前言
LZ77算法是无损压缩算法,由以色列人Abraham Lempel发表于1977年。LZ77是典型的基于字典的压缩算法,现在很多压缩技术都是基于LZ77。鉴于其在数据压缩领域的地位,本文将结合图片和源码详细介绍其原理。
原理介绍:
首先介绍几个专业术语。
1.lookahead buffer(不知道怎么用中文表述,暂时称为待编码区):
等待编码的区域
2. search buffer:
已经编码的区域,搜索缓冲区
3.滑动窗口:
指定大小的窗,包含“搜索缓冲区”(左) + “待编码区”(右)
接下来,介绍具体的编码过程:
为了编码待编码区, 编码器在滑动窗口的搜索缓冲区查找直到找到匹配的字符串。匹配字符串的开始字符串与待编码缓冲区的距离称为“偏移值”,匹配字符串的长度称为“匹配长度”。编码器在编码时,会一直在搜索区中搜索,直到找到最大匹配字符串,并输出(o, l ),其中o是偏移值, l是匹配长度。然后窗口滑动l,继续开始编码。如果没有找到匹配字符串,则输出(0, 0, c),c为待编码区下一个等待编码的字符,窗口滑动“1”。算法实现将类似下面的:
while( lookAheadBuffer not empty )
{
get a pointer (position, match) to the longest match
in the window for the lookAheadBuffer;
output a (position, length, char());
shift the window length+1 characters along;
}主要步骤为:
1.设置编码位置为输入流的开始
2.在滑窗的待编码区查找搜索区中的最大匹配字符串
3.如果找到字符串,输出(偏移值, 匹配长度), 窗口向前滑动“匹配长度”
4.如果没有找到,输出(0, 0, 待编码区的第一个字符),窗口向前滑动一个单位
5.如果待编码区不为空,回到步骤2
描述实在是太复杂,还是结合实例来讲解吧
实例:
现在有字符串“AABCBBABC”,现在对其进行编码。
一开始,窗口滑入如图位置
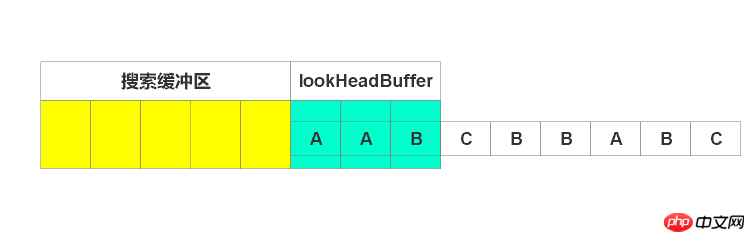
由图可见,待编码缓冲区有“AAB”三个字符,此时搜索缓冲区还是空的。所以编码第一个字符,由于搜索区为空,故找不到匹配串,输出(0,0, A),窗口右移一个单位,如下图
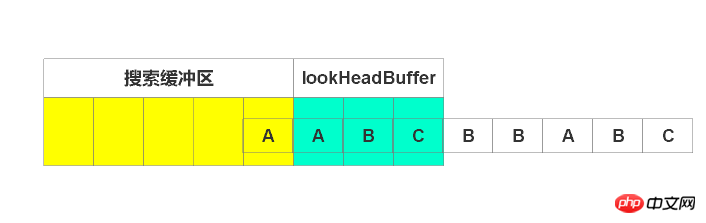
此时待编码区有“ABC”。开始编码。最先编码”A”,在搜索区找到”A”。由于没有超过待编码区,故开始编码”AB”,但在搜索区没有找到匹配字符串,故无法编码。因此只能编码”A”。
输出(1, 1)。即为相对于待编码区,偏移一个单位,匹配长度为1。窗口右滑动匹配长度,即移动1个单位。如下图
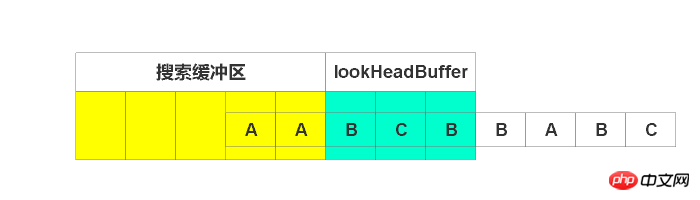
一样,没找到,输出(0, 0, B),右移1个单号,如下图
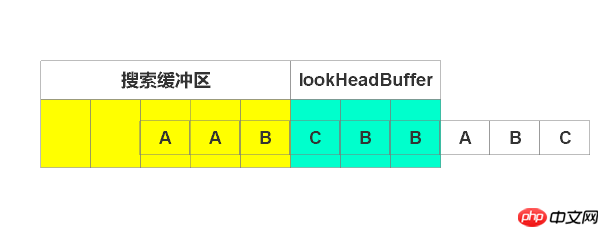
输出(0, 0, C),右移1个单位,如下图
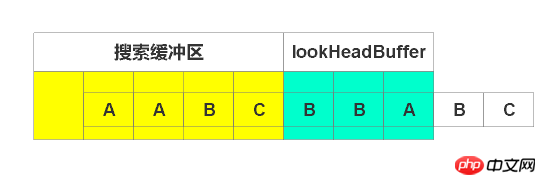
输出(2, 1),右移1个单位,如下图
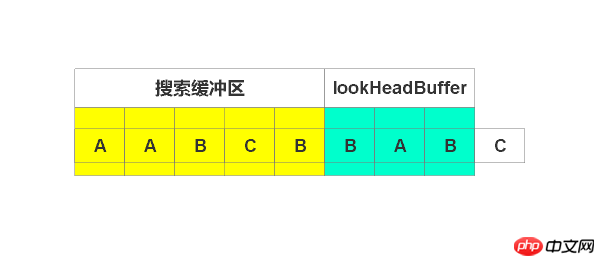
输出(3, 1), 右移1个单位,如下图
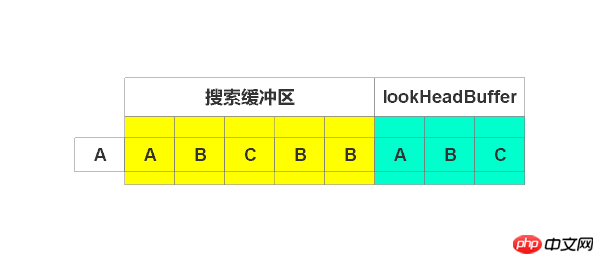
开始编码”A”,在搜索缓冲区查找到匹配字符串。由于待编码缓冲区没有超过,继续编码。开始编码”AB”,也搜索到。不要停止,继续编码“ABC”,找到匹配字符串。由于继续编码,则超过了窗口,故只编码“ABC”,输出(5, 3),偏移5,长度3。右移3个单位,如下图
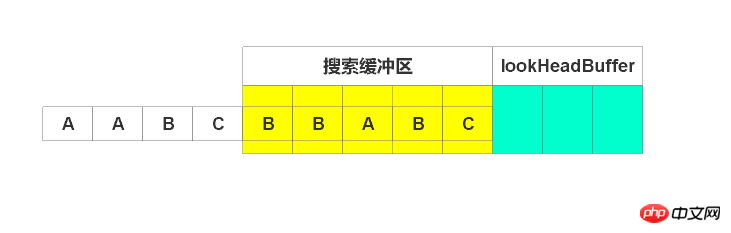
此时待编码缓冲区为空,停止编码。
最终输出结果如下
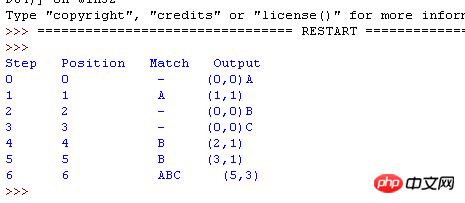
python代码实现:
class Lz77:
def init(self, inputStr):
self.inputStr = inputStr #输入流
self.searchSize = 5 #搜索缓冲区(已编码区)大小
self.aheadSize = 3 #lookAhead缓冲区(待编码区)大小
self.windSpiltIndex = 0 #lookHead缓冲区开始的索引
self.move = 0
self.notFind = -1 #没有找到匹配字符串
#得到滑动窗口的末端索引
def getWinEndIndex(self):
return self.windSpiltIndex + self.aheadSize
#得到滑动窗口的始端索引
def getWinStartIndex(self):
return self.windSpiltIndex - self.searchSize
#判断lookHead缓冲区是否为空
def isLookHeadEmpty(self):
return True if self.windSpiltIndex + self.move> len(self.inputStr) - 1 else False
def encoding(self):
step = 0
print("Step Position Match Output")
while not self.isLookHeadEmpty():
#1.滑动窗口
self.winMove()
#2. 得到最大匹配串的偏移值和长度
(offset, matchLen) = self.findMaxMatch()
#3.设置窗口下一步需要滑动的距离
self.setMoveSteps(matchLen)
if matchLen == 0:
#匹配为0,说明无字符串匹配,输出下一个需要编码的字母
nextChar = self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex]
result = (step, self.windSpiltIndex, '-', '(0,0)' + nextChar)
else:
result = (step, self.windSpiltIndex, self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex - offset: self.windSpiltIndex - offset + matchLen], '(' + str(offset) + ',' + str(matchLen) + ')')
#4.输出结果
self.output(result)
step = step + 1 #仅用来设置第几步
#滑动窗口(移动分界点)
def winMove(self):
self.windSpiltIndex = self.windSpiltIndex + self.move
#寻找最大匹配字符并返回相对于窗口分界点的偏移值和匹配长度
def findMaxMatch(self):
matchLen = 0
offset = 0
minEdge = self.minEdge() + 1 #得到编码区域的右边界
#遍历待编码区,寻找最大匹配串
for i in range(self.windSpiltIndex + 1, minEdge):
#print("i: %d" %i)
offsetTemp = self.searchBufferOffest(i)
if offsetTemp == self.notFind:
return (offset, matchLen)
offset = offsetTemp #偏移值
matchLen = matchLen + 1 #每找到一个匹配串,加1
return (offset, matchLen)
#入参字符串是否存在于搜索缓冲区,如果存在,返回匹配字符串的起始索引
def searchBufferOffest(self, i):
searchStart = self.getWinStartIndex()
searchEnd = self.windSpiltIndex
#下面几个if是处理开始时的特殊情况
if searchEnd < 1:
return self.notFind
if searchStart < 0:
searchStart = 0
if searchEnd == 0:
searchEnd = 1
searchStr = self.inputStr[searchStart : searchEnd] #搜索区字符串
findIndex = searchStr.find(self.inputStr[self.windSpiltIndex : i])
if findIndex == -1:
return -1
return len(searchStr) - findIndex
#设置下一次窗口需要滑动的步数
def setMoveSteps(self, matchLen):
if matchLen == 0:
self.move = 1
else:
self.move = matchLen
def minEdge(self):
return len(self.inputStr) if len(self.inputStr) - 1 < self.getWinEndIndex() else self.getWinEndIndex() + 1
def output(self, touple):
print("%d %d %s %s" % touple)
if name == "main":
lz77 = Lz77("AABCBBABC")
lz77.encoding()只是简单的写了下,没有过多考虑细节,请注意,这不是最终的代码,只是用来阐述原理,仅供参考。输出结果就是上面的输出(格式由于坑爹的博客园固定样式,代码位置有偏移,请注意
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci 图文详解LZ77压缩算法编码Python实现原理. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!
 Pembelajaran Python: Adakah 2 jam kajian harian mencukupi?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Pembelajaran Python: Adakah 2 jam kajian harian mencukupi?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMAdakah cukup untuk belajar Python selama dua jam sehari? Ia bergantung pada matlamat dan kaedah pembelajaran anda. 1) Membangunkan pelan pembelajaran yang jelas, 2) Pilih sumber dan kaedah pembelajaran yang sesuai, 3) mengamalkan dan mengkaji semula dan menyatukan amalan tangan dan mengkaji semula dan menyatukan, dan anda secara beransur-ansur boleh menguasai pengetahuan asas dan fungsi lanjutan Python dalam tempoh ini.
 Python untuk Pembangunan Web: Aplikasi UtamaApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python untuk Pembangunan Web: Aplikasi UtamaApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMAplikasi utama Python dalam pembangunan web termasuk penggunaan kerangka Django dan Flask, pembangunan API, analisis data dan visualisasi, pembelajaran mesin dan AI, dan pengoptimuman prestasi. 1. Rangka Kerja Django dan Flask: Django sesuai untuk perkembangan pesat aplikasi kompleks, dan Flask sesuai untuk projek kecil atau sangat disesuaikan. 2. Pembangunan API: Gunakan Flask atau DjangorestFramework untuk membina Restfulapi. 3. Analisis Data dan Visualisasi: Gunakan Python untuk memproses data dan memaparkannya melalui antara muka web. 4. Pembelajaran Mesin dan AI: Python digunakan untuk membina aplikasi web pintar. 5. Pengoptimuman Prestasi: Dioptimumkan melalui pengaturcaraan, caching dan kod tak segerak
 Python vs C: Meneroka Prestasi dan KecekapanApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs C: Meneroka Prestasi dan KecekapanApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython lebih baik daripada C dalam kecekapan pembangunan, tetapi C lebih tinggi dalam prestasi pelaksanaan. 1. Sintaks ringkas Python dan perpustakaan yang kaya meningkatkan kecekapan pembangunan. 2. Ciri-ciri jenis kompilasi dan kawalan perkakasan meningkatkan prestasi pelaksanaan. Apabila membuat pilihan, anda perlu menimbang kelajuan pembangunan dan kecekapan pelaksanaan berdasarkan keperluan projek.
 Python dalam Tindakan: Contoh dunia nyataApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python dalam Tindakan: Contoh dunia nyataApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMAplikasi dunia sebenar Python termasuk analisis data, pembangunan web, kecerdasan buatan dan automasi. 1) Dalam analisis data, Python menggunakan panda dan matplotlib untuk memproses dan memvisualisasikan data. 2) Dalam pembangunan web, kerangka Django dan Flask memudahkan penciptaan aplikasi web. 3) Dalam bidang kecerdasan buatan, tensorflow dan pytorch digunakan untuk membina dan melatih model. 4) Dari segi automasi, skrip python boleh digunakan untuk tugas -tugas seperti menyalin fail.
 Penggunaan Utama Python: Gambaran Keseluruhan KomprehensifApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Penggunaan Utama Python: Gambaran Keseluruhan KomprehensifApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython digunakan secara meluas dalam bidang sains data, pembangunan web dan bidang skrip automasi. 1) Dalam sains data, Python memudahkan pemprosesan dan analisis data melalui perpustakaan seperti numpy dan panda. 2) Dalam pembangunan web, rangka kerja Django dan Flask membolehkan pemaju dengan cepat membina aplikasi. 3) Dalam skrip automatik, kesederhanaan Python dan perpustakaan standard menjadikannya ideal.
 Tujuan utama python: fleksibiliti dan kemudahan penggunaanApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Tujuan utama python: fleksibiliti dan kemudahan penggunaanApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AMFleksibiliti Python dicerminkan dalam sokongan multi-paradigma dan sistem jenis dinamik, sementara kemudahan penggunaan berasal dari sintaks mudah dan perpustakaan standard yang kaya. 1. Fleksibiliti: Menyokong pengaturcaraan berorientasikan objek, fungsional dan prosedur, dan sistem jenis dinamik meningkatkan kecekapan pembangunan. 2. Kemudahan Penggunaan: Tatabahasa adalah dekat dengan bahasa semulajadi, perpustakaan standard merangkumi pelbagai fungsi, dan memudahkan proses pembangunan.
 Python: Kekuatan pengaturcaraan serba bolehApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python: Kekuatan pengaturcaraan serba bolehApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython sangat disukai kerana kesederhanaan dan kuasa, sesuai untuk semua keperluan dari pemula hingga pemaju canggih. Kepelbagaiannya dicerminkan dalam: 1) mudah dipelajari dan digunakan, sintaks mudah; 2) perpustakaan dan kerangka yang kaya, seperti numpy, panda, dan sebagainya; 3) sokongan silang platform, yang boleh dijalankan pada pelbagai sistem operasi; 4) Sesuai untuk tugas skrip dan automasi untuk meningkatkan kecekapan kerja.
 Belajar python dalam 2 jam sehari: panduan praktikalApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Belajar python dalam 2 jam sehari: panduan praktikalApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMYa, pelajari Python dalam masa dua jam sehari. 1. Membangunkan pelan kajian yang munasabah, 2. Pilih sumber pembelajaran yang betul, 3 menyatukan pengetahuan yang dipelajari melalui amalan. Langkah -langkah ini dapat membantu anda menguasai Python dalam masa yang singkat.


Alat AI Hot

Undresser.AI Undress
Apl berkuasa AI untuk mencipta foto bogel yang realistik

AI Clothes Remover
Alat AI dalam talian untuk mengeluarkan pakaian daripada foto.

Undress AI Tool
Gambar buka pakaian secara percuma

Clothoff.io
Penyingkiran pakaian AI

AI Hentai Generator
Menjana ai hentai secara percuma.

Artikel Panas

Alat panas

Versi Mac WebStorm
Alat pembangunan JavaScript yang berguna

Dreamweaver CS6
Alat pembangunan web visual

Muat turun versi mac editor Atom
Editor sumber terbuka yang paling popular

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) ialah aplikasi web PHP/MySQL yang sangat terdedah. Matlamat utamanya adalah untuk menjadi bantuan bagi profesional keselamatan untuk menguji kemahiran dan alatan mereka dalam persekitaran undang-undang, untuk membantu pembangun web lebih memahami proses mengamankan aplikasi web, dan untuk membantu guru/pelajar mengajar/belajar dalam persekitaran bilik darjah Aplikasi web keselamatan. Matlamat DVWA adalah untuk mempraktikkan beberapa kelemahan web yang paling biasa melalui antara muka yang mudah dan mudah, dengan pelbagai tahap kesukaran. Sila ambil perhatian bahawa perisian ini

Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat
Pelayar Peperiksaan Selamat ialah persekitaran pelayar selamat untuk mengambil peperiksaan dalam talian dengan selamat. Perisian ini menukar mana-mana komputer menjadi stesen kerja yang selamat. Ia mengawal akses kepada mana-mana utiliti dan menghalang pelajar daripada menggunakan sumber yang tidak dibenarkan.






