Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >新Java运动:测试驱动开发3---用户注册4
新Java运动:测试驱动开发3---用户注册4
- 黄舟asal
- 2016-12-30 13:17:151130semak imbas
完成数据库操作的基础架构之后,就是我们真正进行JDBC数据操作的时候了。所涉及的数据库表ER图如下所示:
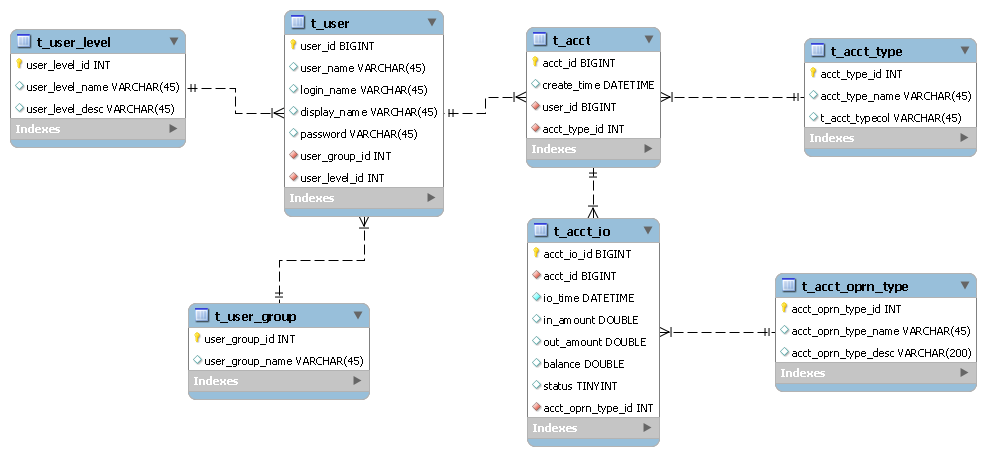
如上图所示,我们第一步是向t_user表中添加记录。由于用户注册需要操作多张表,因此需要用到事务,先写出一个简单的基于JDBC的事务框架,代码如下所示:
@Override
public long registerUser(Map<String, Object> userInfo) {
Connection conn = null;
long userId = 0;
try {
conn = JdbcDs.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
userId = addUser(conn, userInfo);
if (userId <= 0) {
throw new SQLException("Fail to add user in t_user");
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
userId = -1;
} finally {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return userId;
}其次是具体的用户添加操作,具体代码如下所示:
private long addUser(Connection conn, Map<String, Object> userInfo) {
long userId = -1;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet rst = null;
String sql = "insert into t_user(user_name, user_group_id, user_level_id) values(?, 2, 1)";
try {
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
stmt.setString(1, (String)userInfo.get("userName"));
int affectedNum = stmt.executeUpdate();
if (1 == affectedNum) {
rst = stmt.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rst.next()) {
userId = rst.getLong(1);
}
} else {
userId = -1;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
userId = -1;
} finally {
try {
if (rst != null) {
rst.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return userId;
}最后是改变测试用例中的判断成功条件为所返回的userId大于0。
运行测试用例,应该可以成功通过测试用例。
经过以上几篇文章,我们终于可以进行有意义的开发工作了。下一步就是实现所有用户注册业务逻辑,还有一块是异常情况的处理,例如userName重复的情况。当完成所有这些功能后,我们还需要进行端到端测试,这就涉及通过JSP页面进行注册测试。
以上就是新Java运动:测试驱动开发3---用户注册4的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!
Kenyataan:
Kandungan artikel ini disumbangkan secara sukarela oleh netizen, dan hak cipta adalah milik pengarang asal. Laman web ini tidak memikul tanggungjawab undang-undang yang sepadan. Jika anda menemui sebarang kandungan yang disyaki plagiarisme atau pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn
Artikel sebelumnya:新Java运动:测试驱动开发3---用户注册3Artikel seterusnya:Java怎样中断一个运行中的线程(1)

