Rumah >hujung hadapan web >tutorial css >CSS中line-height详解(代码实例)
CSS中line-height详解(代码实例)
- 云罗郡主asal
- 2018-11-30 14:29:232814semak imbas
元素的高度是由什么决定对于我们解决页面显示问题和布局页面都有很大的帮助。 常规的操作表现是为一个块级元素设置height属性,则其拥有了高度:
<style>
.test {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="test"></div>
</body>但是根据熟知,当我们不为元素设置height,而元素中有内容时,该元素依然获取到了高度:
<style>
.test {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="test">1</div>
</body>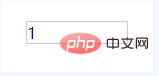
为什么div获取到了高度,并不是由于文字撑起了高度,而是line-height撑起了div,比较一下两端代码
.test {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="test">1</div>
</body>效果如下:

.test {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 100px;
line-height: 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="test">1</div>
</body>显而易见的结果就是因为有了height所以有高度,没有height则因为有了line-height而有了高度 更多详细的细节其实是因为 每一行文字 都有一个line boxes, 这些一个个盒子自然撑起了父元素的高度。
同时,观察上面的例子就能发现文字的中线和line-height的中线是在相同位置的,所以才有了常用的那套居中办法:
<style>
.test {
line-height: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>设置line-height和height相同数值则可以使得其中文字垂直居中
从结果来看确实如此,但是这句话不对,这句话多余了几个字,完全不需要设置height,只需要line-height就可以做到文字垂直居中了。
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci CSS中line-height详解(代码实例). Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Kenyataan:
Kandungan artikel ini disumbangkan secara sukarela oleh netizen, dan hak cipta adalah milik pengarang asal. Laman web ini tidak memikul tanggungjawab undang-undang yang sepadan. Jika anda menemui sebarang kandungan yang disyaki plagiarisme atau pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn
Artikel sebelumnya:在网格布局中创建多个网格的单元格(组合单元格)的方法介绍Artikel seterusnya:css如何清除下划线?css清除下划线有哪些方法

