Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >spring boot知识点一:Hello World
spring boot知识点一:Hello World
- 巴扎黑asal
- 2017-06-23 10:06:081675semak imbas
前言
作为程序员,不管是.net程序员还是java程序员其实从骨子里都不太喜欢各种配置文件的,记得刚开始学java SSH时动不动就装B,来看看我的配置多不多,又是从.net开始写java的程序员提起各种spring配置文件更是头大,那么Spring Boot诞生了,Spring Boot的诞生只为在当前流行的微服务框架下简化开发,不用再一上来就是各种配置文件了。
老生常谈,先从Hello World写起。本篇基于idea、maven搭建spring boot开发环境。
项目结构
先看下项目大致结构,基本骨架和ssm的项目结构保持相同,不同的是多了一个Application.java类,建议放在default package下。
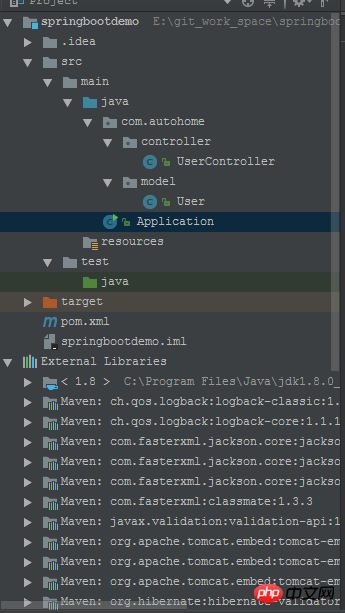
基于idea+maven创建spring boot项目
1、我创建项目时,spring boot的最新版本是1.5.4
2、使用默认的maven项目创建,不勾选任何骨架。
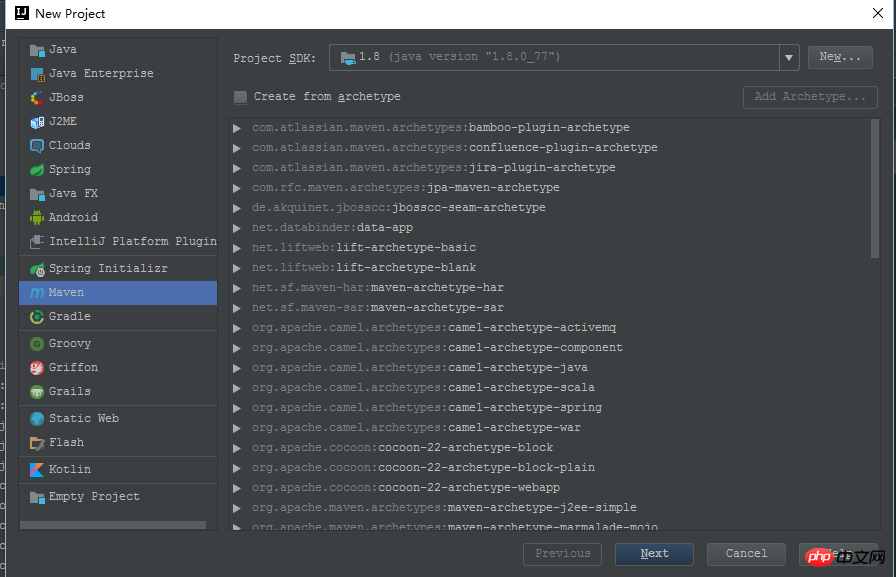
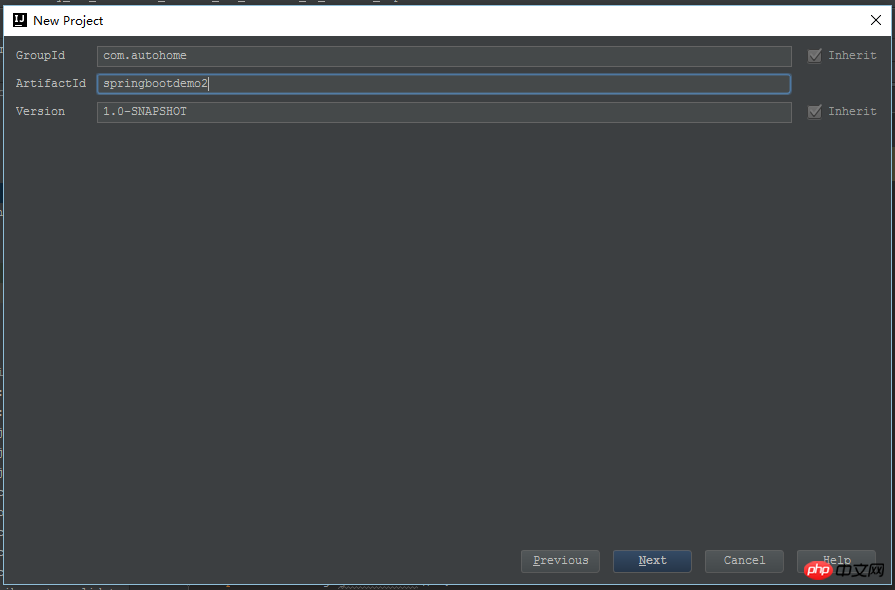
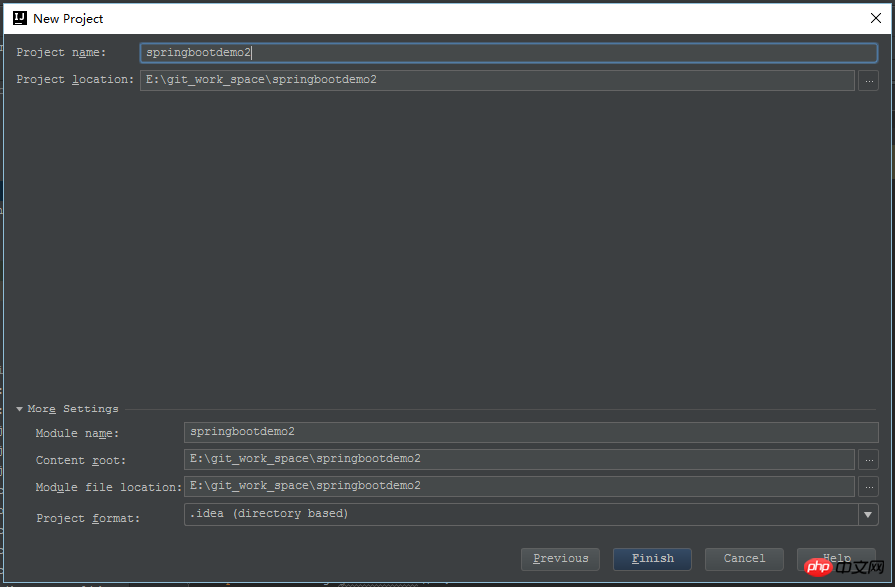
OK、这样一个默认的maven项目就起来了,当然,当前还不叫一个spring boot程序,打开pom.xml,增加spring boot需要的依赖包。最主要的就是spring-boot-starter-parent、
spring-boot-start-web。只需两个依赖就能创建一个spring mvc程序。 是不是很happy。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 ">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.autohome</groupId>
<artifactId>springbootdemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>springbootdemo</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3、也可以用Spring Initializer骨架创建
基于Spring Initializer创建spring boot项目更便捷,会直接让你选择你需要的模块,比如AOP、Web、JPA之类。不过也看到了,这里依赖https://start.spring.io。我创建时提示我连不上服务器,直接看不到下一步的界面了,so sorry。
Spring Boot Hello World
User.java
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String address;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}UserController.java
package com.autohome.controller;
import com.autohome.model.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/detail")
public User detail(Integer id){
User user=new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAddress("china");
return user;
}
}Application.java
这里用到了三个注解属性:
SpringBootApplication:它是Configuration、ComponentScan、EnableAutoConfiguration三个注解集合。 也就是说使用@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.autohome") 就可以替代前面三个注解,算是spring语法糖。
ComponentScan:会自动扫描指定包下含有注解属性的类,比如@Service、@Controller、@Repository。
EnableAutoConfiguration:能够自动配置上下文,试图猜测和配置你想要的类。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
/**
* Created by zhangfei on 2017/6/22.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan("com.autohome")
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("server is running at 8080....");
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
经过以上几句代码,右键运行Application.java,看控制台提示
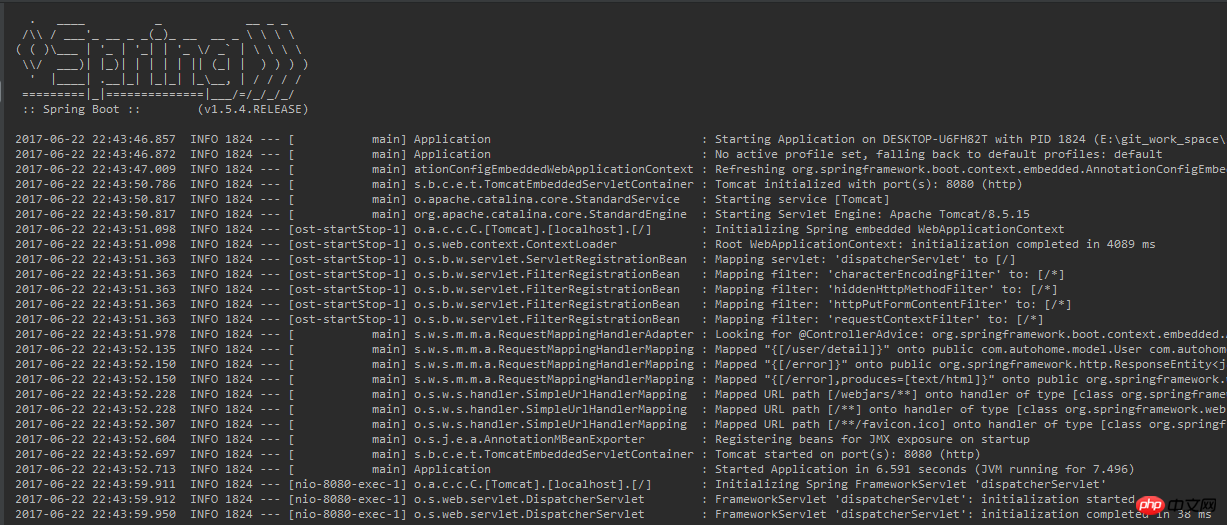
浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/user/detail?id=1
浏览器输出: {"id":1,"name":"zhangsan","address":"china"}
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci spring boot知识点一:Hello World. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

