Rumah >hujung hadapan web >View.js >详解Vue.js中的作用域插槽
详解Vue.js中的作用域插槽
- 青灯夜游ke hadapan
- 2020-09-30 17:37:372931semak imbas

作用域槽是Vue.js的一个有用特性,它可以使组件更加通用和可重用。唯一的问题是它们很难理解!试着让你的头在父母和孩子的范围内交织,就像解决一个棘手的数学方程。
当你不能很容易地理解某件事时,一个好的方法是试着用它来解决问题。在本文中,我将演示如何使用作用域槽来构建可重用列表组件。
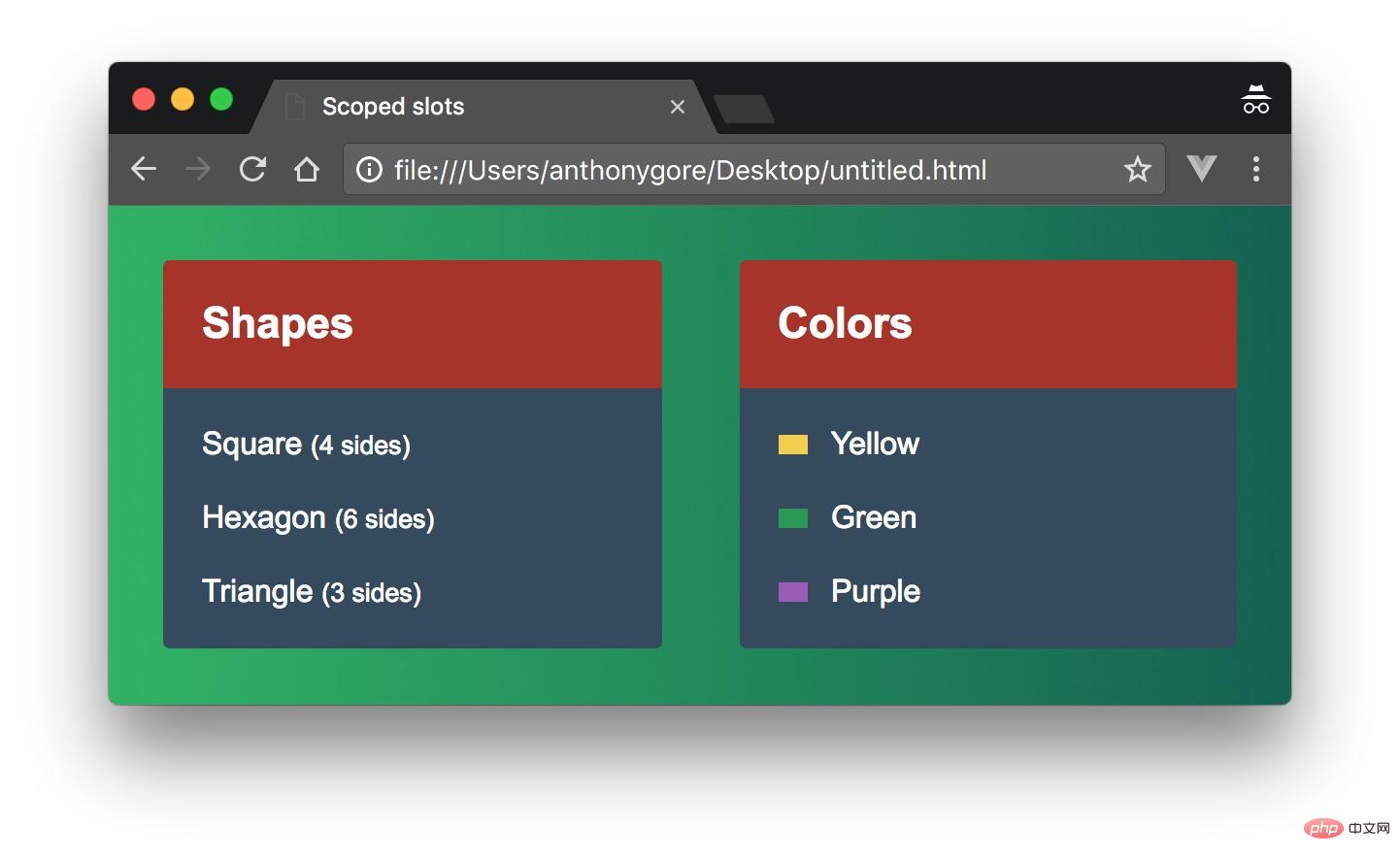
基本组成部分
我们要构建的组件叫做my-list,它显示了很多东西。该特性的特殊之处在于,您可以自定义列表项在每次使用组件时的呈现方式。
让我们首先处理最简单的用例,并获取my-list来呈现一个列表:一个几何形状名称数组和它们的边数。
app.js
Vue.component('my-list', {
template: '#my-list',
data() {
return {
title: 'Shapes',
shapes: [
{ name: 'Square', sides: 4 },
{ name: 'Hexagon', sides: 6 },
{ name: 'Triangle', sides: 3 }
]
};
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app'
});index.html
<div id="app">
<my-list></my-list></div><script type="text/x-template" id="my-list">
<div class="my-list">
<div class="title">{{ title }}</div>
<div class="list">
<div class="list-item" v-for="shape in shapes">
<div>{{ shape.name }} <small>({{ shape.sides }} sides)</small></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
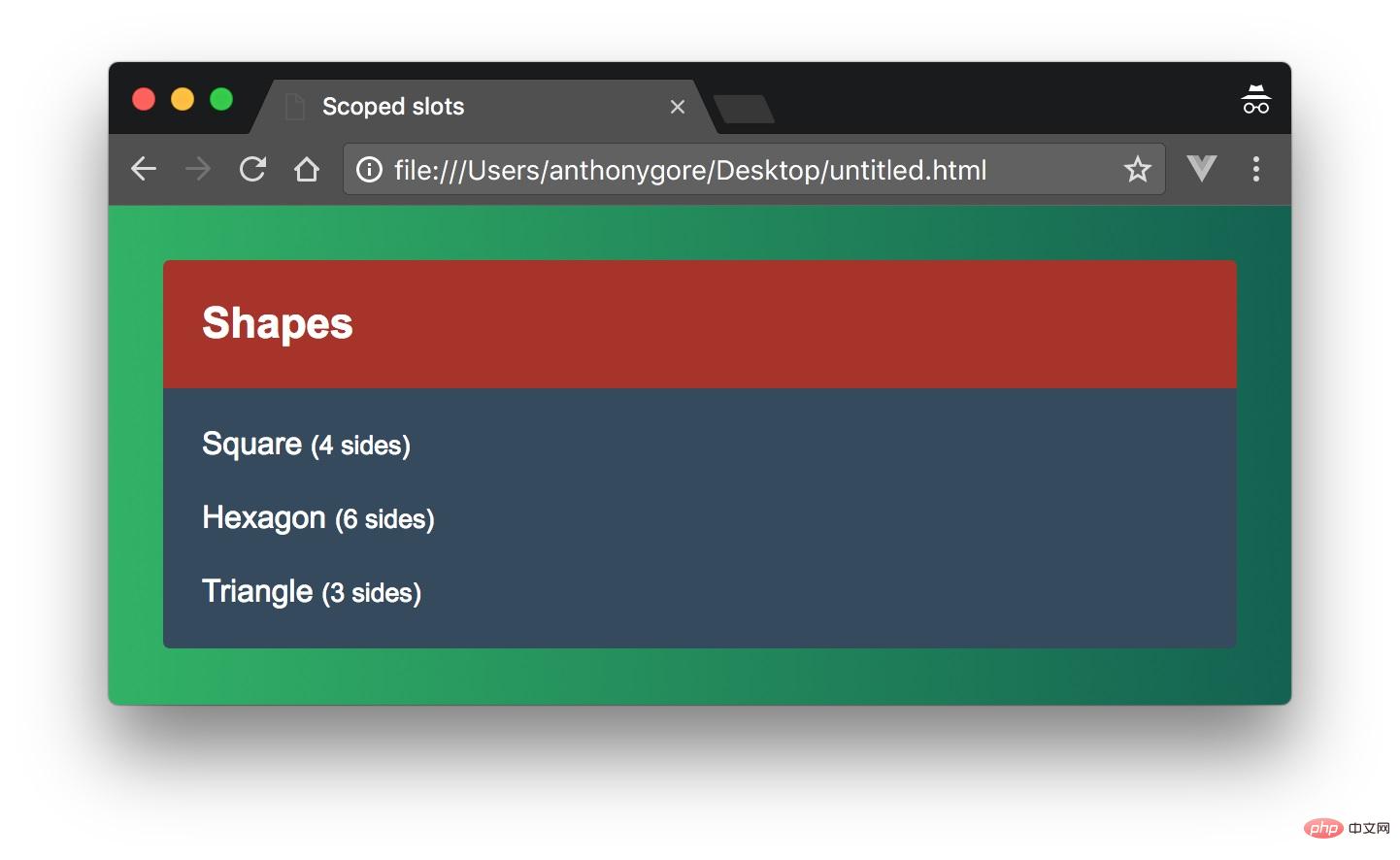
</script>添加了一点CSS后,将会如下图所示:
泛化my-list
现在,我们想要使my-list功能足够多,以呈现任何类型的列表。第二个测试用例将是一个颜色列表,包括一个小样本来显示颜色。
为此,我们必须抽象特定于形状列表的任何数据。由于列表中的项的结构可能不同,我们将为my-list提供一个插槽,以便父列表可以定义任何特定列表的显示方式。
app.js
Vue.component('my-list', {
template: '#my-list',
props: [ 'title' ]
});index.html
<script type="text/x-template" id="my-list">
<div class="my-list">
<div class="title">{{ title }}</div>
<div class="list">
<slot></slot>
</div>
</div>
</script>现在让我们在根实例中创建my-list组件的两个实例来显示我们的两个测试用例列表:
app.js
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
shapes: [
{ name: 'Square', sides: 4 },
{ name: 'Hexagon', sides: 6 },
{ name: 'Triangle', sides: 3 }
],
colors: [
{ name: 'Yellow', hex: '#F4D03F', },
{ name: 'Green', hex: '#229954' },
{ name: 'Purple', hex: '#9B59B6' }
]
}
});<div id="app">
<my-list :title="Shapes">
<div class="list-item" v-for="item in shapes">
<div>{{ shape.name }} <small>({{ shape.sides }} sides)</small></div>
</div>
</my-list>
<my-list :title="Colors">
<div class="list-item" v-for="color in colors">
<div>
<div class="swatch" :style="{ background: color.hex }"></div>
{{ color.name }} </div>
</div>
</my-list></div>就像这样:
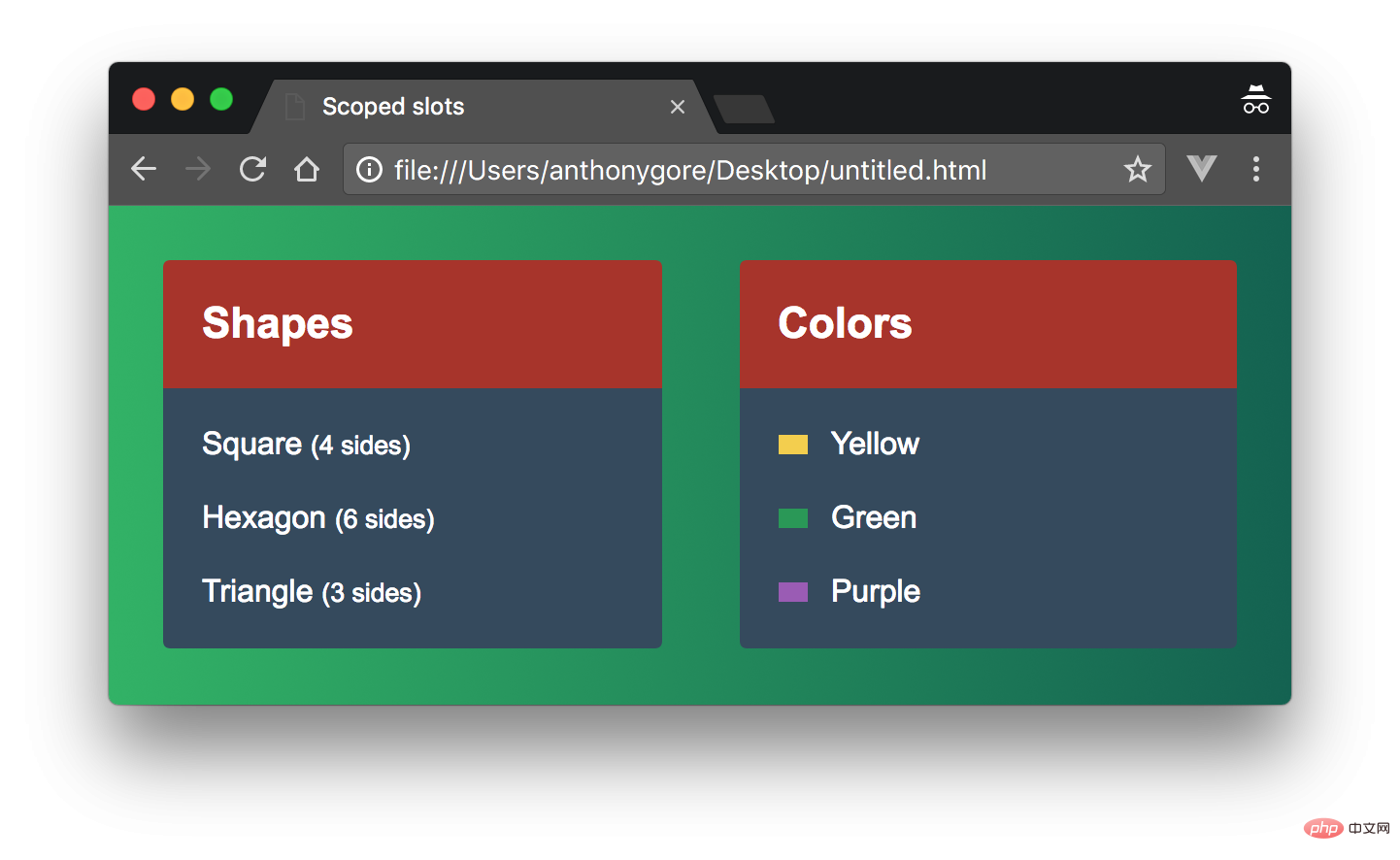
表面成分
我们刚刚创建的代码工作得很好,但是代码并不好。my-list是按名称显示列表的组件。但是我们已经抽象了所有将列表呈现到父列表中的逻辑。组件只是用一些表示标记将列表包装起来。
考虑到组件的两个声明中仍然有重复的代码(例如 作用域的插槽 为了实现这一点,我们将使用作用域槽而不是常规槽。作用域插槽允许您将模板传递给插槽,而不是传递呈现的元素。它被称为“作用域”槽,因为尽管模板是在父作用域中呈现的,但它可以访问特定的子数据。 例如,具有作用域插槽的组件子组件可能如下所示。 使用此组件的父组件将在槽中声明模板元素。此模板元素将具有一个属性范围,该范围指定别名对象。添加到slot(在子模板中)的任何道具都可以作为别名对象的属性使用。 显示为: 在my-list中使用作用域插槽 让我们将列表数组作为道具传递给my-list。然后我们可以用作用域插槽替换插槽。这样my-list就可以负责迭代列表项,但是父级仍然可以定义每个列表项应该如何显示。 index.html 现在我们得到my-list来迭代这些项。在v-for循环中,item是当前列表项的别名。我们可以创建一个槽,并使用v-bind="item"将该列表项绑定到槽。 app.js index.html 注意:如果您以前没有见过v-bind在没有参数的情况下使用,这将把整个对象的属性绑定到元素。这对于作用域插槽非常有用,因为您绑定的对象通常具有任意属性,现在不需要通过名称指定这些属性。 现在我们将返回到根实例,并在my-list的slot中声明一个模板。首先查看形状列表,模板必须包含我们为其分配别名形状的scope属性。这个别名允许我们访问限定范围的道具。在模板内部,我们可以使用与以前完全相同的标记来显示形状列表项。 下面是完整的模板: 结论 尽管这种方法和以前一样有很多标记,但它将公共功能委托给了组件,从而实现了更健壮的设计。 以下是完整代码的代码页: https://codepen.io/anthonygore/pen/zExPZX
相关推荐: 更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!! Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 详解Vue.js中的作用域插槽. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!<div>
<slot my-prop="Hello from child"></slot>
</div>
<child>
<template scope="props">
<span>Hello from parent</span>
<span>{{ props.my-prop }}</span>
</template>
</child><div>
<span>Hello from parent</span>
<span>Hello from child</span>
</div>
<div id="app">
<my-list title="Shapes" :items="shapes">
<!--template will go here-->
</my-list>
<my-list title="Colors" :items="colors">
<!--template will go here-->
</my-list>
</div>Vue.component('my-list', {
template: '#my-list',
props: [ 'title', 'items' ]
});<script type="text/x-template" id="my-list">
<div class="my-list">
<div class="title">{{ title }}</div>
<div class="list">
<div v-for="item in items">
<slot v-bind="item"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</script><my-list title="Shapes" :items="shapes">
<template scope="shape">
<div>{{ shape.name }} <small>({{ shape.sides }} sides)</small></div>
</template>
</my-list><div id="app">
<my-list title="Shapes" :items="shapes">
<template scope="shape">
<div>{{ shape.name }} <small>({{ shape.sides }} sides)</small></div>
</template>
</my-list>
<my-list title="Colors" :items="colors">
<template scope="color">
<div>
<div class="swatch" :style="{ background: color.hex }"></div>
{{ color.name }}
</div>
</template>
</my-list>
</div>

