这篇文章主要为大家详细介绍了java生成可变表头excel的方法,传入一个表头和数据,将数据导入到excel中,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下
本文为大家分享了java生成可变表头excel的具体步骤,供大家参考,具体内容如下
1、实现功能:
传入一个表头和数据,将数据导入到excel中。
为了便于项目的扩展,数据传入通过泛型集合传入,获取数据时,通过反射的方式获取,这样无论你的表头是多少项,我都能很方便的生成。另外为了便于数据的管理,我每天都会自动生成一个文件夹,excel生成在相应的文件夹中。文件的根目录通过读取项目中的properties文件获取(详情可查看:获取tomcat上properties文件内容的方法)。好啦,接下来直接进入代码开发吧。
2、所需jar包
这里使用的是通过poi的方式将数据导入到excel中。

3、代码设计
1)、properties文件内容
filePath=E\:/appData
2)、获取文件保存的根目录(来自项目中的properties文件)
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class GetFilePlace
{
/**
* 读取文件,获取excel保存的根目录
* @return excel保存的根目录
*/
public String getFilePath()
{
String dir = System.getProperty("user.dir"); //获得tomcat所在的工作路径
//获取到存储了文件存储位置的filedir.properties 文件路径
String realDir = dir + File.separator + "src" + File.separator +"META-INF" + File.separator + "filedir.properties";
/*String realDir = dir.substring(0, dir.length()-4) + File.separator +"webapps" + File.separator + "generateExcels"
+ File.separator + "classes" + File.separator + "META-INF" + File.separator + "config" + File.separator + "filedir.properties";
*/
return realDir;
}
/**
* 获取filePath路径【properities文件】中key对应的值,
* @param filePath properities文件路径【包含properities文件】
* @param key 要查找的key值
* @return key对应的value
*/
public String GetValueByKey(String filePath, String key)
{
Properties pps = new Properties();
try {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream (new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in);
String value = pps.getProperty(key);
in.close();
return value;
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 查询properities文件中可以对应的存储地点
* @param key 查询主键
* @return key对应的存储地址
*/
public String getFileDirFromProperties(String key)
{
return GetValueByKey(getFilePath(),key);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(new GetFilePlace().getFileDirFromProperties("filePath"));
}
}3)、生成文件夹
import java.io.File;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class GenerateFold
{
/**
* 查询当前生成的excel需要存在在哪个路径,如果存在则存储在相应的位置,否则生成改目录, 每天生成一个文件夹,文件夹的命名规则为 年月日的时间戳
* @param foldName 生成excel保存路径
* @return 现在的excel需要保存路径
*/
public String getFold(String foldName)
{
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
String todayStr = format.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
String foldPath = foldName + File.separator + todayStr;
File file = new File(foldPath);
if(!file.exists() && !file.isDirectory())
{
System.out.println("不存在");
file.mkdirs();
}
else
{
System.out.println("存在");
}
return foldPath;
}
}4)、生成excel
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.Region;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import com.zcr.until.GetFilePlace;
import com.zcr.until.User;
/**
* 生成excel
* @author zcr
*
*/
public class GenerateExcel
{
/**
* 通过关键字查询properties文件相应文件的存储位置,根据表头顺序将数据保存到相应文件路径的xls文件中, 文件的命名规则是时间戳加一串全球唯一编码
* @param fileDir //查找文件存储根目录
* @param head //表头
* @param list //数据
* @return //文件的保存路径及其名字的字符串
*/
public <T> String generateExcels(String fileDir,String [] head,List<T> list)
{
//获得存储的路径
//String savePath = new GetFilePlace().getFileDirFromProperties(key);
//文件存储名字
String saveFileName = "";
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSS");
saveFileName += format.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID(); //全球唯一编码
saveFileName += "-" + uuid.toString();
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
workbook.setSheetName(0,"APP数据"); //设置表格工作簿名称
HSSFCellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
cellStyle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
cellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(CellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
HSSFRow titleRow = sheet.createRow(0);
sheet.addMergedRegion(new Region(0,(short)0,0,(short)(head.length-1)));
HSSFCell titleCell = titleRow.createCell(0);
titleCell.setCellValue("AAP数据____ ");
titleCell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
HSSFRow row1 = sheet.createRow(1);
//设置表头
for(int i = 0 ; i < head.length ; i++)
{
HSSFCell cell = row1.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(head[i]); //设置值
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);//设置样式
}
if(null != list && list.size() > 0)
{
int size = list.size();
Class classType = list.get(0).getClass();
for(int i = 0,rowNum=2 ; i < size ; i ++,rowNum++)
{
HSSFRow rows = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
T t = list.get(i);
//添加数据行
for(int j = 0 ; j < head.length ; j++)
{
//获得首字母
String firstLetter = head[j].substring(0,1).toUpperCase();
//获得get方法,getName,getAge等
String getMethodName = "get" + firstLetter + head[j].substring(1);
Method method;
try
{
//通过反射获得相应的get方法,用于获得相应的属性值
method = classType.getMethod(getMethodName, new Class[]{});
HSSFCell dataCell = rows.createCell(j);
try
{
System.out.print(getMethodName +":" + method.invoke(t, new Class[]{}) +",");
dataCell.setCellValue(method.invoke(t, new Class[]{}).toString());
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
} //设置值
dataCell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);//设置样式
}
catch (SecurityException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("没有数据");
}
//获得文件存储路径
//String fileDir = new GetFilePlace().getFileDirFromProperties(key);
saveFileName += ".xls";
String saveFilePathAndName = fileDir + File.separator + saveFileName;
OutputStream out = null;
try
{
out = new FileOutputStream(saveFilePathAndName);
try
{
workbook.write(out);//保存文件
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
try
{
out.close();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return saveFilePathAndName;
}
/**
* 提供外界调用的接口,生成以head为表头,list为数据的excel
* @param head //数据表头
* @param list //数据
* @return //excel所在的路径
*/
public <T> String generateExcel(String [] head,List<T> list)
{
final String FilePath = "filePath";
String saveFilePathAndName = "";
//获得存储的根目录
String savePath = new GetFilePlace().getFileDirFromProperties(FilePath);
//获得当天存储的路径
String realSavePath = new GenerateFold().getFold(savePath);
//生成excel并将存储的路径返回(包含文件名)
saveFilePathAndName = generateExcels(realSavePath, head, list);
return saveFilePathAndName;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String [] head = {"name","sex","adress","height","age","jj"};
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
User user1 = new User("zhangsan",1,1.1f,"北京","男","AA");
User user2 = new User("lisi",22222,3.2f,"上海","女","BB");
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
System.out.println(new GenerateExcel().generateExcel(head,list));
//System.out.println(new GenerateExcel().generateExcels("E:\\appData\\20151104",head,list));
}
}5)、测试结果
生成了文件
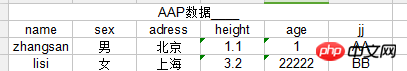
文件内容如下
properties文件读取可查看:获取tomcat上properties文件内容的方法
读取excel可查看:java使用POI批量导入excel数据的方法
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Java如何生成excel的表头可变的示例代码. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Bagaimanakah saya menggunakan Maven atau Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java Lanjutan, Membina Automasi, dan Resolusi Ketergantungan?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
Bagaimanakah saya menggunakan Maven atau Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java Lanjutan, Membina Automasi, dan Resolusi Ketergantungan?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PMArtikel ini membincangkan menggunakan Maven dan Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java, membina automasi, dan resolusi pergantungan, membandingkan pendekatan dan strategi pengoptimuman mereka.
 Bagaimanakah saya membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java Custom (fail JAR) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
Bagaimanakah saya membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java Custom (fail JAR) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PMArtikel ini membincangkan membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java tersuai (fail balang) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul, menggunakan alat seperti Maven dan Gradle.
 Bagaimanakah saya melaksanakan caching pelbagai peringkat dalam aplikasi java menggunakan perpustakaan seperti kafein atau cache jambu?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
Bagaimanakah saya melaksanakan caching pelbagai peringkat dalam aplikasi java menggunakan perpustakaan seperti kafein atau cache jambu?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PMArtikel ini membincangkan pelaksanaan caching pelbagai peringkat di Java menggunakan kafein dan cache jambu untuk meningkatkan prestasi aplikasi. Ia meliputi persediaan, integrasi, dan faedah prestasi, bersama -sama dengan Pengurusan Dasar Konfigurasi dan Pengusiran PRA Terbaik
 Bagaimanakah saya boleh menggunakan JPA (Java Constence API) untuk pemetaan objek-objek dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan malas malas?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
Bagaimanakah saya boleh menggunakan JPA (Java Constence API) untuk pemetaan objek-objek dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan malas malas?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PMArtikel ini membincangkan menggunakan JPA untuk pemetaan objek-relasi dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan pemuatan malas. Ia meliputi persediaan, pemetaan entiti, dan amalan terbaik untuk mengoptimumkan prestasi sambil menonjolkan potensi perangkap. [159 aksara]
 Bagaimanakah mekanisme kelas muatan Java berfungsi, termasuk kelas yang berbeza dan model delegasi mereka?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
Bagaimanakah mekanisme kelas muatan Java berfungsi, termasuk kelas yang berbeza dan model delegasi mereka?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PMKelas kelas Java melibatkan pemuatan, menghubungkan, dan memulakan kelas menggunakan sistem hierarki dengan bootstrap, lanjutan, dan pemuat kelas aplikasi. Model delegasi induk memastikan kelas teras dimuatkan dahulu, yang mempengaruhi LOA kelas tersuai


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

SublimeText3 versi Cina
Versi Cina, sangat mudah digunakan

Muat turun versi mac editor Atom
Editor sumber terbuka yang paling popular

VSCode Windows 64-bit Muat Turun
Editor IDE percuma dan berkuasa yang dilancarkan oleh Microsoft

Hantar Studio 13.0.1
Persekitaran pembangunan bersepadu PHP yang berkuasa

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) ialah aplikasi web PHP/MySQL yang sangat terdedah. Matlamat utamanya adalah untuk menjadi bantuan bagi profesional keselamatan untuk menguji kemahiran dan alatan mereka dalam persekitaran undang-undang, untuk membantu pembangun web lebih memahami proses mengamankan aplikasi web, dan untuk membantu guru/pelajar mengajar/belajar dalam persekitaran bilik darjah Aplikasi web keselamatan. Matlamat DVWA adalah untuk mempraktikkan beberapa kelemahan web yang paling biasa melalui antara muka yang mudah dan mudah, dengan pelbagai tahap kesukaran. Sila ambil perhatian bahawa perisian ini





