Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >tutorial php >php学习正式起航(6)
php学习正式起航(6)
- 黄舟asal
- 2016-12-28 09:23:381056semak imbas
现在讲讲php的错误处理
<?php
$file=fopen("1.txt","r");
?>如果文件不存在 系统会直接报错误
用die就可以自己写错误信息 die是死亡的意思,表示错误
为了避免用户获得类似上面的错误消息,我们在访问文件之前检测该文件是否存在
<?php
if(!file_exists("1.txt"))
{
die("File not found");
}
else
{
$file=fopen("1.txt","r");
}
?>如果文件不存在,会打印File not found,而不是系统冒出的错误
其实php的错误处理远不止这些,后面还有异常等
放在以后在说吧
现在开始重头戏,终于要用php对mysql数据库进行操作了
首先是连接数据库
<?php
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo 'Connection OK'; mysql_close($link);
?>$link 这个又是一个资源变量,表示数据库连接状态,你可以试着打印看看会出现什么
mysql_connect函数就是连接mysql数据库啦
有3个函数 分别是服务器地址 数据库用户名 数据库用户密码
mysql_error函数可以知道连接错误原因
mysql_close是关闭数据库连接
现在先创建一个数据库
create database test;
然后创建一个表
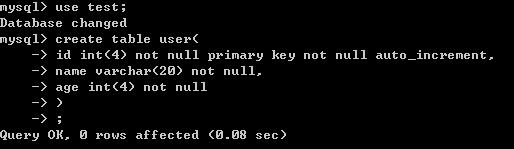
超级简单吧
进入phpmyadmin看看
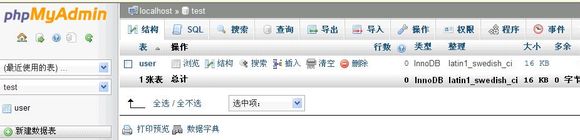
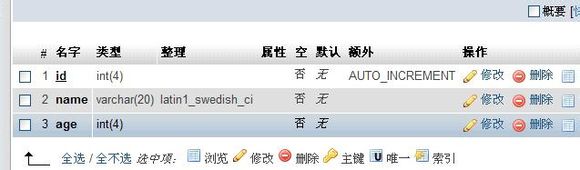
首先我们插入几条数据看看
现在会连接mysql数据库了,接着我们要在mysql其中一个数据库里插入数据了
<?php
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db('test',$link);
mysql_query("insert into user (name,age) values ('harry',15)",$link);
mysql_close($link);
?>mysql_select_db就是选择数据库的函数
mysql_query就是执行sql语句的函数,任何sql都可执行,包括创建数据库和表
两个函数的第2个参数可以省略
mysql_select_db('test');
mysql_query("insert into user (name,age) values ('harry',15)");
如果第2个参数没有指定连接标识符,则使用上一个打开的连接。如果没有打开的连接,将无参数调用 mysql_connect() 来尝试打开一个并使用之
现在看看是否能插入成功
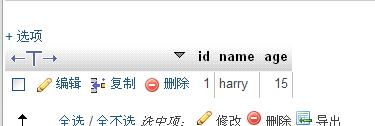
ok 已经插入了
现在我们用表单形式插入数据
<html> <body> <form action="" method="post"> Name: <input type="text" name="name" /> Age: <input type="text" name="age" /> <input type="submit" /> </form> </body> </html>
<?php
$name=$_POST['name'];
$age=$_POST['age'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age))
{
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db('test');
$sql="insert into user (name,age) values ('$name',$age)";
if(mysql_query($sql))
echo "Insert Success!";
else
echo "Insert Fail!".mysql_error();
mysql_close($link);
}
?>mysql_query() 在执行sql语句成功时返回 TRUE,出错时返回 FALSE
现在来显示数据吧
<html>
<body> <form action="" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
<?php
//数据库连接
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db('test'); //插入
$name=$_POST['name'];
$age=$_POST['age'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age))
{ $sql="insert into user (name,age) values ('$name',$age)";
if(mysql_query($sql))
echo "Insert Success!";
else
echo "Insert Fail!".mysql_error(); }
//查询
$sql="select * from user";
$result=mysql_query($sql);
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo "<table>";
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['id'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['name'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['age'] . "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
echo "</table>";
} mysql_free_result($result);
mysql_close($link); ?>
</body>
</html>
$result=mysql_query($sql); $result也是一个资源变量,当mysql_query执行查询sql语句的时候,其返回结果就不再是true和false ,而是个结果集,你可以想象就是mysql_query查询的结果返回一张表给了$result,$result就是一张表(结果集)
mysql_fetch_array函数则是专门处理结果集的,从结果集中取得一行作为关联数组,或数字数组,或二者兼有,mysql_query($sql); 其本身就是结果集了
为什么要循环呢,因为mysql_fetch_array一次只能在结果集(表)取一行数据
然后把这一行数据以一维关联数组的形式给$row,$row就是一维关联数组
mysql_fetch_array有个指针指着每一行,每当执行完这个函数的时候,指针就自动指向下一行,如果当函数再次被执行,就能获取到这行的数据,直到最后一行,指针就会指向空的,所以循环也会因为空而结束
不要以为$row是二维数组,它一直是一维,而且每循环一次就被重新赋值一次
有人可能怀疑,数组也能做为循环条件?可以的
$a=array(1,2)
while($a)
这样是能够循环的,只不过是死循环
因为while括号里只要不为0的东东都能循环
$row['name'] 就个就是从数组里取值了,关联数组还记得吧
其实用数组下标也可以的,之前没说,其实关联数组也具有普通数组的特性,且更强大
所以这是可以的
echo "<td>" . $row[0] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row[1] . "</td>"; echo "<td>" . $row[2] . "</td>";
mysql_free_result是释放资源
不是必须使用,仅需要在考虑到返回很大的结果集时会占用多少内存时调用。在脚本结束后所有关联的内存都会被自动释放的
另外mysql_fetch_row也可以查询结果,不过跟mysql_fetch_array比,弱爆了,这里只是介绍下曾经有这么个东西。。。
//查询
$sql="select * from user";
$result=mysql_query($sql);
while($row = mysql_fetch_row($result))
{
echo "mysql_fetch_row() 从和指定的结果标识关联的结果集中取得一行数据并作为数组返回。每个结果的列储存在一个数组的单元中
则row不再是关联数组而是普通数组,所以只能用数组下标
下面说说几个常用的数据显示函数
int mysql_num_rows ( resource $result )
mysql_num_rows() 返回结果集中行的数目。此命令仅对 SELECT 语句有效
int mysql_num_fields ( resource $result )
mysql_num_fields() 返回结果集中字段的数目
int mysql_insert_id ([ resource $link_identifier ] )
mysql_insert_id() 返回给定的 link_identifier 中上一步 INSERT 查询中产生的 AUTO_INCREMENT 的 ID 号
重新写下
"; echo "
"; echo "每行".mysql_num_fields($result)."字段"; mysql_free_result($result); mysql_close($link); ?>
header("Content-Type:text/html;charset=gbk"); 这个是表明文件编码格式,显示中文需要这样
error_reporting(0); 屏蔽一切系统提示的注意,警告,和错误
现在完成 修改和删除部分
<?php
header("Content-Type:text/html;charset=gbk");
error_reporting(0);
?> <html>
<body> <form action="" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form> <?php
//数据库连接
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db('test');
//插入
$name=$_POST['name'];
$age=$_POST['age'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age))
{ $sql="insert into user (name,age) values ('$name',$age)";
if(mysql_query($sql))
echo "Insert Success!";
else
echo "Insert Fail!".mysql_error(); } /
/查询
$sql="select * from user";
$result=mysql_query($sql);
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
?>
<form action="" method="post">
ID: <?=$row['id']?>
Name: <input type="text" name="_name" value="<?=$row['name']?>"/>
Age: <input type="text" name="_age" value="<?=$row['age']?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?=$row['id']?>" />
<input type="submit" value="修改"/>
<a href="index.php?uid=<?=$row['id']?>">删除</a>
</form> <?php
} echo "总共".mysql_num_rows($result)."记录<br/>";
echo "每行".mysql_num_fields($result)."字段";
//修改
$name=$_POST['_name'];
$age=$_POST['_age'];
$id=$_POST['id'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age)&&isset($id))
{ $sql="update user set name='$name',age='$age' where id=$id";
if(mysql_query($sql))
header("location:index.php");
else
echo "Update Fail!".mysql_error(); }
//删除
$uid=$_GET['uid'];
if(isset($uid))
{ $sql="delete from user where id=$uid";
if(mysql_query($sql))
header("location:index.php");
else
echo "Delete Fail!".mysql_error(); }
mysql_close($link); ?>
</body>
</html>
至此,php对mysql数据库的增删改查操作就全在这一个页面了,灰常的简单
加了个简单的分页,超简单的。。。。暂时就不讲解怎么个来的了,加了简单的注释,大家应该能看懂代码
<?php
header("Content-Type:text/html;charset=gbk");
error_reporting(0);
?> <html>
<body> <form action="" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form> <?php
//数据库连接
$link = mysql_connect('localhost','root','');
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect to MySQL: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db('test'); //插入
$name=$_POST['name'];
$age=$_POST['age'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age))
{ $sql="insert into user (name,age) values ('$name',$age)";
if(mysql_query($sql))
echo "Insert Success!";
else
echo "Insert Fail!".mysql_error(); } //分页查询
if(isset($_GET['pager']))
$pager=($_GET['pager']-1)*5;
else
$pager=0; $sql="select * from user";
$result=mysql_query($sql);
$num=mysql_num_rows($result); //总共记录数
$page=ceil($num/5); //总共多少页 这里每页5条记录 ceil函数四舍五入的。。
for($i=1;$i<=$page;$i++)
echo "<a href='index.php?pager=".$i."'>".$i."</a>"; $
sql="select * from user limit $pager,5";
$result=mysql_query($sql);
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
?>
<form action="" method="post">
ID: <?=$row['id']?>
Name: <input type="text" name="_name" value="<?=$row['name']?>"/>
Age: <input type="text" name="_age" value="<?=$row['age']?>" />
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="<?=$row['id']?>" />
<input type="submit" value="修改"/>
<a href="index.php?uid=<?=$row['id']?>">删除</a>
</form> <?php
} echo "总共".$num."记录<br/>";
echo "每行".mysql_num_fields($result)."字段"; //修改
$name=$_POST['_name'];
$age=$_POST['_age'];
$id=$_POST['id'];
if(isset($name)&&isset($age)&&isset($id))
{ $sql="update user set name='$name',age='$age' where id=$id";
if(mysql_query($sql))
header("location:index.php");
else
echo "Update Fail!".mysql_error(); }
//删除
$uid=$_GET['uid'];
if(isset($uid))
{ $sql="delete from user where id=$uid";
if(mysql_query($sql))
header("location:index.php");
else
echo "Delete Fail!".mysql_error(); }
mysql_close($link); ?>
</body>
</html>暂时先到这里了
php后面内容还有很多,还有对象等知识,光数据操作就还有面向对象的
以上就是php学习正式起航(6)的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Semua simbol ungkapan dalam ungkapan biasa (ringkasan)

