Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >Java自定义注解
Java自定义注解
- 巴扎黑asal
- 2017-06-23 16:38:151768semak imbas
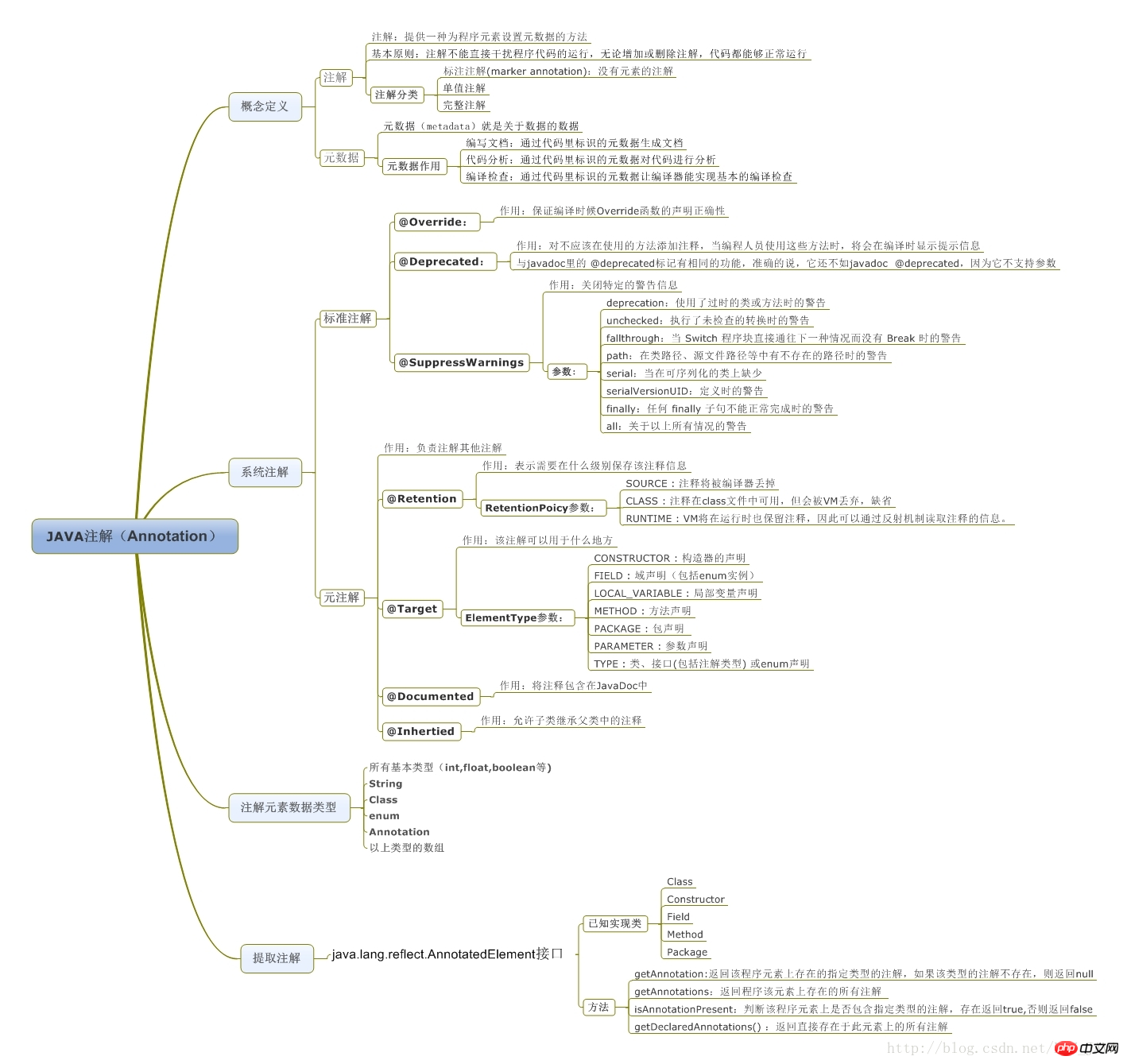
要深入学习注解,我们就必须能定义自己的注解,并使用注解,在定义自己的注解之前,我们就必须要了解Java为我们提供的元注解和相关定义注解的语法。
1 package annotation; 2 3 import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD; 4 import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME; 5 6 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 7 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 8 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 9 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;10 import java.lang.annotation.Target;11 /**12 *
13 * @author Minzhe Xu 2017年4月27日下午3:22:5214 *
15 *@Target 表示该注解用于什么地方,可能的值在枚举类 ElemenetType 中,包括:
16 *ElemenetType.CONSTRUCTOR:构造器声明
17 *ElemenetType.FIELD :域声明(包括 enum 实例)
18 *ElemenetType.LOCAL_VARIABLE:局部变量声明
19 *ElemenetType.METHOD :方法声明
20 *ElemenetType.PACKAGE :包声明
21 *ElemenetType.PARAMETER :参数声明
22 *ElemenetType.TYPE:类,接口(包括注解类型)或enum声明
23 *24 *@Retention 表示在什么级别保存该注解信息。可选的参数值在枚举类型 RetentionPolicy 中,包括:
25 *RetentionPolicy.SOURCE :注解将被编译器丢弃
26 *RetentionPolicy.CLASS :注解在class文件中可用,但会被VM丢弃
27 *RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME VM:将在运行期也保留注释,因此可以通过反射机制读取注解的信息。
28 *29 *@Documented 将此注解包含在 javadoc 中 ,它代表着此注解会被javadoc工具提取成文档。在doc文档中的内容会因为此注解的信息内容不同而不同。相当与@see,@param 等。30 *31 *@Inherited 允许子类继承父类中的注解。32 */33 34 @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER,ElementType.FIELD})35 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)36 public @interface TestA {37 38 /**39 * @interface用来声明一个注解,40 * 其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数。41 * 方法的名称就是参数的名称,返回值类型就是参数的类型(返回值类型只能是基本类型、Class、String、enum)。42 * 可以通过default来声明参数的默认值。43 */44 String name();45 int id() default 0;46 Class gid();47 48 }测试类
1 package annotation; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 /** 7 *
8 * @author Minzhe Xu 2017年4月27日下午3:09:20 9 *10 */11 @TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "type")12 public class UserAnotation {13 @TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "param",id=1)14 private Integer age;15 16 @TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "constract",id=2)17 public UserAnotation(){18 19 }20 @TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "method",id=3)21 public void test1(){22 @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")23 Map m=new HashMap(0);24 }25 26 @TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "method3",id=5)27 public void test2(@TestA(gid = Long.class, name = "inner_param",id=4) Integer a){28 29 }30 31 32 }通过反射的方式 使用注解
package annotation;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/**
*
* @author Minzhe Xu 2017年4月27日下午3:39:17
* */public class ParseAnotation {public static void parseTypeAnnotation() throws ClassNotFoundException{
Class clazz=Class.forName("annotation.UserAnotation");
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();for(Annotation annotation:annotations){
TestA testA=(TestA) annotation;
System.out.println("id="+testA.id()+";name="+testA.name()+";gid="+testA.gid());
}
}public static void parseMethodAnnotation(){
Method[] methods = UserAnotation.class.getDeclaredMethods();for(Method method:methods){boolean hasAnnotation=method.isAnnotationPresent(TestA.class);if(hasAnnotation){
TestA testA=method.getAnnotation(TestA.class);
System.out.println("id="+testA.id()+";name="+testA.name()+";gid="+testA.gid());
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static void parseConstractAnnotation(){
Constructor[] constructors = UserAnotation.class.getConstructors();for(Constructor contructor:constructors){boolean annotationPresent = contructor.isAnnotationPresent(TestA.class);//isAnnotationPresent方法来判断是否使用了某个注解if(annotationPresent){
TestA testA = (TestA) contructor.getAnnotation(TestA.class);
System.out.println("id="+testA.id()+";name="+testA.name()+";gid="+testA.gid());
}
}
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
parseTypeAnnotation();
parseMethodAnnotation();
parseConstractAnnotation();
}
}
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Java自定义注解. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
Kenyataan:
Kandungan artikel ini disumbangkan secara sukarela oleh netizen, dan hak cipta adalah milik pengarang asal. Laman web ini tidak memikul tanggungjawab undang-undang yang sepadan. Jika anda menemui sebarang kandungan yang disyaki plagiarisme atau pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn
Artikel sebelumnya:对于Java程序猿学习当中各个阶段的建议Artikel seterusnya:Java中重载与重写的区别
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Apakah JavaBeans dan Bagaimana Ia Digunakan dalam Aplikasi Java?
- Bagaimanakah anda membuat salinan sebenar tatasusunan dua dimensi di Jawa tanpa akibat yang tidak diingini?
- Bagaimana untuk Menghuraikan Output `Date.toString()` dengan Amanah dalam Java?
- Apakah Panjang Maksimum Rentetan Java?
- Bagaimana untuk Mengira Perbezaan Antara Dua Tarikh dalam Hari menggunakan Java?

