Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >Tutorial Python >Python自动化运维课程学习
Python自动化运维课程学习
- 高洛峰asal
- 2017-02-13 17:25:462005semak imbas
本文为参加老男孩Python自动化运维课程第一天学习内容的总结。
大致内容如下:
Python介绍
第一个Python程序: Hello World
Python变量
用户交互(用户输入、输出)
流程控制:条件语句(if/elif/else)、循环语句(for/while/break/continue)
一、Python语言介绍:
1、Python是一门解释型语言、动态类型、强类型定义语言的高级编程语言。由Guido van Rossum于1989圣诞期间开发,首个正式版本Python编译器诞生于1991年。现已成为主流的编程语言之一。
2、主要应用于云计算、WEB开发、科学去处和数据分析、人工智能、金融、系统运维、图形GUI等方面。
3、Python的优缺点:
优点:简单、明确、优雅;开发效率高;可移植性强;可扩展性;可嵌入性。
缺点:比C语言/JAVA执行速度慢(PyPy解释器的执行速度有时比C还快);代码不能加密(解释型语言);线程不能利用多CPU问题。
4、Python的解释器:Python解释器有很多,如CPython、IPython、PyPy、Jython、IronPython等,但使用最广泛的还是CPython。
二、关于本文中所有运行Python代码的环境:
--操作系统:Ubuntu 16.10 (Linux 4.8.0)

--Python版本:3.5.2

--Python IDE: PyCharm 2016.3.2

三、第一个程序:Hello World
通过vim/vi命令新建一个Python File,命令为“HelloWorld.py” , vim HelloWorld.py 。
在HelloWorld.py中输入正面的内容:
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# 告诉Linux系统,要通过/usr/bin/python3.5解释器来执行正面的代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Python2中必须添加这个一行,告诉Python解释器,要以UTF-8的编码形式执行正面的代码;Python3中默认UTF-8,可以不用添加本行。
# Author: Spencer Jiang
# 作者
print("Hello, World!")
# 打印Hello, World!
两种运行方式:
1)、给HelloWorld.py赋可执行权限,然后执行: chmod 755 HelloWorld.py
> chmod 755 HelloWorld.py > ./HelloWorld.py

2)、直接通过Python执行:python安装路径
> /usr/bin/python3.5 HelloWorld.py

三、Python变量
1、变量定义的规则:
变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
以下关键字不能声明为变量名
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']标识符名称的例子有i、__my_name、name_23和a1b2_c3。
标识符名称的例子有2things、this is spaced out和my-name。
2、变量赋值:通过一个等号给变量赋值
示例: name = "Spencer Jiang"
也可以在一行能多个变量进行赋值。如:
a, b = 3, "jmw" print(a, b) print(type(b), type(a)) ######### 下面为输出结果: 3 jmw <class 'str'> <class 'int'>
四、用户交互 与 格式化输出:
用户输入 Python3用input()函数就好了, Pyhton2有点儿复杂先不去学。
input()函数能接收从用户输入的任务字符,并以字符串类型返回用户输入的字符。
示例1(UserInput.py): name = input("Please input your name: ")
age = int(input("Please input you age: ")) # 将用户输入的字符转换成int类型,再赋值给变量 age。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
name = input("Please input your name: ")
age = int(input("Please input you age: "))
print("Your Name: %s, Your Age: %d" % (name, age))

示例2: 用户名、密码的输入,通过getpass模块,将密码隐藏显示。(HidePassword.py)
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
import getpass
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = getpass.getpass("Please input your password: ")
print(username, password)

格式化输出:
1)、print()函数中添加%号来格式化输出。
输出字符串:%s ,输出数值 %d, 输出浮点数%f等, 示例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Function : The format output
# Date : 2017-02-10
# Author : Spencer Jiang
username = "Spencer Jiang"
age = 45
salary = 231.32
print("Your name is : %s " % username)
print("Your age is : %d " % age)
print("Your salary is : %f " % salary)
print("Your salary2f is : %.2f " % salary)
# 保留2位小数

2)、 通过format()函数进行格式化输出。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # Function : The format output # Date : 2017-02-10 # Author : Spencer Jiang username = "Spencer Jiang" age = 45 job = "IT Service" salary = 231.32 info = ''' Name: [_username] Age: [_age] Job: [_job] Salary: [_salary] '''.format(_username = username, _age = age, _job = job, _salary = salary) print(info)

五、流程控制:条件判断语句(if/elif/else):
每个条件后面都以冒号结束,换行(条件为真时要执行的代码,以缩进作为代码块标志,python官方建议缩进4个空格)
示例1:猜年龄(数字)游戏(GuessAge.py)。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
#先设定的年龄的数值
guess_age = int(input("guess an age: "))
if guess_age == age_of_spencer :
print("Yes, You got it!")
elif guess_age > age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller")

六、流程控制:for循环(for x in range(10))、break、continue:
当满足循环条件时,执行循环语句块的代码,当不满足循环条件时,循环语句就结束。
for/while 循环外也可以跟一个else。
break: 当执行break时,就结束整个循环;
continue: 当执行continue,就结束本次循环,直接进行下次循环。
示例1:输出0到15中的2、4、6、8等4个数字(PrintNumber.py)。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: Spencer Jiang for i in range(0,15,2): if i == 0 : # 跳过 0 这个数字 continue if i > 9 : # 大于9 就退出循环 break else: print(i)

七、流程控制:while循环、break、continue(与for循环类似)
while 循环,需要有一个计数器,或者在循环语句块中有终止while条件的语句,否则会一直运行下去。
示例1(WhileLoop.py): 打印0~9数字
#!/usr/bin/python3.5 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Author: Spencer Jiang count = 0 # 计数器 while True : print(count) count = count + 1 if count > 9 : break

示例2(GuessAgeWhile.py):猜年龄(数字): 只能猜3次机会。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
count = 0
while count < 3 :
guess_age = int(input("guess an age: "))
if guess_age == age_of_spencer :
print("Yes, You got it!")
break
elif guess_age > age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller")
count += 1
else:
print("You guess to much times!!!")
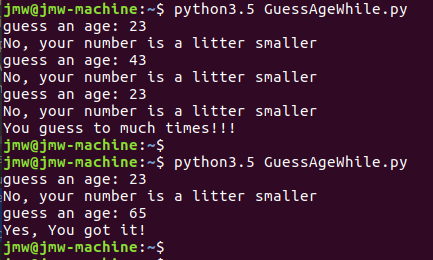
示例2,每猜3次不正确后,弹出提示,看用户是否还要继续猜下去。如果用户输入的是“n"就表示停止。
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: Spencer Jiang
age_of_spencer = 65
count = 0
while count < 3 :
guess_age = int(input("guess an age: "))
if guess_age == age_of_spencer :
print("Yes, You got it!")
break
elif guess_age > age_of_spencer :
print("No, your number is a litter bigger")
else:
print("No, your number is a litter smaller")
count += 1 if count == 3 :
continue_confirm = input("Do you want to continue to guess?")
if continue_confirm != 'n' :
count = 0else:
print("You guess to much times!!!")

八、 Python代码注释:
# 单行注释用 井号“#” 开头
''' 或者 """ 多行注释采用3对单引号或3对双引号将要注释的行包围进来。
同时3对引号,也可以表示对字符串的赋值(段落文字),如:
info = """ your information : name : jmw age : 32 """
九、作业:
1、模拟用户登录接口:1)由用户输入用户名、密码;2)登录成功,则显示欢迎信息;3)登录失败超过3次就要锁定账号。
2、三级菜单:省、市、县3级地区为菜单。
更多Python自动化运维课程学习相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

