Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >JAVA--线程与多线程 图文详解
JAVA--线程与多线程 图文详解
- php是最好的语言asal
- 2018-08-08 10:28:411337semak imbas
【线程】Java程序中的单任务流。我们把每个任务放在相对独立的线程中去实现。main是主线程
【并发】同时完成多个任务。程序执行的步骤都是有顺序的,但很多时候我们需要并发处理一个问题,而不是按顺序处理一个问题
【多线程】线程也看成对象,多线程指多个线程对象
【API中支持线程的类】java.lang.Thread。Thread类的对象就是线程对象
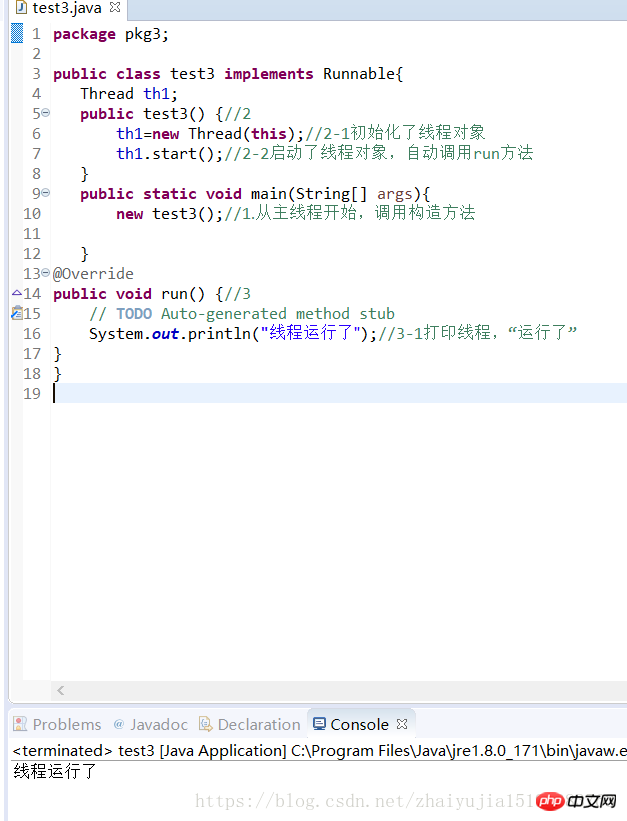
练习一、初始化线程对象,打印线程
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”}
}
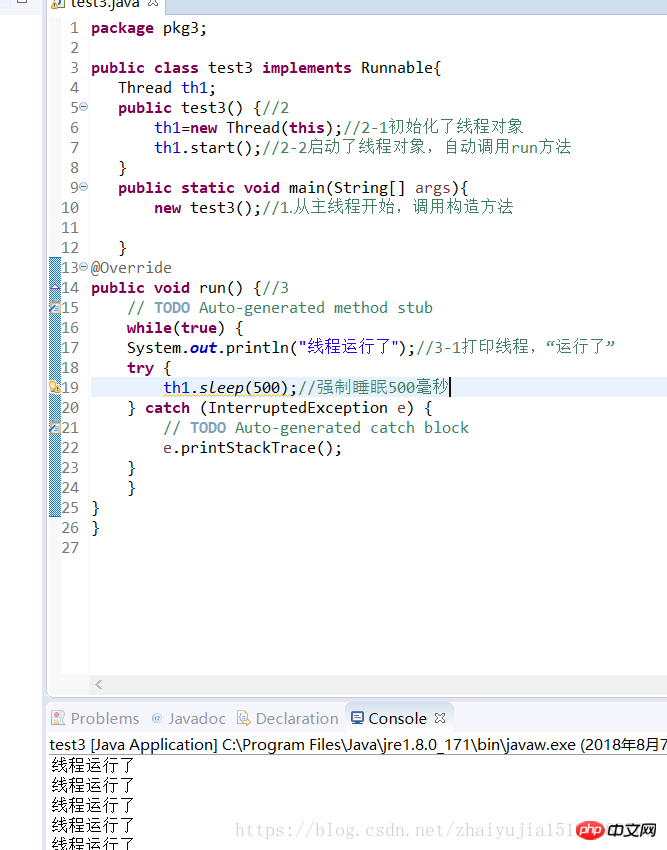
练习二、线程的生命周期:new、runnable、not runnable、dead
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(true) {
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”
try {
th1.sleep(500);//强制睡眠500毫秒,进入非运行状态not runnable(睡眠、堵塞、排队)
} catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
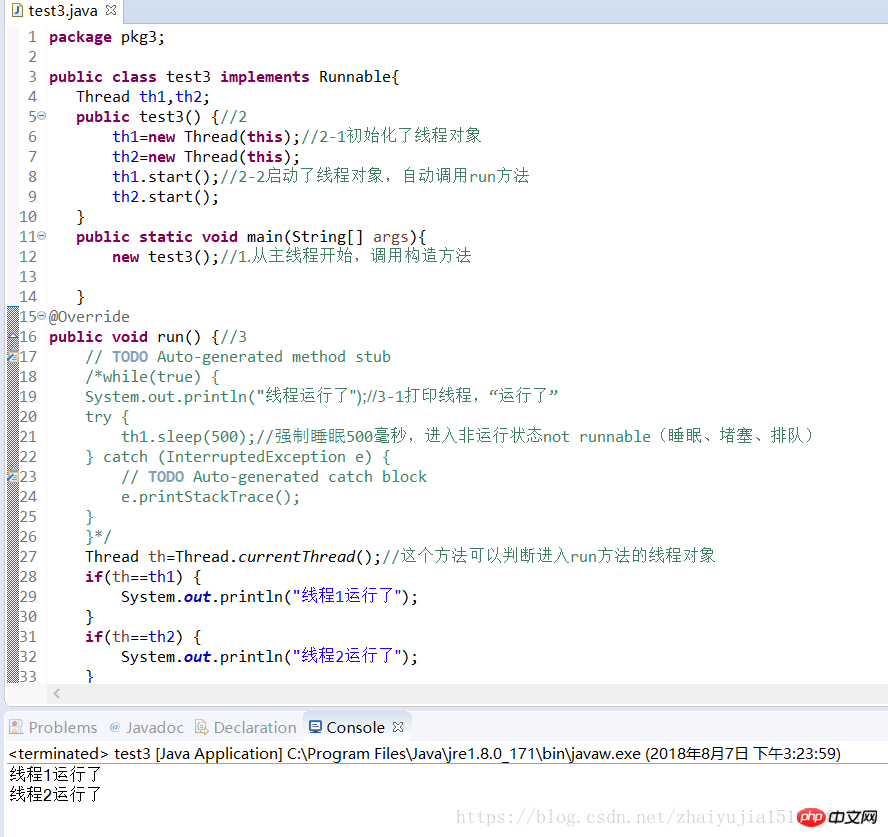
练习三、多线程
package pkg3;public class test3 implements Runnable{
Thread th1,th2; public test3() {//2
th1=new Thread(this);//2-1初始化了线程对象
th2=new Thread(this);
th1.start();//2-2启动了线程对象,自动调用run方法
th2.start();
} public static void main(String[] args){ new test3();//1.从主线程开始,调用构造方法
}@Overridepublic void run() {//3
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/*while(true) {
System.out.println("线程运行了");//3-1打印线程,“运行了”
try {
th1.sleep(500);//强制睡眠500毫秒,进入非运行状态not runnable(睡眠、堵塞、排队)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}*/
Thread th=Thread.currentThread();//这个方法可以判断进入run方法的线程对象
if(th==th1) {
System.out.println("线程1运行了");
} if(th==th2) {
System.out.println("线程2运行了");
}
}
}
相关推荐:
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci JAVA--线程与多线程 图文详解. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Kenyataan:
Kandungan artikel ini disumbangkan secara sukarela oleh netizen, dan hak cipta adalah milik pengarang asal. Laman web ini tidak memikul tanggungjawab undang-undang yang sepadan. Jika anda menemui sebarang kandungan yang disyaki plagiarisme atau pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn
Artikel sebelumnya:Java学习基础知识教程:Java 数据结构Artikel seterusnya:java类的初始化什么时候进行?(附代码)
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Bagaimanakah Penegasan Java Boleh Meningkatkan Kualiti Kod dan Mencegah Ralat?
- Adakah Mengisytiharkan Rentetan sebagai `akhir` di Jawa Mempengaruhi `==` Perbandingan?
- Manipulasi Rentetan di Jawa
- Bagaimana untuk Mengemas kini JLabel Secara Berterusan dengan Keputusan Tugasan Berjangka Panjang?
- Bagaimana untuk Menukar int[] kepada Integer[] untuk Digunakan sebagai Kunci Peta dalam Java?

