这篇文章主要介绍了Struts1教程之ActionMapping,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧
首先断点走出了processpath方法,
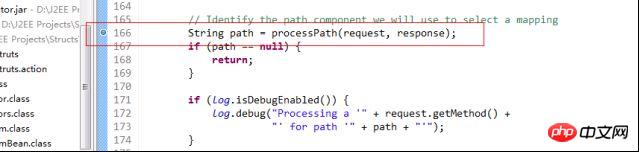
这个方法是用来截取字符串的,今天我们来看怎样获得ActionMapping的方法---processMapping。
在此之前简单说一下ActionMapping,它的源代码中可以看出,其中最重要的属性和我们的mvc小实例中的ActionMapping类似,都是有path、type还有forwardMap,主要是对应的struts-config配置文件而来,这个就是保存这个配置文件的信息到内存中。
具体的mvc小实例的ActionMapping代码如下:
package com.cjq.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionMapping {
private String path;
private Object type;
private Map forwardMap;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Object getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Object type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map getForwardMap() {
return forwardMap;
}
public void setForwardMap(Map forwardMap) {
this.forwardMap = forwardMap;
}
}而Struts中的Actionconfig(因为ActionMapping是继承这个ActionConfig的,所以我们来看ActionConfig更加直接)的代码如下:
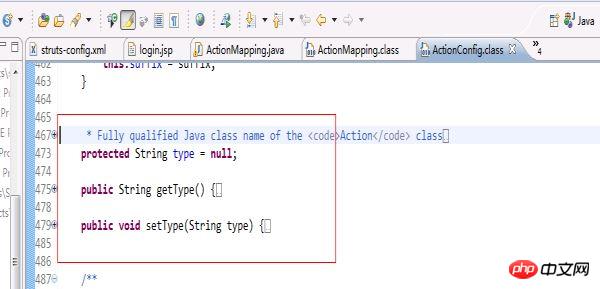
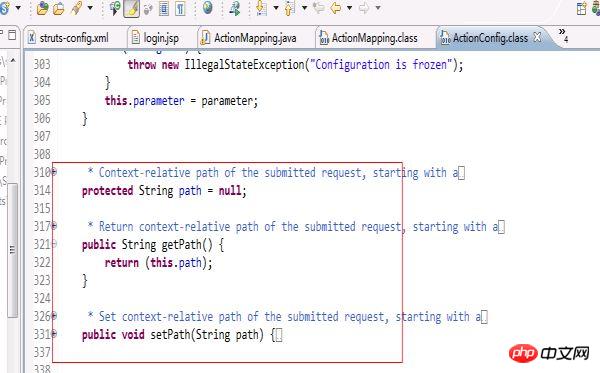

从这两部分代码来看,更加印证了我在开篇写的mvc小实例是一个struts框架的雏形。
讲完ActionMapping的一些内容后,相信对ActionMapping有所了解,那么系统是如何生成ActionMapping和如何找到ActionMapping的呢?这就是今天要说的整体:
我们看下web.xml中有一个4781e2cbaa93c386271b418d3a01af0823065abc64b27fbca30c0905ab93e8ea0 配置信息,这个信息就是说明了但服务器已启动就动态读取struts-config配置文件把配置文件的信息put到ActionMapping中。所以当我们运行服务器的时候,我们在内存中已经存在对应struts-config配置文件信息对应的ActionMapping。今天就是要通过processMapping读取这个ActionMapping类。
进入断点调试,首先在processMapping方法上设置断点。

进入源代码中:
/**
* <p>Select the mapping used to process theselection path for this request
* If no mapping can be identified, createan error response and return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param path The portion of the requestURI for selecting a mapping
*
* @exception IOException if an input/outputerror occurs
*/
protectedActionMapping processMapping(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
String path)
throws IOException {
// Is there a mapping for this path?
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping)
moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
// If a mapping is found, put it in the request and return it
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
// Locate the mapping for unknown paths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfig.findActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configs.length; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
}首先我们传入我们在上一步截取的路径,通过moduleConfig的findAction方法来查找ActionConfig,并且返回ActionMapping。具体代码是:
ActionMapping mapping =(ActionMapping) moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
如果找到,那么就讲ActionMapping存放到request的context中。代码:
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}如果没有通过path找到mapping,则在Actionconfig中遍历为未知路径寻找mapping,如果找到则存放到request中,如果没有找到,则返回错误信息,具体代码如下:
// Locate the mapping for unknownpaths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfigfindActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configslength; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;来看下ActionServlet中的一个方法processActionForm,当我们在截取字符串,再根据字符串取得ActionMapping(这是前两篇文章中介绍的)之后,我们就要用利用ActionMapping来创建ActionForm了,并且把ActionForm放到request或session中管理。
先来看具体struts中processActionForm方法的具体实现:
/**
* <p>Retrieve and return the <code>ActionForm</code> associatedwith
* this mapping, creating and retaining oneif necessary. If there is no
* <code>ActionForm</code> associated with this mapping,return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param mapping The mapping we are using
*/
protectedActionForm processActionForm(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) {
// Create (if necessary) a form bean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtilscreateActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}
// Store the new instance in the appropriate scope
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Storing ActionForm bean instance in scope '" +
mapping.getScope() + "' under attribute key '" +
mapping.getAttribute() + "'");
}
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) {
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =requestgetSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
return (instance);
}这个方法的大体流程是:根据ActionMapping中的name名称查找ActionForm,如果配置了ActionForm,那么就到request或session中查找,如果在request或session中存在已经创建的ActionForm,那么将返回。如果不存在那么会根据ActionForm的完成路径采用反射进行创建,再将创建好的ActionForm放到request或session中,之后返回ActionForm。
具体我们可以跟随断点调试来看看这个方法是如何运行的。
先设置断点,之后进入processActionForm方法。
第一个步骤就是创建ActionForm:
// Create (if necessary) a formbean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtils.createActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}通过调用RequestUtils.createActionForm的方法把ActionMapping中的ActionForm字符串生成对象,并且返回。进入这段代码中:
publicstaticActionForm createActionForm(
HttpServletRequest request,
ActionMapping mapping,
ModuleConfig moduleConfig,
ActionServlet servlet) {
// Is there a form bean associated with this mapping?
String attribute = mappinggetAttribute();
if (attribute == null) {
return (null);
}
// Look up the form bean configuration information to use
String name = mapping.getName();
FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfigfindFormBeanConfig(name);
if (config == null) {
log.warn("No FormBeanConfig found under '"+ name + "'");
return (null);
}
ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mappinggetScope());
// Can we recycle the existing form bean instance (if there is one)?
try {
if (instance != null && canReuseActionForm(instance,config)) {
return (instance);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(servlet.getInternal().getMessage("formBean",config.getType()), e);
return (null);
}
return createActionForm(config,servlet);
}方法首先定义变量name,并且从mapping中获取值,String name = mapping.getName();也就是我们实例中的LoginForm字符串。之后通过调用FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfig.findFormBeanConfig(name);这句话把相应的LoginForm字符串生成相应的对象。
这里要说明的是我们在struts-config配置文件中,配置过这样一个标签信息:
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="loginForm" type=".struts.LoginActionForm"/>
</form-beans>这个标签在服务器一启动的时候就会利用digester读取这里的配置信息,并且放在FormBeanConfig类中,这样我们可以通过上面那一句话就可以把LoginForm字符串生成相应的对象。
之后调用了ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mapping.getScope());这个方法,这个方法主要是查找scope属性中有没有存在ActionForm。具体实现:
if ("request".equals(scope)){
instance = (ActionForm)request.getAttribute(attribute);
} else {
session = request.getSession();
instance = (ActionForm)session.getAttribute(attribute);
}这里判断scope属性值是否为request,如果是则从request中读出ActionForm,如果不是则从session中读出。程序如果是第一次执行,那么ActionForm会是为空的。因为这里的ActionForm为空,所以就进入了if判断语句中,最后通过调用return createActionForm(config, servlet);创建ActionForm并且返回。
之后processActionForm就会把返回来的ActionForm放入request或者session中。具体实现就是:
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())){
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}到此为止,ActionForm就创建完成,当ActionForm创建完成之后,就要用其他的方法来往ActionForm中赋值了
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 关于Struts1之ActionMapping的示例详解. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Bagaimanakah saya menggunakan Maven atau Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java Lanjutan, Membina Automasi, dan Resolusi Ketergantungan?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
Bagaimanakah saya menggunakan Maven atau Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java Lanjutan, Membina Automasi, dan Resolusi Ketergantungan?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PMArtikel ini membincangkan menggunakan Maven dan Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java, membina automasi, dan resolusi pergantungan, membandingkan pendekatan dan strategi pengoptimuman mereka.
 Bagaimanakah saya membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java Custom (fail JAR) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
Bagaimanakah saya membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java Custom (fail JAR) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PMArtikel ini membincangkan membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java tersuai (fail balang) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul, menggunakan alat seperti Maven dan Gradle.
 Bagaimanakah saya melaksanakan caching pelbagai peringkat dalam aplikasi java menggunakan perpustakaan seperti kafein atau cache jambu?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
Bagaimanakah saya melaksanakan caching pelbagai peringkat dalam aplikasi java menggunakan perpustakaan seperti kafein atau cache jambu?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PMArtikel ini membincangkan pelaksanaan caching pelbagai peringkat di Java menggunakan kafein dan cache jambu untuk meningkatkan prestasi aplikasi. Ia meliputi persediaan, integrasi, dan faedah prestasi, bersama -sama dengan Pengurusan Dasar Konfigurasi dan Pengusiran PRA Terbaik
 Bagaimanakah saya boleh menggunakan JPA (Java Constence API) untuk pemetaan objek-objek dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan malas malas?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
Bagaimanakah saya boleh menggunakan JPA (Java Constence API) untuk pemetaan objek-objek dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan malas malas?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PMArtikel ini membincangkan menggunakan JPA untuk pemetaan objek-relasi dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan pemuatan malas. Ia meliputi persediaan, pemetaan entiti, dan amalan terbaik untuk mengoptimumkan prestasi sambil menonjolkan potensi perangkap. [159 aksara]
 Bagaimanakah mekanisme kelas muatan Java berfungsi, termasuk kelas yang berbeza dan model delegasi mereka?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
Bagaimanakah mekanisme kelas muatan Java berfungsi, termasuk kelas yang berbeza dan model delegasi mereka?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PMKelas kelas Java melibatkan pemuatan, menghubungkan, dan memulakan kelas menggunakan sistem hierarki dengan bootstrap, lanjutan, dan pemuat kelas aplikasi. Model delegasi induk memastikan kelas teras dimuatkan dahulu, yang mempengaruhi LOA kelas tersuai


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

MinGW - GNU Minimalis untuk Windows
Projek ini dalam proses untuk dipindahkan ke osdn.net/projects/mingw, anda boleh terus mengikuti kami di sana. MinGW: Port Windows asli bagi GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), perpustakaan import yang boleh diedarkan secara bebas dan fail pengepala untuk membina aplikasi Windows asli termasuk sambungan kepada masa jalan MSVC untuk menyokong fungsi C99. Semua perisian MinGW boleh dijalankan pada platform Windows 64-bit.

SublimeText3 Linux versi baharu
SublimeText3 Linux versi terkini

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) ialah aplikasi web PHP/MySQL yang sangat terdedah. Matlamat utamanya adalah untuk menjadi bantuan bagi profesional keselamatan untuk menguji kemahiran dan alatan mereka dalam persekitaran undang-undang, untuk membantu pembangun web lebih memahami proses mengamankan aplikasi web, dan untuk membantu guru/pelajar mengajar/belajar dalam persekitaran bilik darjah Aplikasi web keselamatan. Matlamat DVWA adalah untuk mempraktikkan beberapa kelemahan web yang paling biasa melalui antara muka yang mudah dan mudah, dengan pelbagai tahap kesukaran. Sila ambil perhatian bahawa perisian ini

Muat turun versi mac editor Atom
Editor sumber terbuka yang paling popular

Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat
Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat ialah persekitaran pelayar selamat untuk mengambil peperiksaan dalam talian dengan selamat. Perisian ini menukar mana-mana komputer menjadi stesen kerja yang selamat. Ia mengawal akses kepada mana-mana utiliti dan menghalang pelajar daripada menggunakan sumber yang tidak dibenarkan.





