
ES8 引入的 async/await 在 JavaScript 的异步编程中是一个极好的改进。它提供了使用同步样式代码异步访问 resoruces 的方式,而不会阻塞主线程。然而,它们也存在一些坑及问题。在本文中,将从不同的角度探讨 async/await,并演示如何正确有效地使用这对兄弟。
前置知识
async 作用是什么
从 MDN 可以看出:
async 函数返回的是一个 Promise 对象。async 函数(包含函数语句、函数表达式、Lambda表达式)会返回一个 Promise 对象,如果在函数中 return 一个直接量,async 会把这个直接量通过 Promise.resolve() 封装成 Promise 对象。
如果 async 函数没有返回值, 它会返回 Promise.resolve(undefined)。
await 作用是什么
从 MDN 了解到:
await 等待的是一个表达式,这个表达式的计算结果是 Promise 对象或者其它值(换句话说,await 可以等任意表达式的结果)。
如果它等到的不是一个 Promise 对象,那 await 表达式的运算结果就是它等到的东西。
如果它等到的是一个 Promise 对象,await 就忙起来了,它会阻塞后面的代码,等着 Promise 对象 resolve,然后得到 resolve 的值,作为 await 表达式的运算结果。
这就是 await 必须用在 async 函数中的原因。async 函数调用不会造成阻塞,它内部所有的阻塞都被封装在一个 Promise 对象中异步执行。
async/await 的优点
async/await 带给我们的最重要的好处是同步编程风格。让我们看一个例子:
// async/await
async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait(authorId) {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
return books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId);
}// promise
getBooksByAuthorWithPromise(authorId) {
return bookModel.fetchAll()
.then(books => books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId));
}很明显,async/await 版本比 promise 版本更容易理解。如果忽略 await 关键字,代码看起来就像任何其他同步语言,比如 Python。
最佳的地方不仅在于可读性。async/await 到今天为止,所有主流浏览器都完全支持异步功能。
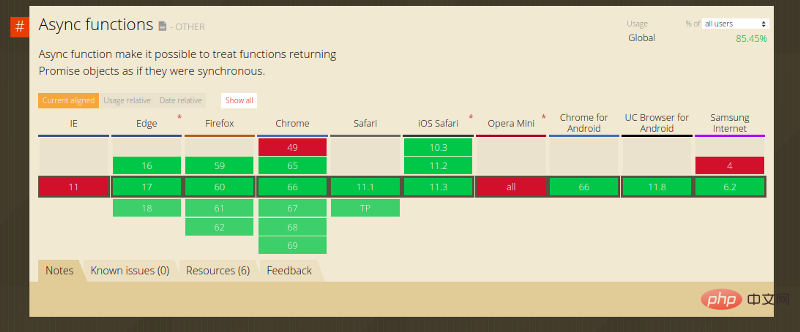
本地浏览器的支持意味着你不必转换代码。更重要的是,它便于调试。当在函数入口点设置断点并跨过 await 行时,将看到调试器在 bookModel.fetchAll() 执行其任务时暂停片刻,然后它将移动到下一个.filter 行,这比 promise 代码要简单得多,在 promise 中,必须在 .filter 行上设置另一个断点。
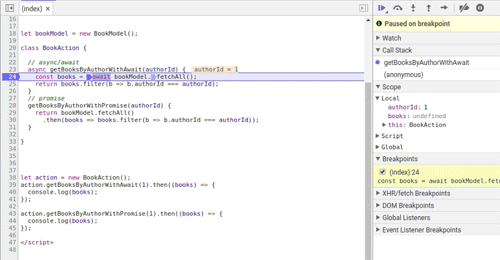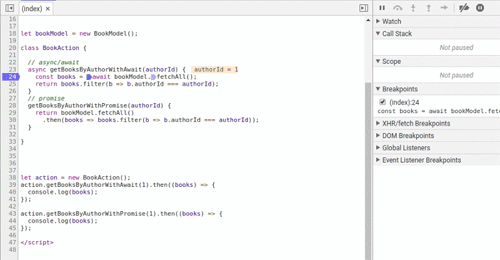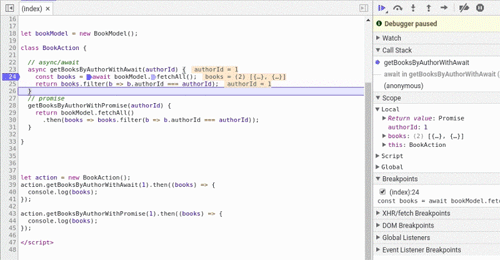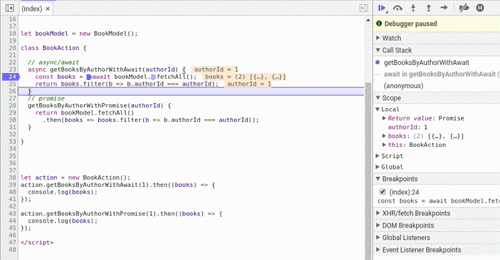
另一个不太明显的优点是 async 关键字。 async声明 getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()函数返回值确保是一个 promise,因此调用者可以安全地使用 getBooksByAuthorWithAwait().then(...) 或await getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()。 想想下面的例子(不好的做法!):
getBooksByAuthorWithPromise(authorId) {
if (!authorId) {
return null;
}
return bookModel.fetchAll()
.then(books => books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId));
}在上述代码中,getBooksByAuthorWithPromise 可能返回 promise(正常情况下)或 null 值(异常情况下),在异常情况下,调用者不能调用 .then()。有了async 声明,这种情况就不会出现了。
async/await 可能会产生误导
一些文章将 async/wait 与 Promise 进行了比较,并声称它是 JavaScript 下一代异步编程风格,对此作者深表异议。async/await 是一种改进,但它只不过是一种语法糖,不会完全改变我们的编程风格。
从本质上说,async 函数仍然是 promise。在正确使用 async 函数之前,你必须先了解 promise,更糟糕的是,大多数时候你需要在使用 promises 的同时使用 async 函数。
考虑上面示例中的 getBooksByAuthorWithAwait() 和getbooksbyauthorwithpromise() 函数。请注意,它们不仅功能相同,而且具有完全相同的接口!
这意味着 getbooksbyauthorwithwait() 将返回一个 promise,所以也可以使用 .then(...)方式来调用它。
嗯,这未必是件坏事。只有 await 的名字给人一种感觉,“哦,太好了,可以把异步函数转换成同步函数了”,这实际上是错误的。
async/await
那么在使用 async/await 时可能会犯什么错误呢?下面是一些常见的例子。
太过串行化
尽管 await 可以使代码看起来像是同步的,但实际它们仍然是异步的,必须小心避免太过串行化。
async getBooksAndAuthor(authorId) {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
const author = await authorModel.fetch(authorId);
return {
author,
books: books.filter(book => book.authorId === authorId),
};
}上述代码在逻辑上看似正确的,然而,这是错误的。
-
await bookModel.fetchAll()会等待fetchAll()直到fetchAll()返回结果。 - 然后
await authorModel.fetch(authorId)被调用。
注意,authorModel.fetch(authorId) 并不依赖于 bookModel.fetchAll() 的结果,实际上它们可以并行调用!然而,用了 await,两个调用变成串行的,总的执行时间将比并行版本要长得多得多。
下面是正确的方式:
async getBooksAndAuthor(authorId) {
const bookPromise = bookModel.fetchAll();
const authorPromise = authorModel.fetch(authorId);
const book = await bookPromise;
const author = await authorPromise;
return {
author,
books: books.filter(book => book.authorId === authorId),
};
}更糟糕的是,如果你想要一个接一个地获取项目列表,你必须依赖使用 promises:
async getAuthors(authorIds) {
// WRONG, this will cause sequential calls
// const authors = _.map(
// authorIds,
// id => await authorModel.fetch(id));// CORRECT
const promises = _.map(authorIds, id => authorModel.fetch(id));
const authors = await Promise.all(promises);
}简而言之,你仍然需要将流程视为异步的,然后使用 await 写出同步的代码。在复杂的流程中,直接使用 promise 可能更方便。
错误处理
在 promise中,异步函数有两个可能的返回值: resolved 和 rejected。我们可以用 .then() 处理正常情况,用 .catch() 处理异常情况。然而,使用 async/await方式的,错误处理可能比较棘手。
try…catch
最标准的(也是作者推荐的)方法是使用 try...catch 语法。在 await 调用时,在调用 await 函数时,如果出现非正常状况就会抛出异常,await 命令后面的 promise 对象,运行结果可能是 rejected,所以最好把await 命令放在 try...catch 代码块中。如下例子:
class BookModel {
fetchAll() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
window.setTimeout(() => { reject({'error': 400}) }, 1000);
});
}
}// async/await
async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait(authorId) {
try {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
} catch (error) {
console.log(error); // { "error": 400 }
}在捕捉到异常之后,有几种方法来处理它:
- 处理异常,并返回一个正常值。(不在
catch块中使用任何return语句相当于使用return undefined,undefined 也是一个正常值。) - 如果你想让调用者处理它,你可以直接抛出普通的错误对象,如
throw errorr,它允许你在 promise 链中使用async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()函数(也就是说,可以像getBooksByAuthorWithAwait().then(...).catch(error => ...) 处理错误); 或者可以用Error对象将错误封装起来,如throw new Error(error),当这个错误在控制台中显示时,它将给出完整的堆栈跟踪信息。 - 拒绝它,就像
return Promise.reject(error),这相当于throw error,所以不建议这样做。
使用 try...catch 的好处:
- 简单,传统。只要有Java或c++等其他语言的经验,理解这一点就不会有任何困难。
- 如果不需要每步执行错误处理,你仍然可以在一个
try ... catch块中包装多个await调用来处理一个地方的错误。
这种方法也有一个缺陷。由于 try...catch 会捕获代码块中的每个异常,所以通常不会被 promise 捕获的异常也会被捕获到。比如:
class BookModel {
fetchAll() {
cb(); // note `cb` is undefined and will result an exception
return fetch('/books');
}
}try {
bookModel.fetchAll();
} catch(error) {
console.log(error); // This will print "cb is not defined"
}运行此代码,你将得到一个错误 ReferenceError: cb is not defined。这个错误是由console.log()打印出来的的,而不是 JavaScript 本身。有时这可能是致命的:如果 BookModel 被包含在一系列函数调用中,其中一个调用者吞噬了错误,那么就很难找到这样一个未定义的错误。
让函数返回两个值
另一种错误处理方法是受到Go语言的启发。它允许异步函数返回错误和结果。详情请看这篇博客文章:
How to write async await without try-catch blocks in Javascript
简而言之,你可以像这样使用异步函数:
[err, user] = await to(UserModel.findById(1));
作者个人不喜欢这种方法,因为它将 Go 语言的风格带入到了 JavaScript 中,感觉不自然。但在某些情况下,这可能相当有用。
使用 .catch
这里介绍的最后一种方法就是继续使用 .catch()。
回想一下 await 的功能:它将等待 promise 完成它的工作。值得注意的一点是 promise.catch() 也会返回一个 promise ,所以我们可以这样处理错误:
// books === undefined if error happens,
// since nothing returned in the catch statement
let books = await bookModel.fetchAll()
.catch((error) => { console.log(error); });这种方法有两个小问题:
- 它是 promises 和 async 函数的混合体。你仍然需要理解 是promises 如何工作的。
- 错误处理先于正常路径,这是不直观的。
结论
ES7引入的 async/await 关键字无疑是对J avaScrip t异步编程的改进。它可以使代码更容易阅读和调试。然而,为了正确地使用它们,必须完全理解 promise,因为 async/await 只不过是 promise 的语法糖,本质上仍然是 promise。
英文原文地址:https://hackernoon.com/javascript-async-await-the-good-part-pitfalls-and-how-to-use-9b759ca21cda
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 详解JavaScript中async/await的使用方法. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Memahami Enjin JavaScript: Butiran PelaksanaanApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Memahami Enjin JavaScript: Butiran PelaksanaanApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMMemahami bagaimana enjin JavaScript berfungsi secara dalaman adalah penting kepada pemaju kerana ia membantu menulis kod yang lebih cekap dan memahami kesesakan prestasi dan strategi pengoptimuman. 1) aliran kerja enjin termasuk tiga peringkat: parsing, penyusun dan pelaksanaan; 2) Semasa proses pelaksanaan, enjin akan melakukan pengoptimuman dinamik, seperti cache dalam talian dan kelas tersembunyi; 3) Amalan terbaik termasuk mengelakkan pembolehubah global, mengoptimumkan gelung, menggunakan const dan membiarkan, dan mengelakkan penggunaan penutupan yang berlebihan.
 Python vs JavaScript: Keluk Pembelajaran dan Kemudahan PenggunaanApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs JavaScript: Keluk Pembelajaran dan Kemudahan PenggunaanApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython lebih sesuai untuk pemula, dengan lengkung pembelajaran yang lancar dan sintaks ringkas; JavaScript sesuai untuk pembangunan front-end, dengan lengkung pembelajaran yang curam dan sintaks yang fleksibel. 1. Sintaks Python adalah intuitif dan sesuai untuk sains data dan pembangunan back-end. 2. JavaScript adalah fleksibel dan digunakan secara meluas dalam pengaturcaraan depan dan pelayan.
 Python vs JavaScript: Komuniti, Perpustakaan, dan SumberApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs JavaScript: Komuniti, Perpustakaan, dan SumberApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython dan JavaScript mempunyai kelebihan dan kekurangan mereka sendiri dari segi komuniti, perpustakaan dan sumber. 1) Komuniti Python mesra dan sesuai untuk pemula, tetapi sumber pembangunan depan tidak kaya dengan JavaScript. 2) Python berkuasa dalam bidang sains data dan perpustakaan pembelajaran mesin, sementara JavaScript lebih baik dalam perpustakaan pembangunan dan kerangka pembangunan depan. 3) Kedua -duanya mempunyai sumber pembelajaran yang kaya, tetapi Python sesuai untuk memulakan dengan dokumen rasmi, sementara JavaScript lebih baik dengan MDNWebDocs. Pilihan harus berdasarkan keperluan projek dan kepentingan peribadi.
 Dari C/C ke JavaScript: Bagaimana semuanya berfungsiApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Dari C/C ke JavaScript: Bagaimana semuanya berfungsiApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMPeralihan dari C/C ke JavaScript memerlukan menyesuaikan diri dengan menaip dinamik, pengumpulan sampah dan pengaturcaraan asynchronous. 1) C/C adalah bahasa yang ditaip secara statik yang memerlukan pengurusan memori manual, manakala JavaScript ditaip secara dinamik dan pengumpulan sampah diproses secara automatik. 2) C/C perlu dikumpulkan ke dalam kod mesin, manakala JavaScript adalah bahasa yang ditafsirkan. 3) JavaScript memperkenalkan konsep seperti penutupan, rantaian prototaip dan janji, yang meningkatkan keupayaan pengaturcaraan fleksibiliti dan asynchronous.
 Enjin JavaScript: Membandingkan PelaksanaanApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Enjin JavaScript: Membandingkan PelaksanaanApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMEnjin JavaScript yang berbeza mempunyai kesan yang berbeza apabila menguraikan dan melaksanakan kod JavaScript, kerana prinsip pelaksanaan dan strategi pengoptimuman setiap enjin berbeza. 1. Analisis leksikal: Menukar kod sumber ke dalam unit leksikal. 2. Analisis Tatabahasa: Menjana pokok sintaks abstrak. 3. Pengoptimuman dan Penyusunan: Menjana kod mesin melalui pengkompil JIT. 4. Jalankan: Jalankan kod mesin. Enjin V8 mengoptimumkan melalui kompilasi segera dan kelas tersembunyi, Spidermonkey menggunakan sistem kesimpulan jenis, menghasilkan prestasi prestasi yang berbeza pada kod yang sama.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript di dunia nyataApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript di dunia nyataApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMAplikasi JavaScript di dunia nyata termasuk pengaturcaraan sisi pelayan, pembangunan aplikasi mudah alih dan Internet of Things Control: 1. Pengaturcaraan sisi pelayan direalisasikan melalui node.js, sesuai untuk pemprosesan permintaan serentak yang tinggi. 2. Pembangunan aplikasi mudah alih dijalankan melalui reaktnatif dan menyokong penggunaan silang platform. 3. Digunakan untuk kawalan peranti IoT melalui Perpustakaan Johnny-Five, sesuai untuk interaksi perkakasan.
 Membina aplikasi SaaS Multi-penyewa dengan Next.js (Integrasi Backend)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Membina aplikasi SaaS Multi-penyewa dengan Next.js (Integrasi Backend)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMSaya membina aplikasi SaaS multi-penyewa berfungsi (aplikasi edTech) dengan alat teknologi harian anda dan anda boleh melakukan perkara yang sama. Pertama, apakah aplikasi SaaS multi-penyewa? Aplikasi SaaS Multi-penyewa membolehkan anda melayani beberapa pelanggan dari Sing
 Cara Membina Aplikasi SaaS Multi-Tenant dengan Next.js (Integrasi Frontend)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Cara Membina Aplikasi SaaS Multi-Tenant dengan Next.js (Integrasi Frontend)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMArtikel ini menunjukkan integrasi frontend dengan backend yang dijamin oleh permit, membina aplikasi edtech SaaS yang berfungsi menggunakan Next.Js. Frontend mengambil kebenaran pengguna untuk mengawal penglihatan UI dan memastikan permintaan API mematuhi dasar peranan


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Penyesuai Pelayan SAP NetWeaver untuk Eclipse
Integrasikan Eclipse dengan pelayan aplikasi SAP NetWeaver.

Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat
Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat ialah persekitaran pelayar selamat untuk mengambil peperiksaan dalam talian dengan selamat. Perisian ini menukar mana-mana komputer menjadi stesen kerja yang selamat. Ia mengawal akses kepada mana-mana utiliti dan menghalang pelajar daripada menggunakan sumber yang tidak dibenarkan.

Muat turun versi mac editor Atom
Editor sumber terbuka yang paling popular

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

Dreamweaver Mac版
Alat pembangunan web visual






