Rumah >Java >javaTutorial >Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi di Jawa
Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi di Jawa
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBasal
- 2024-08-30 15:27:381263semak imbas
Panduan lengkap mengenai Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi di Jawa. Array ialah struktur Multidimensi data homogen yang merupakan koleksi elemen dengan jenis data yang serupa. Mereka disimpan di lokasi memori bersebelahan. Dalam tatasusunan, elemen pertama disimpan dalam indeks 0; elemen kedua disimpan dalam indeks 1, dan seterusnya. Tatasusunan boleh terdiri daripada satu dimensi atau berbilang dimensi. Dalam dokumen ini, kita akan melihat tatasusunan berbilang dimensi dalam Java. Tatasusunan berbilang dimensi ialah tatasusunan tatasusunan yang boleh memuatkan lebih daripada satu baris dan lajur. Sekarang, mari kita lihat sintaks dan pelaksanaan tatasusunan Berbilang dimensi dalam bahagian berikut.
IKLAN Kursus Popular dalam kategori ini JAVA MASTERY - Pengkhususan | 78 Siri Kursus | 15 Ujian Olok-olokSintaks:
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
- data_type: jenis data tatasusunan, Contoh: int, char, float, dll.
- dimensi: dimensi tatasusunan, Contoh: 1D, 2D, dsb.
- nama_tatasusunan: Nama tatasusunan.
- saiz1, saiz2, …, saizN: Saiz dimensi.
Jenis Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi dalam Java
Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi yang paling biasa di Jawa ialah:
- Tatasusunan Dua Dimensi atau Tatasusunan 2D.
- Tatasusunan Tiga Dimensi atau Tatasusunan 3D.
1. Tatasusunan Dua Dimensi
Susun atur 2D biasanya digunakan dalam permainan video platform seperti Super Mario untuk mewakili rupa bumi atau skrin. Ia juga boleh digunakan untuk melukis papan Catur, mewakili struktur seperti hamparan, dsb.
Kod:
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
Contoh:
9 10
7 66
Ini ialah tatasusunan 2D dengan dua baris dan dua lajur.
2. Tatasusunan Tiga Dimensi
Tatasusunan Tiga Dimensi tidak biasa digunakan dalam aplikasi masa nyata. Oleh itu, tatasusunan dua dimensi juga diberi keutamaan dalam contoh pengaturcaraan.
Kod:
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
Contoh:
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
Bagaimana untuk Mengisytiharkan Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi dalam Java?
Adalah mudah untuk memahami Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi dalam Java jika tatasusunan biasa diketahui. Tatasusunan berbilang dimensi boleh diisytiharkan seperti yang ditunjukkan di bawah:
Pertama, mari kita lihat pengisytiharan tatasusunan 2D:
- int[][] tatasusunan1 = int baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan Integer dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- String[][] tatasusunan1 = Rentetan baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan Rentetan dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- char[][] tatasusunan1 = aksara baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan aksara dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- boolean[][] tatasusunan1 = boolean baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan boolean dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- double[][] tatasusunan1 = ganda baru[2][2]; // Tatasusunan berganda dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- apung[][] tatasusunan1 = apungan baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan apungan dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- panjang[][] tatasusunan1 = panjang baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan panjang dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- pendek[][] tatasusunan1 = pendek baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan pendek dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
- bait[][] tatasusunan1 = bait baharu[2][2]; // Tatasusunan bait dua dimensi dengan 2 baris dan 2 lajur.
Pastikan pengisytiharan yang betul dibuat semasa pengaturcaraan dalam Java.
Contoh #1
Kod:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Output:

Pengisytiharan Tatasusunan Tiga Dimensi boleh dibincangkan.
- int[][][] tatasusunan2 = int baharu[12][24][36]; // Tatasusunan tiga dimensi
Tatasusunan ini boleh terdiri daripada sebarang jenis data. Di bawah ialah beberapa tatasusunan tiga dimensi dengan jenis data yang berbeza.
- int [][][] IntArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Integer.
- bait[][][] ByteArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Bait.
- pendek[][][][] Susunan Pendek; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Shorts.
- panjang[][][] LongArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Long.
- float[][][] FloatArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Terapung.
- ganda[][][] DoubleArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Beregu.
- boolean[][][] BooleanArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Booleans.
- char[][][] CharArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Aksara.
- String[][][] StringArray; // mengisytiharkan tatasusunan tiga dimensi Rentetan.
Contoh #2
Kod:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:

Bagaimana untuk Memulakan Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi dalam Java?
Tatasusunan berbilang dimensi boleh dimulakan dalam pelbagai cara:
1. Declare and Create a Java Multidimensional Array
- int[][][] a= new int[3][5][4];
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
- a[0][1][0] = 15; // Initializing Array elements at position [0][1][0]
- a[1][2][0] = 45; // Initializing Array elements at position [1][2][0]
- a[2][1][1] = 65; // Initializing Array elements at position [2][1][1]
2. Directly Specify the Elements
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };
In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
3. Nested For Loop
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }
4. Assigning Values to One Row
int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Operations on Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Example #1
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Example #2
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
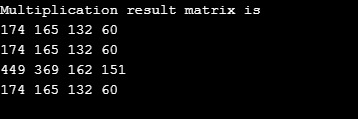
Output:
Conclusion
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Multidimensional Array in C
- 2D Arrays in Java
- 2D Arrays in C#
- Multidimensional Array in PHP
Atas ialah kandungan terperinci Tatasusunan Berbilang Dimensi di Jawa. Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila ikut artikel berkaitan lain di laman web China PHP!

