Rumah > Artikel > pangkalan data > MySQL中两种子查询的写法
MySQL中两种子查询的写法
- 零下一度asal
- 2017-06-29 11:09:063498semak imbas
MySQL的测试环境
测试表如下
create table test_table2 ( id int auto_increment primary key, pay_id int, pay_time datetime, other_col varchar(100) )
建一个存储过程插入测试数据,测试数据的特点是pay_id可重复,这里在存储过程处理成,循环插入300W条数据的过程中,每隔100条数据插入一条重复的pay_id,时间字段在一定范围内随机
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`%` PROCEDURE `test_insert`(IN `loopcount` INT) LANGUAGE SQLNOT DETERMINISTICCONTAINS SQL SQL SECURITY DEFINER COMMENT ''BEGINdeclare cnt int;set cnt = 0;while cnt< loopcount doinsert into test_table2 (pay_id,pay_time,other_col) values (cnt,date_add(now(), interval floor(300*rand()) day),uuid());if (cnt mod 100 = 0) theninsert into test_table2 (pay_id,pay_time,other_col) values (cnt,date_add(now(), interval floor(300*rand()) day),uuid());end if;set cnt = cnt + 1; end while;END
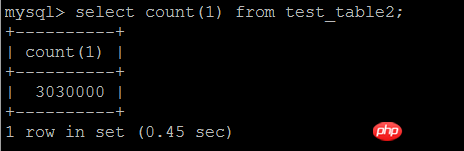
执行 call test_insert(3000000); 插入303000行数据
两种子查询的写法
查询大概的意思是查询某个时间段之内的业务Id大于1的数据,于是就出现两种写法。
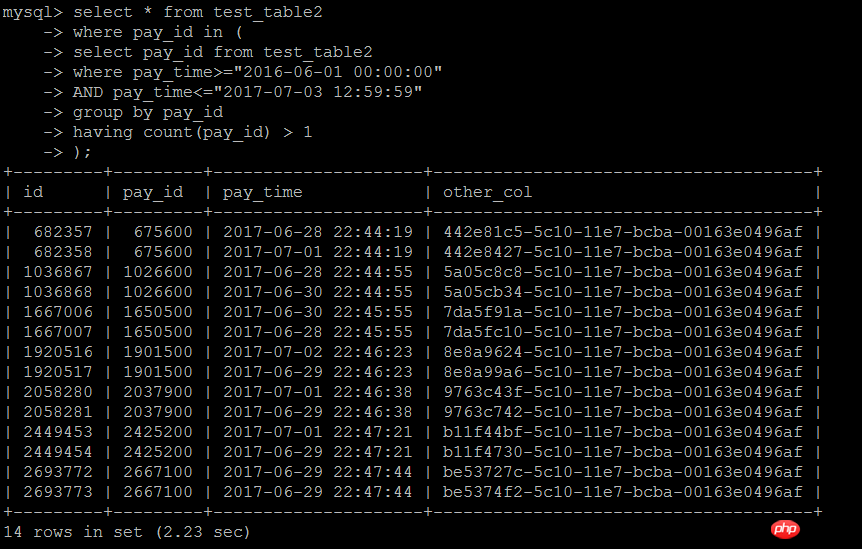
第一种写法如下:IN子查询中是某段时间内业务统计行数大于1的业务Id,外层按照IN子查询的结果进行查询,业务Id的列pay_id上有索引,逻辑也比较简单,
这种写法,在数据量大的时候确实效率比较低,用不到索引
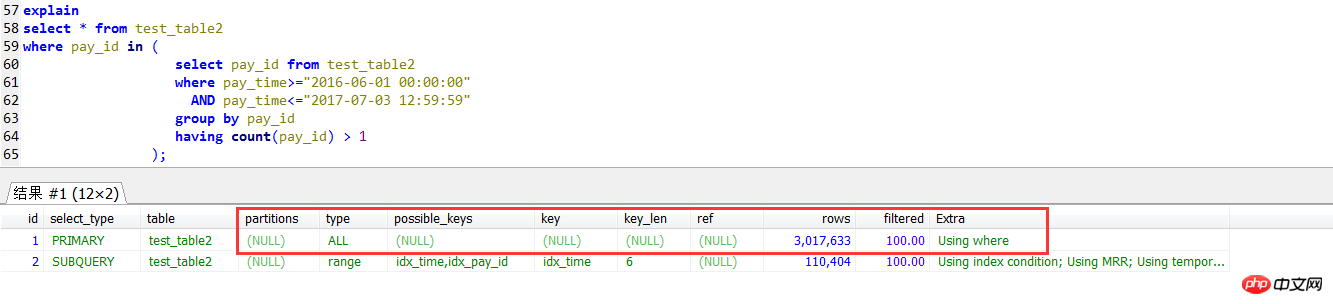
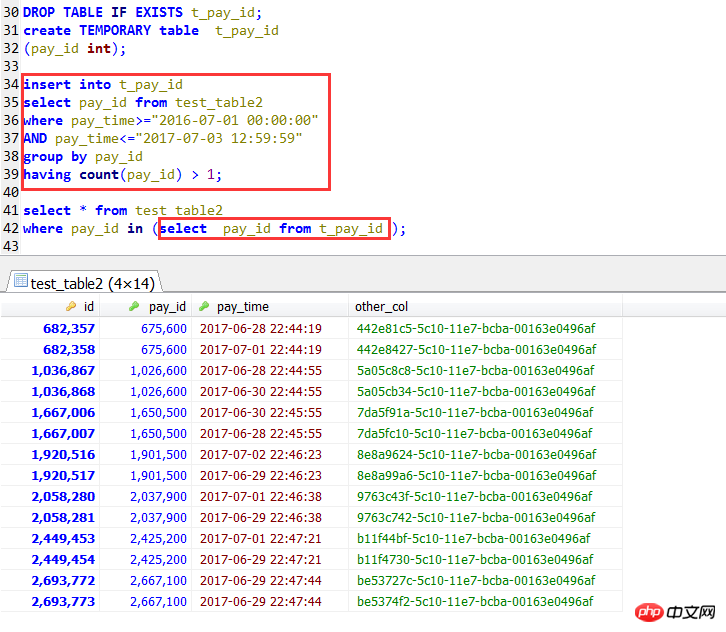
select * from test_table2 force index(idx_pay_id)where pay_id in ( select pay_id from test_table2 where pay_time>="2016-06-01 00:00:00" AND pay_time<="2017-07-03 12:59:59" group by pay_id having count(pay_id) > 1);
执行结果:2.23秒
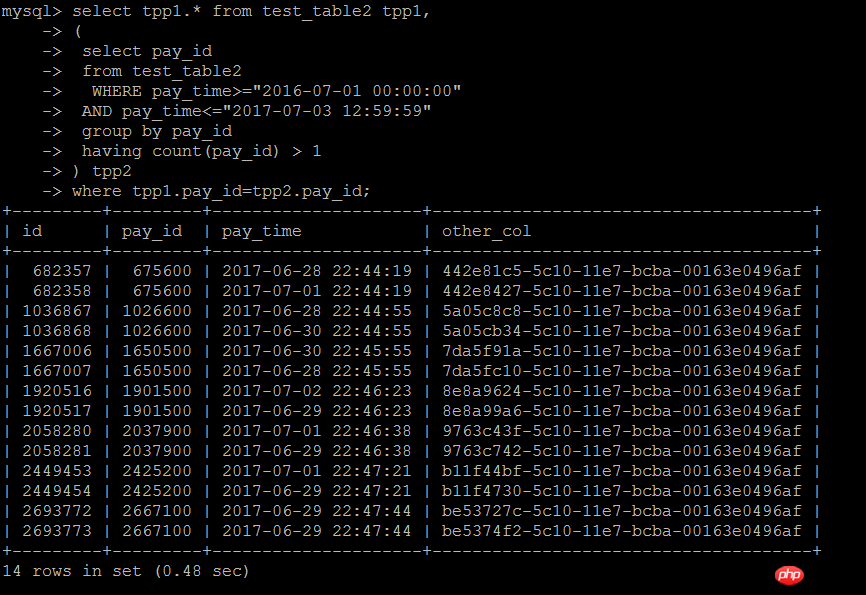
第二种写法,与子查询进行join关联,这种写法相当于上面的IN子查询写法,下面测试发现,效率确实有不少的提高
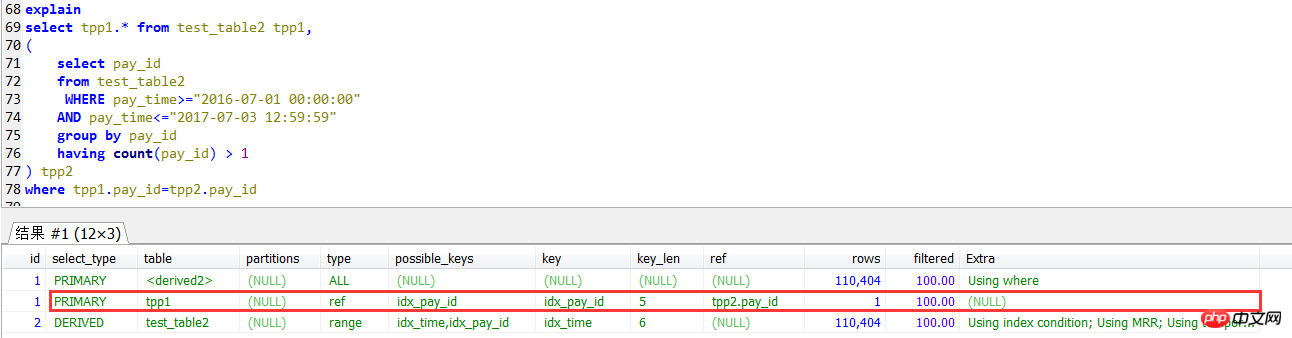
select tpp1.* from test_table2 tpp1,
( select pay_id
from test_table2
WHERE pay_time>="2016-07-01 00:00:00"
AND pay_time<="2017-07-03 12:59:59"
group by pay_id
having count(pay_id) > 1) tpp2
where tpp1.pay_id=tpp2.pay_id执行结果:0.48秒
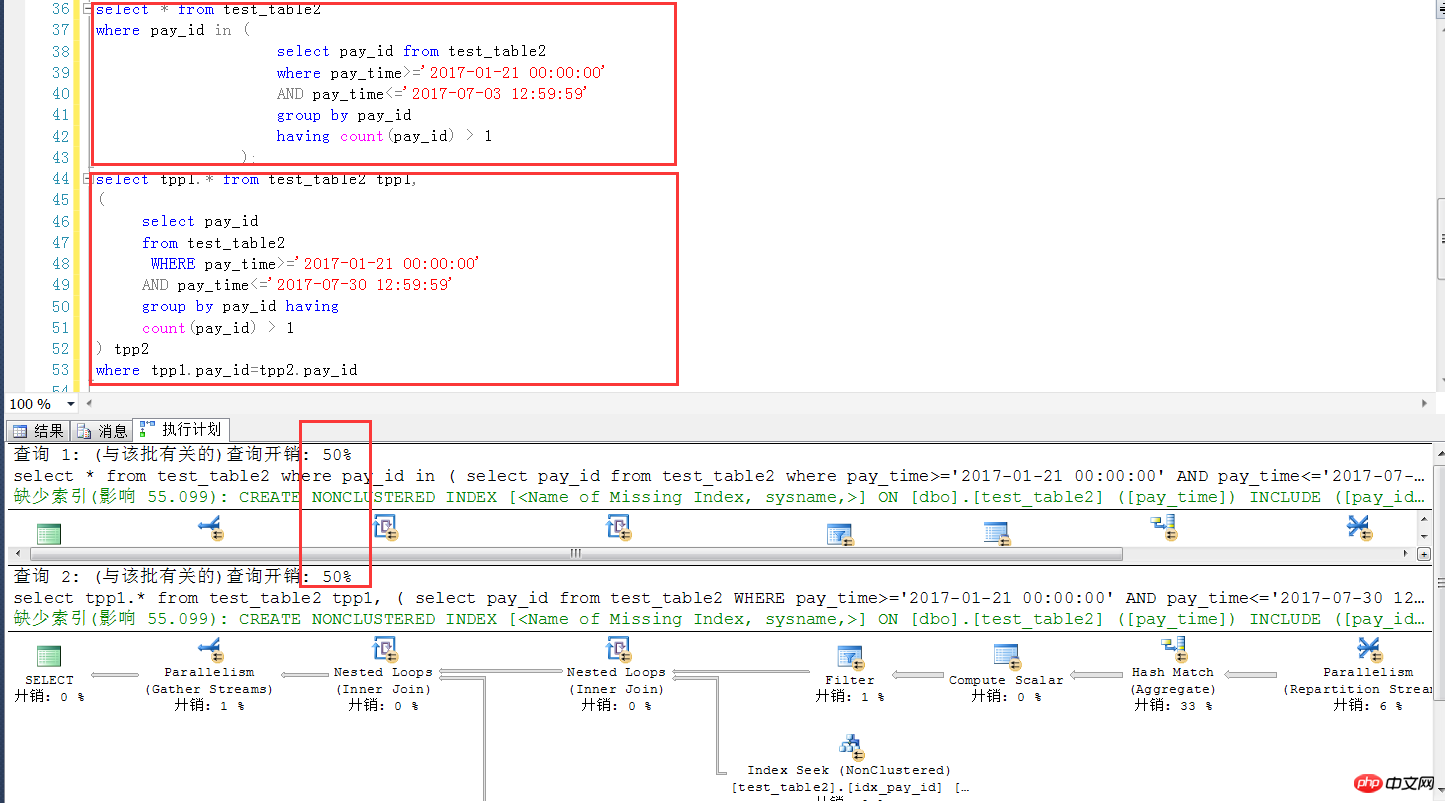
In子查询的执行计划,发现外层查询是一个全表扫描的方式,没有用到pay_id上的索引
join自查的执行计划,外层(tpp1别名的查询)是用到pay_id上的索引的。
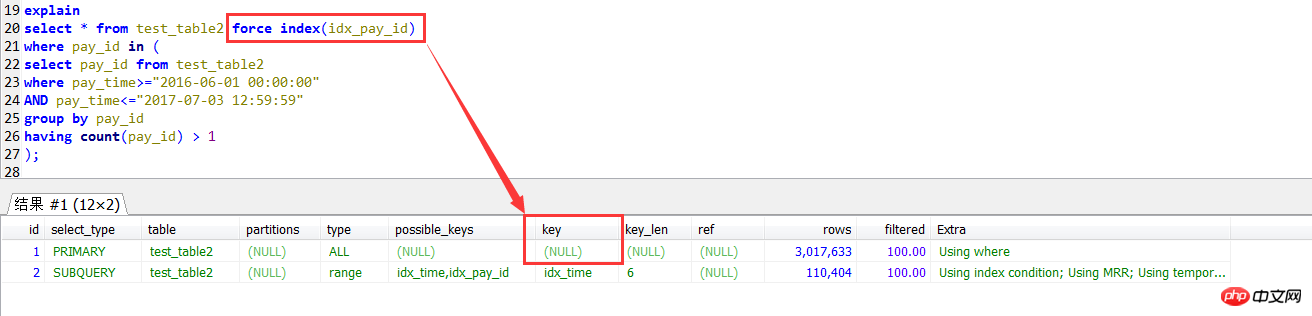
后面想对第一种查询方式使用强制索引,虽然是不报错的,但是发现根本没用
如果子查询是直接的值,则是可以正常使用索引的。
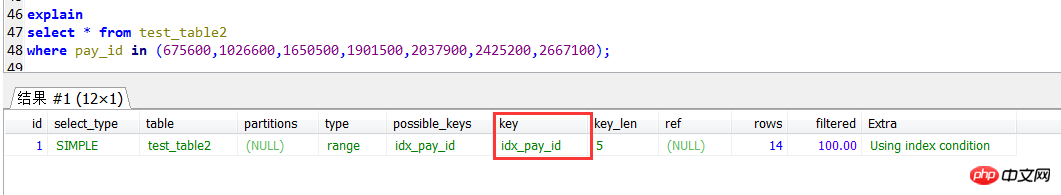
可见MySQL对IN子查询的支持,做的确实不怎么样。
另外:加一个使用临时表的情况,虽然比不少join方式查询的,但是也比直接使用IN子查询效率要高,这种情况下,也是可以使用到索引的,不过这种简单的情况,是没有必要使用临时表的。
下面是类似案例在sqlserver 2014中的测试,几万完全一样的测试表结构和数量,可见这种情况下,两种写法,在SQL Server中可以认为是完全一样的(执行计划+效率),这一点SQL Server要比MySQL强不少
下面是sqlserver中的测试环境脚本。
create table test_table2
(
id int identity(1,1) primary key,
pay_id int,
pay_time datetime,
other_col varchar(100)
)begin trandeclare @i int = 0while @i<300000begininsert into test_table2 values (@i,getdate()-rand()*300,newid());
if(@i%1000=0)begininsert into test_table2 values (@i,getdate()-rand()*300,newid());endset @i = @i + 1endCOMMITGOcreate index idx_pay_id on test_table2(pay_id);
create index idx_time on test_table2(pay_time);GOselect * from test_table2
where pay_id in (select pay_id from test_table2 where pay_time>='2017-01-21 00:00:00' AND pay_time<='2017-07-03 12:59:59' group by pay_id having count(pay_id) > 1);
select tpp1.* from test_table2 tpp1,
( select pay_id
from test_table2
WHERE pay_time>='2017-01-21 00:00:00' AND pay_time<='2017-07-30 12:59:59'
group by pay_id having
count(pay_id) > 1) tpp2
where tpp1.pay_id=tpp2.pay_id总结:在MySQL数据中,截止5.7.18版本,对IN子查询,仍要慎用
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci MySQL中两种子查询的写法. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!