Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >Comparable与Comparator的比较与使用
Comparable与Comparator的比较与使用
- 零下一度asal
- 2017-07-24 10:19:141418semak imbas
一 概述
1.Comparable与Comparator使用背景
数值型数据(byte int short long float double)天生可对比大小,可排序,String实现了Comparable接口也可以对比大小与排序,而自定义类多种多样,没有一个共有的可以用作排序的指标,因此需要在自定义类中手动建立对比的方法,出于这个目的,java提供了两个接口Comparable与Comparator。
2.集合排序
Collections.sort()底层排序依靠的是Arrays.sort(),而Arrays.sort()排序时采用的是冒泡法。
二 Comparable
需要对比大小的对象可以实现Comparable接口,实现其中的抽象方法,该抽象方法用来设定比较的方式。下面以一个示例进行说明:
1.实体类
package com.javase.collections.comparable;public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {private String name;private int score;public Student() {super();
}public Student(String name, int score) {super();this.name = name;this.score = score;
}public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public int getScore() {return score;
}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;
}
@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student stu) {return this.score - stu.score;// 操作对象减去参数对象,升序排列,反之降序。 }
}在compareTo()方法中,以属性score为排序指标,采用“this.score-stu.score”,最终结果以升序排列,反之降序。
2.测试类
package com.javase.collections.comparable;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;import org.junit.Test;public class ComparableTest {
@Testpublic void testComparable() {
List<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan", 100);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 90);
Student wanger = new Student("wanger", 95);
stus.add(zhangsan);
stus.add(lisi);
stus.add(wanger);
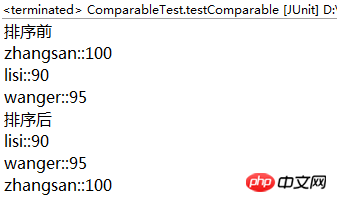
System.out.println("排序前");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
System.out.println("排序后");
Collections.sort(stus);for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
}
}输出:
三 Comparator
如果一个类在创建时未实现Comparable接口,希望在不修改源码的情况下对其对象进行排序,可以在调用排序方法时实现Comparator比较器接口,指定排序方法。下面以一个示例进行说明:
1.实体类
package com.javase.collections.comparator;public class Student {private String name;private int score;public Student() {super();
}public Student(String name, int score) {super();this.name = name;this.score = score;
}public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public int getScore() {return score;
}public void setScore(int score) {this.score = score;
}
}2.测试类
package com.javase.collections.comparator;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.List;import org.junit.Test;public class ComparatorTest {
@Testpublic void test() {
List<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student zhangsan = new Student("zhangsan", 100);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 90);
Student wanger = new Student("wanger", 95);
stus.add(zhangsan);
stus.add(lisi);
stus.add(wanger);
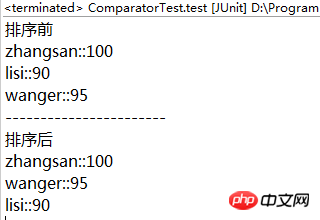
System.out.println("排序前");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Collections.sort(stus, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Overridepublic int compare(Student stu01, Student stu02) {// return stu01.getScore() - stu02.getScore();//升序return stu02.getScore() - stu01.getScore();// 降序 }
});
System.out.println("排序后");for (Student x : stus) {
System.out.println(x.getName() + "::" + x.getScore());
}
}
}在compare(Student stu01, Student stu02)方法中,以属性score为排序指标,采用“stu01.score-stu02.score”,最终结果升序排列,反之降序。
输出:
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Comparable与Comparator的比较与使用. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Bagaimanakah saya membuat dan menggunakan perpustakaan Java Custom (fail JAR) dengan pengurusan versi dan pergantungan yang betul?
- Bagaimanakah mekanisme kelas muatan Java berfungsi, termasuk kelas yang berbeza dan model delegasi mereka?
- Bagaimanakah saya boleh menggunakan JPA (Java Constence API) untuk pemetaan objek-objek dengan ciri-ciri canggih seperti caching dan malas malas?
- Bagaimanakah saya melaksanakan caching pelbagai peringkat dalam aplikasi java menggunakan perpustakaan seperti kafein atau cache jambu?
- Bagaimanakah saya menggunakan Maven atau Gradle untuk Pengurusan Projek Java Lanjutan, Membina Automasi, dan Resolusi Ketergantungan?

