Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >java中多线程的一些基本方法的使用介绍(附示例)
java中多线程的一些基本方法的使用介绍(附示例)
- 不言ke hadapan
- 2018-10-08 15:12:342676semak imbas
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于java中多线程中的一些基本方法的使用介绍(附示例),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
线程睡眠sleep()
Thread.sleep(毫秒);我们可以通过sleep方法设置让线程睡眠。可以看到sleep是个静态方法
public static native void sleep(long var0) throws InterruptedException;
try {
System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}setDaemon守护线程
非守护线程停止,那么守护线程自动退出
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {
System.out.println("非守护线程");
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
System.out.println("守护线程");
}
}
};
thread2.setDaemon(true);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}可以很明显的看到thread2本应该执行200次输出,但是这里只输出了几行。因为当thread1执行完毕后,thread2作为守护线程就自动停止了。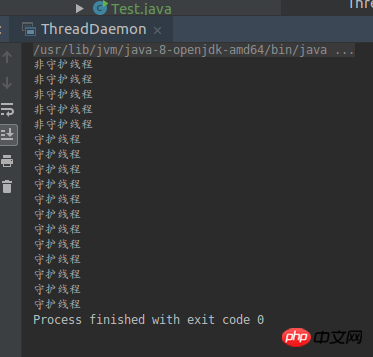
多线程jion
如果执行了jion方法,那么停止当前线程,先跑执行了jion()的线程。相当于插队执行。如下,在执行thread2线程的时候,如果i==20的时候,则让thread1插队先执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println("thread1---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i == 20) {
try {
//插队执行
thread1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}join()方法也可以传参数long 毫秒 join(毫秒)
表示让执行join的线程,插队执行XXX毫秒,过了时间后,两个线程交替执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println("thread1---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i == 20) {
try {
//插队执行1毫秒
thread1.join(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}yeild 礼让线程
yeild会让出cpu,让其他线程执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i % 5 == 0) {
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}setPriority给线程设置优先级
默认优先级是5 最小1,最大10
越大优先级越高
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}synchronized
同步代码块
当多线程并发,多段代码同时执行的时候。希望在执行其中代码的时候,cpu不切换线程
不用synchronized的情况
我们来看一下不用synchronized的情况会发生什么
public class ThreadSynchronied {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
void say() {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
void say1() {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
我们发现有些输出并没有打印全,在执行线程thread1的过程中,cpu被thread2抢占。这种情况下,肯定是不符合我们的业务逻辑的。所以我们要保证线程执行了一个完整的方法后,cpu才会被其他线程抢占
使用synchronized
public class ThreadSynchronied {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
String s = "hahaah";
void say() {
synchronized (s) {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
}
void say1() {
synchronized (s) {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
}
使用synchronized同步代码块后,就发现不会出现上述情况了
同步方法
public class ThreadSynchroniedMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
//在方法上加锁
static synchronized void say() {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
static void say1() {
synchronized (Say.class) {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
}同步方法指的就是在方法上加锁
静态同步方法的所对象是该类的字节码对象
非静态的同步方法锁对象是this
多个线程使用同一资源锁,容易造成死锁
什么是死锁?
死锁是指两个或两个以上的进程在执行过程中,由于竞争资源或者由于彼此通信而造成的一种阻塞的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去。此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁,这些永远在互相等待的进程称为死锁进程。
线程安全类
Vector
StringBuffer
HashTable
线程不安全
ArrayList
StringBuilder
HashSet
java.util.Collections中有synchronizedList等方法,支持我们把线程不安全的集合转成线程安全的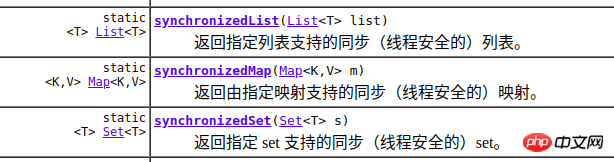
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci java中多线程的一些基本方法的使用介绍(附示例). Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

