这次给大家带来深入JavaScript之JS的运动,使用JavaScript之JS的运动注意事项有哪些,下面就是实战案例,一起来看一下。
JS运动基础
运动框架
在开始运动时,关闭已有定时器
把运动和停止隔开(if/else)
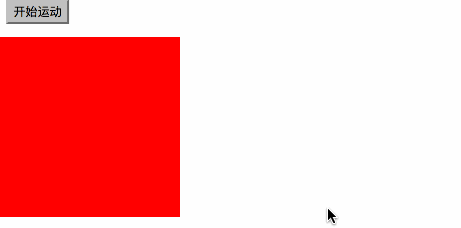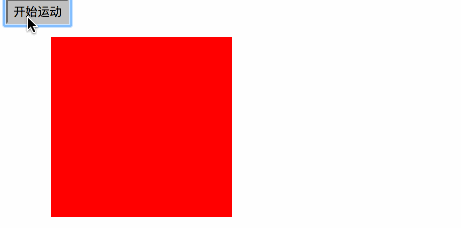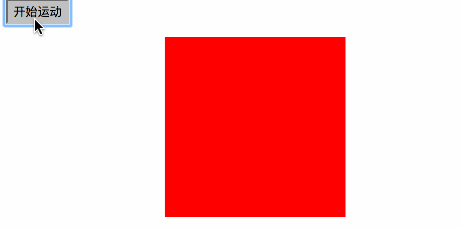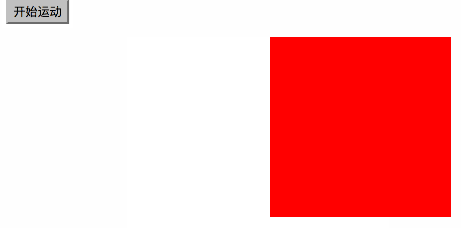
1.匀速运动
9a78f9382cfffc6c56b2ff1d7da5de14100db36a723c770d327fc0aef2ce13b193f0f5c25f18dab9d176bd4f6de5d30e
4d0d87937f6c83b675e896c64d3eb7c9
b2386ffb911b14667cb8f0f91ea547a701-运动基础6e916e0f7d1e588d4f442bf645aedb2f
c9ccee2e6ea535a969eb3f532ad9fe89
#div1 {width:200px; height:200px; background:red; position:absolute; top:50px; left:0px;} 531ac245ce3e4fe3d50054a55f265927
3f1c4e4b6b16bbbd69b2ee476dc4f83a
//定时器
var timer=null; function startMove() { var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1'); //为了保证只有一个定时器工作,把之前的定时器全关了
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){ var speed=1; if(oDiv.offsetLeft>=300)
{
clearInterval(timer);
} else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
} 2cacc6d41bbb37262a98f745aa00fbf09c3bca370b5104690d9ef395f2c5f8d16c04bd5ca3fcae76e30b72ad730ca86dfe739c9f8c7c7066ccc8668c0cff58f264cb571ed5952d9b43da1f2d70a36e9116b28748ea4df4d9c2150843fecfba6836cc49f0c466276486e50c850b7e495673a6ac4ed44ffec12cee46588e518a5e
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>无标题文档</title><style>#div1 {width:150px; height:200px; background:green; position:absolute; left:-150px;}#div1 span {position:absolute; width:20px; height:60px; line-height:20px; background:blue; right:-20px; top:70px;}</style><script>window.onload=function (){ var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function () {
startMove(0);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function () {
startMove(-150);
};
};var timer=null;function startMove(iTarget){ var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){ //先初始化速度
var speed=0; //开始位置 > 终点位置:比方 起点:350 终点 50 要想到50这个位置,速度得为:-10;
//oDiv.offsetLeft : 起点位置
//iTarget终点位置
if(oDiv.offsetLeft>iTarget)
{
speed=-10;
} else
{
speed=10;
} //这个函数存在一个漏洞,如果oDiv.offsetLef 刚好t >=iTarget 定时器不会停止
if(oDiv.offsetLeft==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
} else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}</script></head><body><div id="div1">
<span>分享到</span></div></body></html>
3.淡入淡出
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>03-淡入淡出</title>
<style>
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
opacity:0.3; //兼容chrome和ff
filtr:alpha(opacity:30);//兼容低版本的IE
} </style>
<script>
window.onload = function () { var oDiv = document.getElementsByTagName('div')[0];
oDiv.onmouseover = function () {
changeAlpha(100);
};
oDiv.onmouseout = function () {
changeAlpha(30);
}; var timer = null; var alpha = 30; function changeAlpha(isTarget) {
clearInterval(timer); var speed = 0;
timer = setInterval(function () { //注意这个速度判断要写在定时器里面
if (alpha < isTarget){
speed = 10;
}else {
speed = -10;
} if (alpha == isTarget){
clearInterval(timer);
}else {
alpha += speed;
oDiv.style.opacity = alpha/100;
oDiv.style.filter = 'alpha(opacity:'+alpha+')';
}
},30);
}
} </script></head><body><div></div></body></html>
3.缓冲运动
逐渐变慢,最后停止
距离越远速度越大
速度由距离决定
速度=(目标值-当前值)/缩放系数
Math.ceil():向上取整 Math.ceil(3.41) 结果是4 ,Math.ceil(-9.8) 结果是 -9; Math.floor():向下取整 Math.floor(-0.9) 结果是 -1;
例子:缓冲菜单
Bug:速度取整,取小数会出事!!!
<html><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>无标题文档</title> <style> *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } #div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:0; top:50px;} #div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;} </style> <script> function startMove() { var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1'); setInterval(function (){ var speed=(300-oDiv.offsetLeft)/10; //缓冲运动一定要取整,否则会出事的!!!! //Math.ceil():向上取整 Math.ceil(3.41) 结果是4 ,Math.ceil(-9.8) 结果是 -9; //Math.floor():向下取整 Math.floor(-0.9) 结果是 -1; //speed=Math.floor(speed); //速度大于0,向上取整,速度小于0,向下取整; speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed); //速度不能为小数:速度里面有小数,导致oDiv.style.left的值带有小数,而oDiv.style.left会自动取整,导致他把小数抹掉了,导致误差!!! //故把速度向上取整,来避免此误差 oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px'; document.title=oDiv.offsetLeft+','+speed; }, 30); } </script></head><body><input type="button" value="开始运动" onclick="startMove()" /><div id="div1"></div><div id="div2"></div></body></html>
缓冲运动一(chorme浏览器上有兼容问题)
跟随页面滚动的缓冲侧边栏
潜在问题:目标值不是整数时,会出现抖动的情况,只要强转成整数就可以了!可能会有0.5像素的误差,可以忽略不计!
右侧悬浮框
先了解下一些基础知识
获取浏览器滚动条滚动的距离
1.在设计页面时可能经常会用到固定层的位置,这就需要获取一些html对象的坐标以更灵活的设置目标层的坐标,这里可能就会用到document.body.scrollTop等属性,但是此属性在xhtml标准网页或者更简单的说是带58c6eaad61274c35998f01392fc4d2c9标签的页面里得到的结果是0,如果不要此标签则一切正常,那么在xhtml页面怎么获得body的坐标呢,当然有办法-使用document.documentElement来取代document.body,可以这样写
例:
获取浏览器滚动条滚动的距离
var top = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop;
在JavaScript里||是个好东西,除了能用在if等条件判断里,还能用在变量赋值上。那么上例等同于下例。
例:var top = document.documentElement.scrollTop ? document.documentElement.scrollTop : document.body.scrollTop;
这么写可以得到很好的兼容性。
相反,如果不做声明的话,document.documentElement.scrollTop反而会显示为0。
document.body.clientWidth ==> BODY对象宽度document.body.clientHeight ==> BODY对象高度document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 可见区域宽度document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 可见区域高度
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>右侧悬浮窗</title><style>#div1 {width:100px; height:150px; background:red; position:absolute; right:0; bottom:0;}</style><script>window.onscroll=function (){ var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1'); var scrollTop=document.documentElement.scrollTop||document.body.scrollTop; //oDiv.style.top=document.documentElement.clientHeight-oDiv.offsetHeight+scrollTop+'px'; startMove(document.documentElement.clientHeight-oDiv.offsetHeight+scrollTop);};var timer=null;function startMove(iTarget){ var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1'); clearInterval(timer); timer=setInterval(function (){ var speed=(iTarget-oDiv.offsetTop)/4; speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed); if(oDiv.offsetTop==iTarget) { clearInterval(timer); } else { oDiv.style.top=oDiv.offsetTop+speed+'px'; } }, 30);}</script></head><body style="height:2000px;"><div id="div1"></div></body></html>
匀速停止
//绝对值,
Math.abs()
比如:(Math.abs(-6)) 和 (Math.abs(6))结果都是6,他的意思就是把值变成没有正负号的样子,都是正的.
<html><head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;} #div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;} #div3 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:100px; top:0; background:black;} </style>
<script>
var timer=null; function startMove(iTarget) { var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){ var speed=0; if(oDiv.offsetLeft<iTarget)
{
speed=10;
} else
{
speed=-10;
} //目标和物体之间的距离的绝对值小于等于速度,就算他达到目标了.
if(Math.abs(iTarget-oDiv.offsetLeft)<=Math.abs(speed))
{
clearInterval(timer); //目标和物体之间的有一小小的距离,计算误差导致的.
//让left直接等于目标点
oDiv.style.left=iTarget+'px';
} else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
} </script></head><body><input type="button" value="到100" onclick="startMove(100)" /><input type="button" value="到300" onclick="startMove(300)" /><div id="div1"></div><div id="div2"></div><div id="div3"></div></body></html>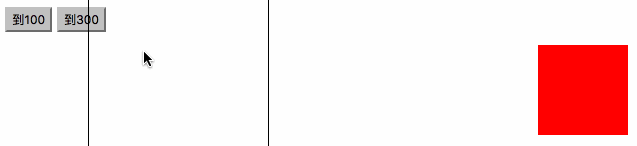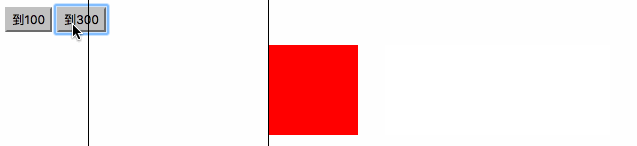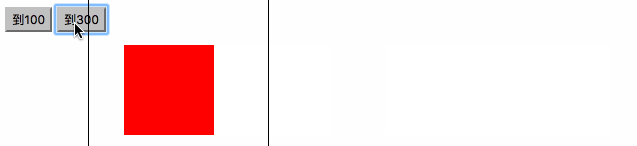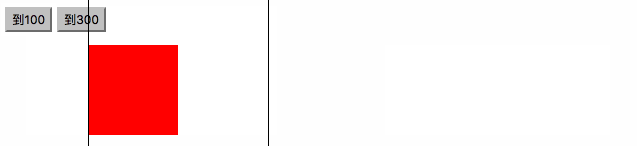
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 深入JavaScript之JS的运动. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Adakah JavaScript ditulis dalam C? Memeriksa buktiApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Adakah JavaScript ditulis dalam C? Memeriksa buktiApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AMYa, teras enjin JavaScript ditulis dalam C. 1) Bahasa C menyediakan prestasi yang efisien dan kawalan asas, yang sesuai untuk pembangunan enjin JavaScript. 2) Mengambil enjin V8 sebagai contoh, terasnya ditulis dalam C, menggabungkan kecekapan dan ciri-ciri berorientasikan objek C. 3) Prinsip kerja enjin JavaScript termasuk parsing, penyusun dan pelaksanaan, dan bahasa C memainkan peranan penting dalam proses ini.
 Peranan JavaScript: Membuat Web Interaktif dan DinamikApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Peranan JavaScript: Membuat Web Interaktif dan DinamikApr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript adalah di tengah -tengah laman web moden kerana ia meningkatkan interaktiviti dan dinamik laman web. 1) Ia membolehkan untuk menukar kandungan tanpa menyegarkan halaman, 2) memanipulasi laman web melalui Domapi, 3) menyokong kesan interaktif kompleks seperti animasi dan drag-and-drop, 4) mengoptimumkan prestasi dan amalan terbaik untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna.
 C dan JavaScript: Sambungan dijelaskanApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C dan JavaScript: Sambungan dijelaskanApr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC dan JavaScript mencapai interoperabilitas melalui webassembly. 1) Kod C disusun ke dalam modul WebAssembly dan diperkenalkan ke dalam persekitaran JavaScript untuk meningkatkan kuasa pengkomputeran. 2) Dalam pembangunan permainan, C mengendalikan enjin fizik dan rendering grafik, dan JavaScript bertanggungjawab untuk logik permainan dan antara muka pengguna.
 Dari laman web ke aplikasi: Aplikasi pelbagai JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Dari laman web ke aplikasi: Aplikasi pelbagai JavaScriptApr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript digunakan secara meluas di laman web, aplikasi mudah alih, aplikasi desktop dan pengaturcaraan sisi pelayan. 1) Dalam pembangunan laman web, JavaScript mengendalikan DOM bersama -sama dengan HTML dan CSS untuk mencapai kesan dinamik dan menyokong rangka kerja seperti JQuery dan React. 2) Melalui reaktnatif dan ionik, JavaScript digunakan untuk membangunkan aplikasi mudah alih rentas platform. 3) Rangka kerja elektron membolehkan JavaScript membina aplikasi desktop. 4) Node.js membolehkan JavaScript berjalan di sisi pelayan dan menyokong permintaan serentak yang tinggi.
 Python vs JavaScript: Gunakan Kes dan Aplikasi MembandingkanApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs JavaScript: Gunakan Kes dan Aplikasi MembandingkanApr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython lebih sesuai untuk sains data dan automasi, manakala JavaScript lebih sesuai untuk pembangunan front-end dan penuh. 1. Python berfungsi dengan baik dalam sains data dan pembelajaran mesin, menggunakan perpustakaan seperti numpy dan panda untuk pemprosesan data dan pemodelan. 2. Python adalah ringkas dan cekap dalam automasi dan skrip. 3. JavaScript sangat diperlukan dalam pembangunan front-end dan digunakan untuk membina laman web dinamik dan aplikasi satu halaman. 4. JavaScript memainkan peranan dalam pembangunan back-end melalui Node.js dan menyokong pembangunan stack penuh.
 Peranan C/C dalam JavaScript Jurubah dan PenyusunApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Peranan C/C dalam JavaScript Jurubah dan PenyusunApr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC dan C memainkan peranan penting dalam enjin JavaScript, terutamanya digunakan untuk melaksanakan jurubahasa dan penyusun JIT. 1) C digunakan untuk menghuraikan kod sumber JavaScript dan menghasilkan pokok sintaks abstrak. 2) C bertanggungjawab untuk menjana dan melaksanakan bytecode. 3) C melaksanakan pengkompil JIT, mengoptimumkan dan menyusun kod hot-spot semasa runtime, dan dengan ketara meningkatkan kecekapan pelaksanaan JavaScript.
 JavaScript in Action: Contoh dan projek dunia nyataApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Contoh dan projek dunia nyataApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMAplikasi JavaScript di dunia nyata termasuk pembangunan depan dan back-end. 1) Memaparkan aplikasi front-end dengan membina aplikasi senarai TODO, yang melibatkan operasi DOM dan pemprosesan acara. 2) Membina Restfulapi melalui Node.js dan menyatakan untuk menunjukkan aplikasi back-end.
 JavaScript dan Web: Fungsi teras dan kes penggunaanApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript dan Web: Fungsi teras dan kes penggunaanApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMPenggunaan utama JavaScript dalam pembangunan web termasuk interaksi klien, pengesahan bentuk dan komunikasi tak segerak. 1) kemas kini kandungan dinamik dan interaksi pengguna melalui operasi DOM; 2) pengesahan pelanggan dijalankan sebelum pengguna mengemukakan data untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna; 3) Komunikasi yang tidak bersesuaian dengan pelayan dicapai melalui teknologi Ajax.


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

Video Face Swap
Tukar muka dalam mana-mana video dengan mudah menggunakan alat tukar muka AI percuma kami!

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Penyesuai Pelayan SAP NetWeaver untuk Eclipse
Integrasikan Eclipse dengan pelayan aplikasi SAP NetWeaver.

Versi Mac WebStorm
Alat pembangunan JavaScript yang berguna

SublimeText3 Linux versi baharu
SublimeText3 Linux versi terkini

MinGW - GNU Minimalis untuk Windows
Projek ini dalam proses untuk dipindahkan ke osdn.net/projects/mingw, anda boleh terus mengikuti kami di sana. MinGW: Port Windows asli bagi GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), perpustakaan import yang boleh diedarkan secara bebas dan fail pengepala untuk membina aplikasi Windows asli termasuk sambungan kepada masa jalan MSVC untuk menyokong fungsi C99. Semua perisian MinGW boleh dijalankan pada platform Windows 64-bit.






