MongoDB replication (replica set)
MongoDB replication is the process of synchronizing data across multiple servers.
Replication provides redundant backup of data and stores data copies on multiple servers, improving data availability. And can ensure the security of data.
Replication also allows you to recover data from hardware failures and service interruptions.
What is replication?
Ensure data security
High data availability (24*7)
Disaster recovery
No need for downtime maintenance (such as backup, rebuild index, compression)
Distributed reading of data
MongoDB replication principle
Mongodb replication requires at least two nodes. One of them is the master node, responsible for processing client requests, and the rest are slave nodes, responsible for replicating data on the master node.
The common matching methods of each node of mongodb are: one master and one slave, one master and multiple slaves.
The master node records all operations oplog on it. The slave node periodically polls the master node to obtain these operations, and then performs these operations on its own data copy to ensure that the data of the slave node is consistent with the master node.
MongoDB replication structure diagram is as follows:
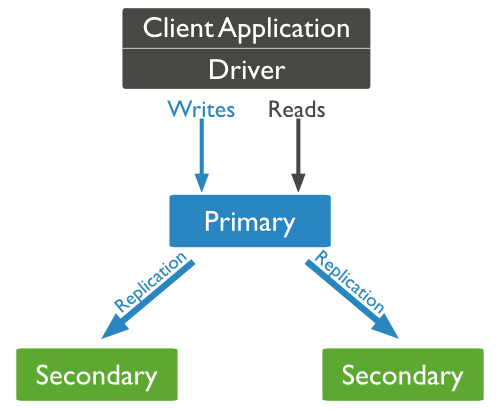
# In the above structure diagram, the client master node reads data, and the client writes data to The master node is, Data interaction between the master node and slave nodes ensures data consistency.
Replica set features:
Cluster with N nodes
Any node can serve as the master node
All write operations are on the primary node
Automatic failover
Automatic recovery
MongoDB replica set settings
In this tutorial we use the same MongoDB to do the MongoDB master-slave experiment. The steps are as follows:
1. Close the running MongoDB server.
Now we start mongoDB by specifying the --replSet option. The basic syntax format of --replSet is as follows:
mongod --port "PORT" --dbpath "YOUR_DB_DATA_PATH" --replSet "REPLICA_SET_INSTANCE_NAME"
Instance
mongod --port 27017 --dbpath "D:\set up\mongodb\data" --replSet rs0
The above example will start a MongoDB instance named rs0, and its port number is 27017.
After startup, open the command prompt box and connect to the mongoDB service.
Use the command rs.initiate() on the Mongo client to start a new replica set.
We can use rs.conf() to view the configuration of the replica set
To view the status of the replica set, use the rs.status() command
Add members to the replica set
To add members of the replica set, we need to use multiple servers to start the mongo service. Enter the Mongo client and use the rs.add() method to add members of the replica set.
Syntax
The basic syntax format of the rs.add() command is as follows:>rs.add(HOST_NAME:PORT)
Example
Assume that you have started a Mongo named mongod1.net with the port number 27017 Serve. Use the rs.add() command in the client command window to add it to the replica set. The command is as follows:
>rs.add("mongod1.net:27017")
>In MongoDB, you can only add the Mongo service to the replica set through the master node. To determine whether the currently running Mongo service is the master node, you can use the command db.isMaster().
MongoDB's replica set is different from our common master-slave. All services of the master-slave will stop after the host goes down, while in the replica set, after the host goes down, the replica will take over the master node and become the master node. There will be no downtime.








