Rumah >pembangunan bahagian belakang >tutorial php >PHP设计模式之适配器模式
PHP设计模式之适配器模式
- 高洛峰asal
- 2016-11-17 10:23:161190semak imbas
简介
适配器模式(有时候也称包装样式或者包装)将一个类的接口适配成用户所期待的。一个适配允许通常因为接口不兼容而不能在一起工作的类工作在一起。
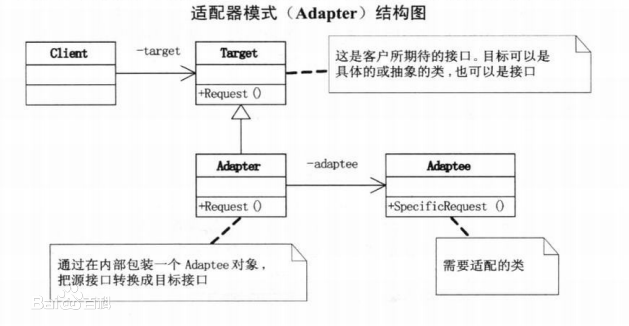
UML
角色
Target适配目标 : 该角色定义把其他类转换为何种接口,也就是我们的期望接口。
Adaptee被适配者 :就是需要被适配的接口。
Adapter适配器:其他的两个角色都是已经存在的角色,而适配器角色是需要新建立的,它用来对Adaptee与Target接口进行适配。
应用场景
如程序数据库有关联mysql、mysqli、pdo、sqlite、postgresql等操作,而你需要根据情况换数据库操作时,可以使用适配器模式统一接口,这样代码中除了数据库配置之外,就不需要做而外的更改。
同理cache(缓存)的场景也是,无论使用memcache还是redis等,在更换的时候都会很方便,节约时间。
注:在一些流行框架中都可以看到此模式,详情请自行参阅框架源码。
实现
代码:
<?php
header('Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8');
/**
* 适配器模式演示代码
* Target适配目标: IDataBase接口
* Adaptee被适配者: mysql和mysql_i、postgresql的数据库操作函数
* Adapter适配器 :mysql类和mysql_i、postgresql类
*/
/**
* Interface IDatabase 适配目标,规定的接口将被适配对象实现
* 约定好统一的api行为
*/
interface IDatabase
{
// 定义数据库连接方法
public function connect($host, $username, $password, $database);
// 定义数据库查询方法
public function query($sql);
// 关闭数据库
public function close();
}
/**
* Class Mysql 适配器
*/
class Mysql implements IDatabase
{
protected $connect; // 连接资源
/**
* 实现连接方法
*
* @param $host host
* @param $username 用户名
* @param $password 密码
* @param $database 数据库名
*/
public function connect($host, $username, $password, $database)
{
$connect = mysql_connect($host, $username, $password);
mysql_select_db($database, $connect);
$this->connect = $connect;
//其他操作
}
/**
* 实现查询方法
*
* @param $sql 需要被查询的sql语句
* @return mi
*/
public function query($sql)
{
return mysql_query($sql);
}
// 实现关闭方法
public function close()
{
mysql_close();
}
}
/**
* Class Mysql 适配器
*/
class Mysql_i implements IDatabase
{
protected $connect; // 连接资源
/**
* 实现连接方法
*
* @param $host host
* @param $username 用户名
* @param $password 密码
* @param $database 数据库名
*/
public function connect($host, $username, $password, $database)
{
$connect = mysqli_connect($host, $username, $password, $database);
$this->connect = $connect;
//其他操作
}
/**
* 实现查询方法
*
* @param $sql 需要被查询的sql语句
*/
public function query($sql)
{
return mysqli_query($this->connect, $sql);
}
// 实现关闭
public function close()
{
mysqli_close($this->connect);
}
}
/**
* Class Postgresql 适配器
*/
class Postgresql implements IDatabase
{
protected $connect; // 连接资源
/**
* 实现连接方法
*
* @param $host
* @param $username
* @param $password
* @param $database
*/
public function connect($host, $username, $password, $database)
{
$this->connect = pg_connect("host=$host dbname=$database user=$username password=$password");
//其他操作
}
/**
* 实现查询方法
*
* @param $sql 需要被查询的sql语句
*/
public function query($sql)
{
// 其他操作
}
// 实现关闭方法
public function close()
{
}
}
/**
* 客户端使用演示
* 这里以mysql为例
* 只要模式设计好,不论有多少种数据库,实现和调用方式都是一样的
* 因为都是实现的同一个接口,所以都是可以随意切换的
*/
$host = 'localhost';
$username = 'root';
$password = 'root';
$database = 'mysql';
//$client = new Postgresql();
//$client = new Mysql();
$client = new Mysql_i();
$client->connect($host, $username, $password, $database);
$result = $client->query("select * from db");
while ($rows = mysqli_fetch_array($result)) {
var_dump($rows);
}
$client->close();运行结果:
array(44) {
[0]=>
string(1) "%"
["Host"]=>
string(1) "%"
[1]=>
string(4) "test"
["Db"]=>
string(4) "test"
[2]=>
string(0) ""
["User"]=>
string(0) ""
[3]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Select_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[4]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Insert_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[5]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Update_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[6]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Delete_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[7]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Create_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[8]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Drop_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[9]=>
string(1) "N"
["Grant_priv"]=>
string(1) "N"
[10]=>
string(1) "Y"
["References_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[11]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Index_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[12]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Alter_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[13]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Create_tmp_table_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[14]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Lock_tables_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[15]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Create_view_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[16]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Show_view_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[17]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Create_routine_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[18]=>
string(1) "N"
["Alter_routine_priv"]=>
string(1) "N"
[19]=>
string(1) "N"
["Execute_priv"]=>
string(1) "N"
[20]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Event_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
[21]=>
string(1) "Y"
["Trigger_priv"]=>
string(1) "Y"
}从以上结果可看出,数据库连接以及查询语句都已经执行成功。
Kenyataan:
Kandungan artikel ini disumbangkan secara sukarela oleh netizen, dan hak cipta adalah milik pengarang asal. Laman web ini tidak memikul tanggungjawab undang-undang yang sepadan. Jika anda menemui sebarang kandungan yang disyaki plagiarisme atau pelanggaran, sila hubungi admin@php.cn
Artikel sebelumnya:php语法基础Artikel seterusnya:PHP - 解决curl扩展无法开启问题
Artikel berkaitan
Lihat lagi- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Cara menggunakan cURL untuk melaksanakan permintaan Dapatkan dan Hantar dalam PHP
- Semua simbol ungkapan dalam ungkapan biasa (ringkasan)

