JavaScript mengendalikan DOM bersama -sama dengan HTML dan CSS untuk mencapai kesan dinamik dan menyokong rangka kerja seperti JQuery dan React. 2) Melalui reaktnatif dan ionik, JavaScript digunakan untuk membangunkan aplikasi mudah alih rentas platform. 3) Rangka kerja elektron membolehkan JavaScript membina aplikasi desktop. 4) Node.js membolehkan JavaScript berjalan di sisi pelayan dan menyokong permintaan serentak yang tinggi.
 Python vs JavaScript: Gunakan Kes dan Aplikasi MembandingkanApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs JavaScript: Gunakan Kes dan Aplikasi MembandingkanApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython lebih sesuai untuk sains data dan automasi, manakala JavaScript lebih sesuai untuk pembangunan front-end dan penuh. 1. Python berfungsi dengan baik dalam sains data dan pembelajaran mesin, menggunakan perpustakaan seperti numpy dan panda untuk pemprosesan data dan pemodelan. 2. Python adalah ringkas dan cekap dalam automasi dan skrip. 3. JavaScript sangat diperlukan dalam pembangunan front-end dan digunakan untuk membina laman web dinamik dan aplikasi satu halaman. 4. JavaScript memainkan peranan dalam pembangunan back-end melalui Node.js dan menyokong pembangunan stack penuh.
 Peranan C/C dalam JavaScript Jurubah dan PenyusunApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Peranan C/C dalam JavaScript Jurubah dan PenyusunApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC dan C memainkan peranan penting dalam enjin JavaScript, terutamanya digunakan untuk melaksanakan jurubahasa dan penyusun JIT. 1) C digunakan untuk menghuraikan kod sumber JavaScript dan menghasilkan pokok sintaks abstrak. 2) C bertanggungjawab untuk menjana dan melaksanakan bytecode. 3) C melaksanakan pengkompil JIT, mengoptimumkan dan menyusun kod hot-spot semasa runtime, dan dengan ketara meningkatkan kecekapan pelaksanaan JavaScript.
 JavaScript in Action: Contoh dan projek dunia nyataApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Contoh dan projek dunia nyataApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMAplikasi JavaScript di dunia nyata termasuk pembangunan depan dan back-end. 1) Memaparkan aplikasi front-end dengan membina aplikasi senarai TODO, yang melibatkan operasi DOM dan pemprosesan acara. 2) Membina Restfulapi melalui Node.js dan menyatakan untuk menunjukkan aplikasi back-end.
 JavaScript dan Web: Fungsi teras dan kes penggunaanApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript dan Web: Fungsi teras dan kes penggunaanApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMPenggunaan utama JavaScript dalam pembangunan web termasuk interaksi klien, pengesahan bentuk dan komunikasi tak segerak. 1) kemas kini kandungan dinamik dan interaksi pengguna melalui operasi DOM; 2) pengesahan pelanggan dijalankan sebelum pengguna mengemukakan data untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna; 3) Komunikasi yang tidak bersesuaian dengan pelayan dicapai melalui teknologi Ajax.


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat
Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat ialah persekitaran pelayar selamat untuk mengambil peperiksaan dalam talian dengan selamat. Perisian ini menukar mana-mana komputer menjadi stesen kerja yang selamat. Ia mengawal akses kepada mana-mana utiliti dan menghalang pelajar daripada menggunakan sumber yang tidak dibenarkan.

PhpStorm versi Mac
Alat pembangunan bersepadu PHP profesional terkini (2018.2.1).

MinGW - GNU Minimalis untuk Windows
Projek ini dalam proses untuk dipindahkan ke osdn.net/projects/mingw, anda boleh terus mengikuti kami di sana. MinGW: Port Windows asli bagi GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), perpustakaan import yang boleh diedarkan secara bebas dan fail pengepala untuk membina aplikasi Windows asli termasuk sambungan kepada masa jalan MSVC untuk menyokong fungsi C99. Semua perisian MinGW boleh dijalankan pada platform Windows 64-bit.

MantisBT
Mantis ialah alat pengesan kecacatan berasaskan web yang mudah digunakan yang direka untuk membantu dalam pengesanan kecacatan produk. Ia memerlukan PHP, MySQL dan pelayan web. Lihat perkhidmatan demo dan pengehosan kami.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Muat Turun
Editor IDE percuma dan berkuasa yang dilancarkan oleh Microsoft





