데이터 저장 및 액세스 - 파일 저장, 읽기 및 쓰기
이 섹션 소개:
안녕하세요, 이 제목을 보면 일부 독자들이 '이전 부분 작성을 마쳤나요? 글쎄요, 예시를 원하고 필요해서 아직 글을 다 쓰지 못했습니다. 효율성을 높이기 위해 멀티스레딩처럼 튜토리얼을 동시에 작성하기로 결정했습니다. 이렇게 하면 튜토리얼 작성 속도가 빨라질 수 있습니다. 지금까지 정확히 60개의 글을 썼고, 입문 튜토리얼을 마치려면 아직 멀었다고 말씀드렸듯이, 한 달 반에서 두 달 안에 끝내고 싶습니다. 이 튜토리얼 세트는 오늘 9.1에 공개되었으니 계속해서 열심히 하세요~ 좋아요, 말도 안 되는 소리가 너무 많습니다. 이 섹션에서는 Android 데이터 저장 및 액세스 방법 중 하나는 파일 저장 및 읽기 및 쓰기입니다. 물론 이 방법 외에도 SharedPreference, 데이터베이스에 저장할 수 있습니다. 또는 Application에 대해서는 나중에 논의하겠지만, 이 섹션부터 시작하겠습니다~
1. Android 파일 작업 모드
Java를 공부한 학생들은 새로운 파일을 만든 다음 데이터를 쓸 수 있다는 것을 알고 있습니다. 하지만 안드로이드는 다릅니다. 왜냐하면 안드로이드는 다르기 때문입니다. Linux 기반에서는 파일을 읽고 쓸 때 파일 작업 모드도 추가해야 합니다. Android의 작업 모드는 다음과 같습니다.
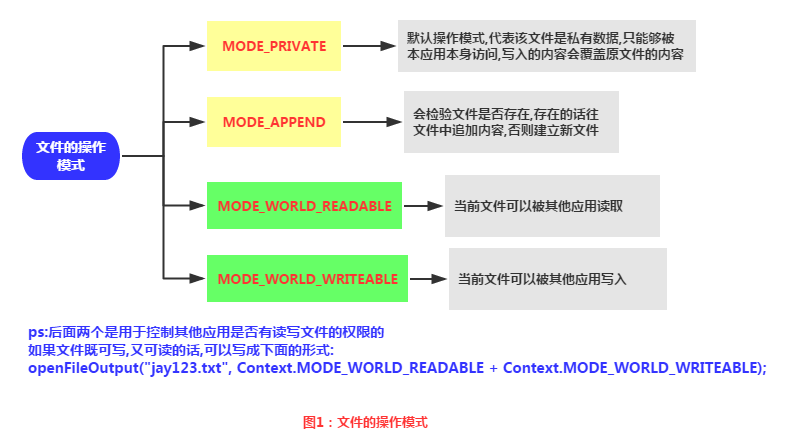
2. 파일 관련 작업 방법

3. 읽기 및 쓰기의 파일 구현
Android의 파일 읽기 및 쓰기는 Java의 파일 I/O와 동일하며 프로세스도 매우 간단합니다. 아래에 간단한 예를 작성해 보겠습니다.
구현 렌더링:
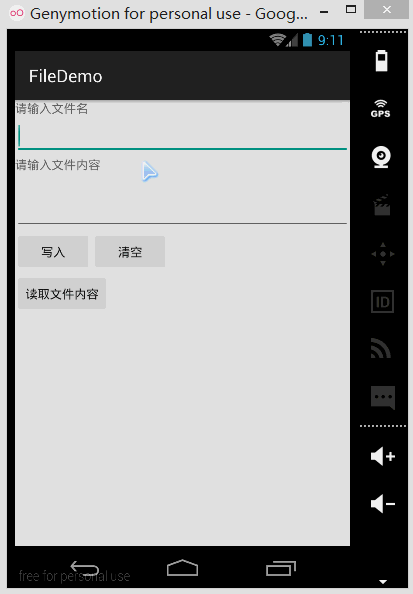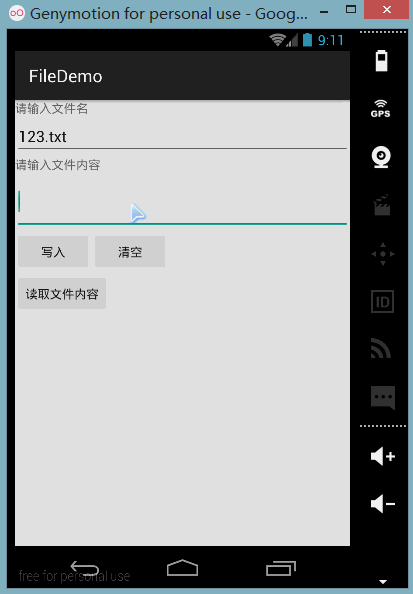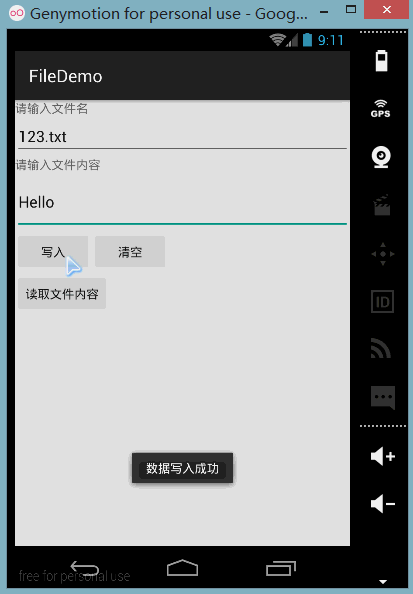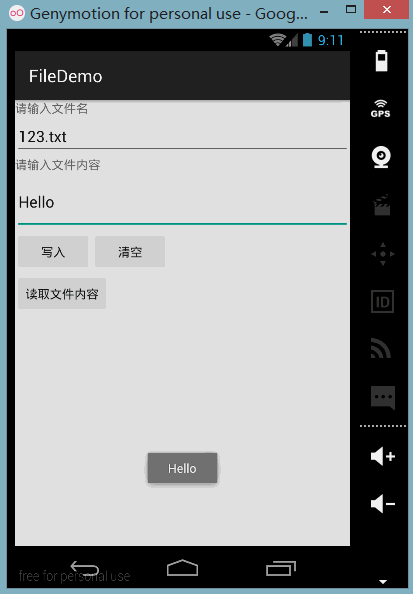
PS:작성자의 N5에는 루트가 없고 파일 저장 디렉터리를 볼 수 없기 때문에 여기서는 시뮬레이터를 사용합니다. 다음으로 DDMS를 엽니다. 파일 탐색기에서는 data/data/<패키지 이름>/파일에 작성한 파일이 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
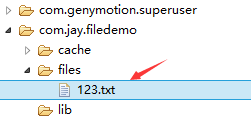
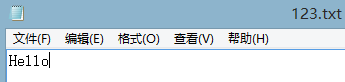
오른쪽 상단에 있는 응답 아이콘을 클릭하여 파일을 컴퓨터로 가져와서 열 수 있습니다. 작성된 내용 확인:
 코드 구현:
코드 구현:
먼저 레이아웃 파일은 main_activity입니다. 여기서 관련 작업을 완료합니다.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.jay.example.filedemo1.MainActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/nametitle" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editname" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/detailtitle" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editdetail" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:minLines="2" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:id="@+id/btnsave" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/btnwrite" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnclean" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/btnclean" /> </LinearLayout> <Button android:id="@+id/btnread" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/btnread" /> </LinearLayout>
4. SD 카드에
읽기 흐름도:
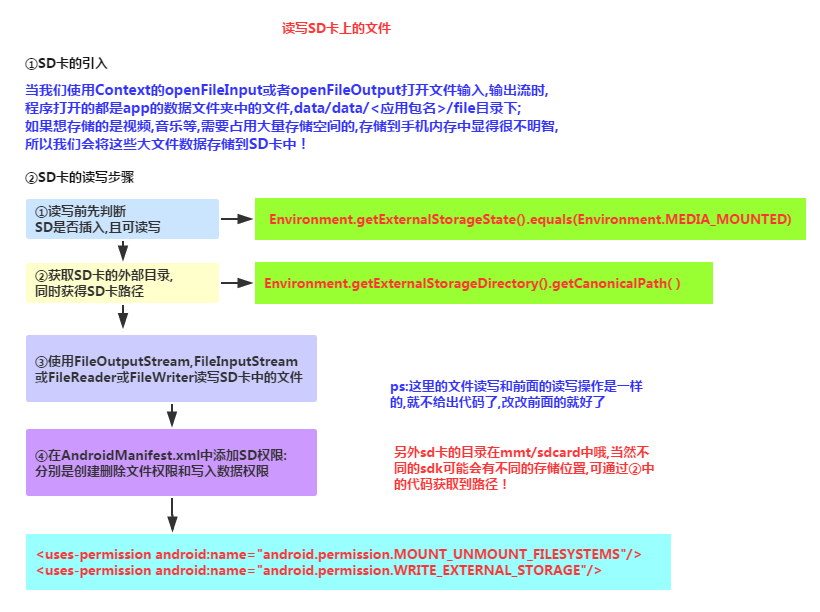
코드 샘플:
런닝 렌더링:
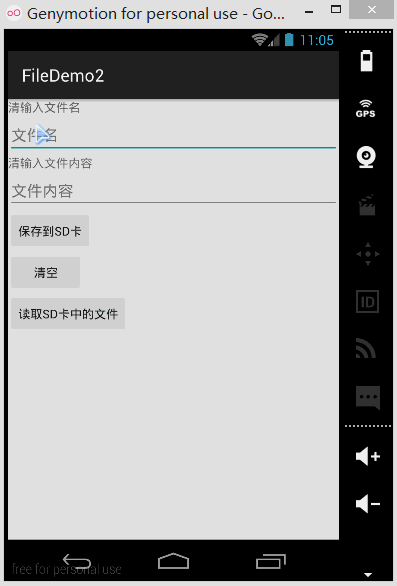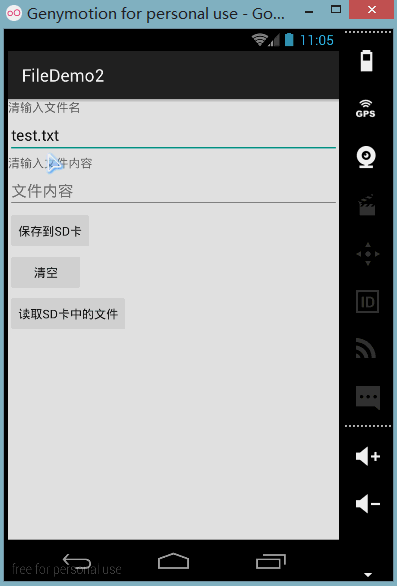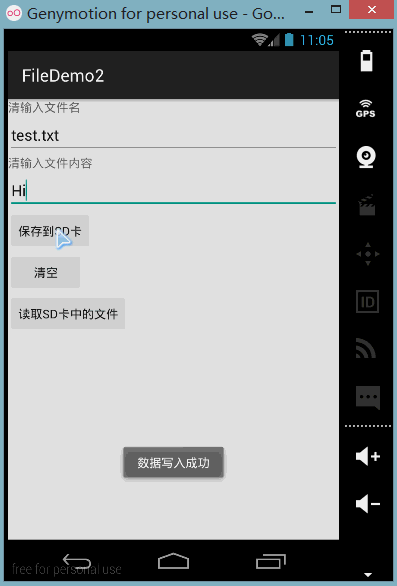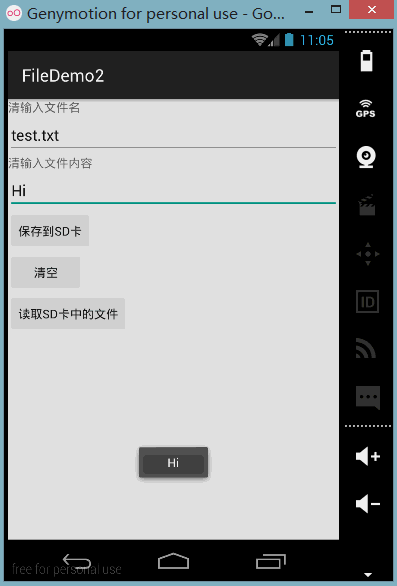
또한 DDMS의 파일 탐색기를 엽니다. 이전 버전의 시스템에서는 mmtsdcard에서 직접 찾을 수 있지만 새 버전에서는 가능합니다. 먼저 다음 경로로 이동합니다.
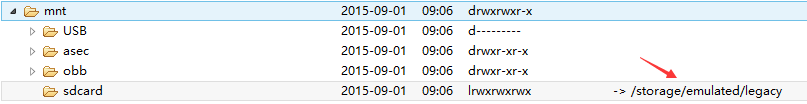
sdcard를 클릭했지만 아무것도 없습니다. /storage/emulated/legacy:
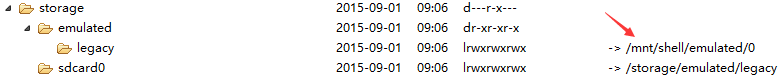
좋아요, 그는 다시 다른 곳으로 이동했습니다. 우리는 계속해서 /storage/shell/emilated/0
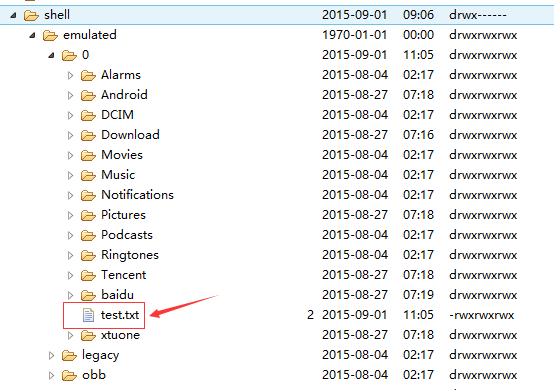
을 찾았고, 확실히 SD 카드에서 생성한 test.txt를 찾았습니다! 컴퓨터로 내보내고 안에 내용을 살펴보세요:
물론이죠, SD 카드를 읽고 쓰는 데 성공했습니다~ 다음으로 코드가 어떻게 작성되었는지 살펴보겠습니다.
Code 구현:
main_activity.xml:
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/1 0001.
*/
public class FileHelper {
private Context mContext;
public FileHelper() {
}
public FileHelper(Context mContext) {
super();
this.mContext = mContext;
}
/*
* 这里定义的是一个文件保存的方法,写入到文件中,所以是输出流
* */
public void save(String filename, String filecontent) throws Exception {
//这里我们使用私有模式,创建出来的文件只能被本应用访问,还会覆盖原文件哦
FileOutputStream output = mContext.openFileOutput(filename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
output.write(filecontent.getBytes()); //将String字符串以字节流的形式写入到输出流中
output.close(); //关闭输出流
}
/*
* 这里定义的是文件读取的方法
* */
public String read(String filename) throws IOException {
//打开文件输入流
FileInputStream input = mContext.openFileInput(filename);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
int len = 0;
//读取文件内容:
while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) {
sb.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
//关闭输入流
input.close();
return sb.toString();
}
}그런 다음 SD 작업 클래스를 작성해 보겠습니다. SDFileHelper.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText editname;
private EditText editdetail;
private Button btnsave;
private Button btnclean;
private Button btnread;
private Context mContext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = getApplicationContext();
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
editdetail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editdetail);
editname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editname);
btnclean = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnclean);
btnsave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnsave);
btnread = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnread);
btnclean.setOnClickListener(this);
btnsave.setOnClickListener(this);
btnread.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btnclean:
editdetail.setText("");
editname.setText("");
break;
case R.id.btnsave:
FileHelper fHelper = new FileHelper(mContext);
String filename = editname.getText().toString();
String filedetail = editdetail.getText().toString();
try {
fHelper.save(filename, filedetail);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btnread:
String detail = "";
FileHelper fHelper2 = new FileHelper(getApplicationContext());
try {
String fname = editname.getText().toString();
detail = fHelper2.read(fname);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), detail, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}그런 다음 MainActivity.java관련 논리를 구현합니다.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.jay.example.filedemo2.MainActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="清输入文件名" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/edittitle" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="文件名" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="清输入文件内容" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editdetail" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="文件内容" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnsave" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="保存到SD卡" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnclean" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="清空" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnread" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="读取sd卡中的文件" /> </LinearLayout>
마지막으로, 잊어버리다 AndroidManifest.xml에 SD 카드를 읽고 쓸 수 있는 권한을 쓰려면 아!
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/9/1 0001.
*/
public class SDFileHelper {
private Context context;
public SDFileHelper() {
}
public SDFileHelper(Context context) {
super();
this.context = context;
}
//往SD卡写入文件的方法
public void savaFileToSD(String filename, String filecontent) throws Exception {
//如果手机已插入sd卡,且app具有读写sd卡的权限
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + "/" + filename;
//这里就不要用openFileOutput了,那个是往手机内存中写数据的
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(filename);
output.write(filecontent.getBytes());
//将String字符串以字节流的形式写入到输出流中
output.close();
//关闭输出流
} else Toast.makeText(context, "SD卡不存在或者不可读写", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
//读取SD卡中文件的方法
//定义读取文件的方法:
public String readFromSD(String filename) throws IOException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + "/" + filename;
//打开文件输入流
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filename);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//读取文件内容:
while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) {
sb.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
//关闭输入流
input.close();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}5. 네이티브 시뮬레이터의 SD 카드 문제에 관해서
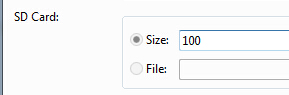
실제 머신에서 디버깅하는 경우에는 일반적으로 네이티브 가상 머신의 경우 문제가 많습니다. Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED) 가능 항상 false를 반환하는 것은 SD 카드가 존재하지 않는다는 것입니다. 이것이 주요 문제입니다. 이제 SDK의 새 버전이 출시됩니다. AVD를 생성할 때 SD 카드의 저장 영역이 동시에 적용됩니다
이전 버전의 SDK 또는 기타 이유로 SD 카드를 수동으로 연결해야 할 수 있습니다. 설정은 다음과 같습니다. 다음과 같습니다:
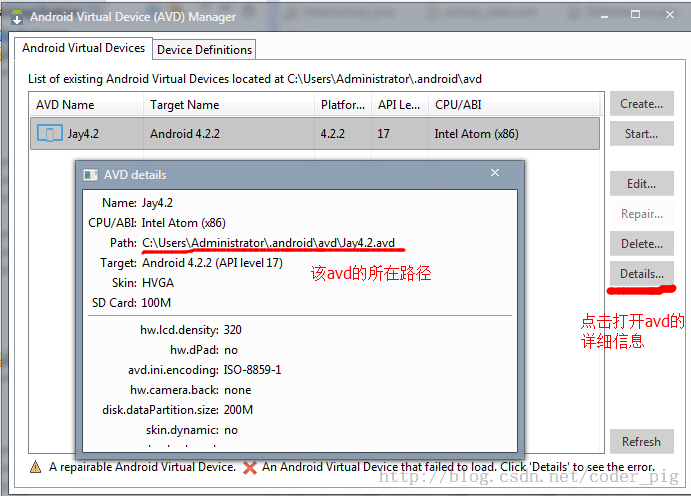
① 생성된 AVD 이미지의 경로 찾기:
클릭하여 avd 인터페이스를 열고 세부정보를 클릭한 후 avd 이미지의 디렉터리를 확인하세요
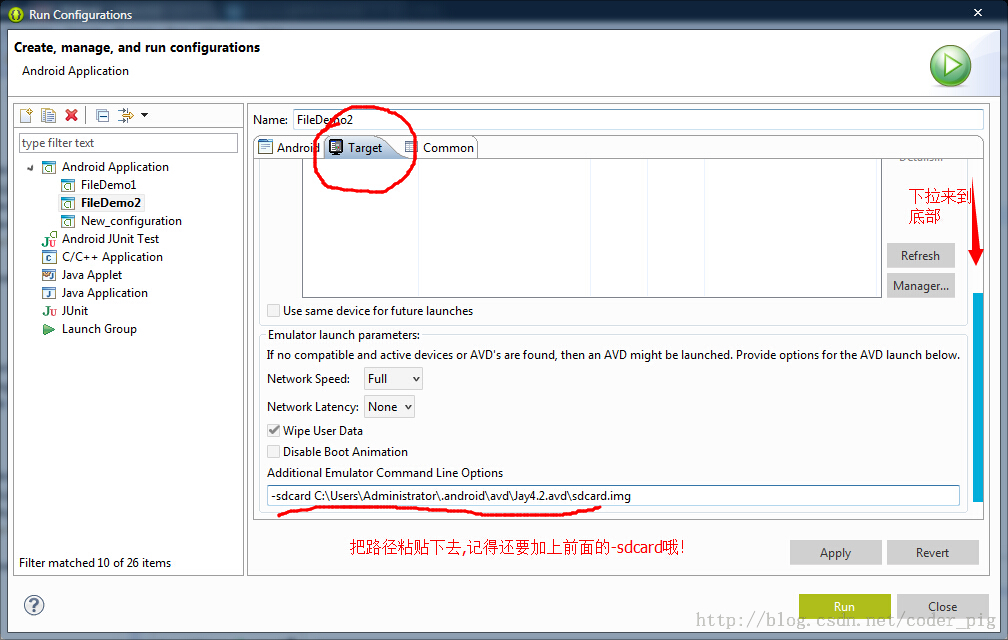
②avd 이미지가 있는 경로로 이동하여 복사합니다. sdcard.img의 경로:
예를 들어, 광산: -sdcard C: UsersAdministrator.androidavdJay4.2.avdsdcard.img
3그런 다음 클릭하여 다음 인터페이스로 이동하세요.
마지막으로 다음을 적용한 다음 실행하세요!
6. raw 및 자산 폴더의 파일을 읽으세요.
우리 자신의 파일을 원하지 않는다면 모두가 두 폴더에 익숙하다고 생각합니다. 바이너리 파일로 컴파일하면, 이 두 디렉터리에 파일을 넣을 수 있으며 두 디렉터리의 차이점은 다음과 같습니다.
- res/raw: 파일은 R.java 파일에 매핑되며 리소스 ID를 통해 직접 액세스할 수 있습니다. . 그리고 디렉터리 구조를 가질 수 없습니다. 즉, 더 이상 폴더를 생성할 수 없습니다
- assets: R.java 파일에 매핑되지 않으며 AssetManager를 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다. 자신만의 폴더를 만들 수 있습니다.
파일 리소스 읽기:
res/raw:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private EditText editname;
private EditText editdetail;
private Button btnsave;
private Button btnclean;
private Button btnread;
private Context mContext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = getApplicationContext();
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
editname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edittitle);
editdetail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editdetail);
btnsave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnsave);
btnclean = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnclean);
btnread = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnread);
btnsave.setOnClickListener(this);
btnclean.setOnClickListener(this);
btnread.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.btnclean:
editdetail.setText("");
editname.setText("");
break;
case R.id.btnsave:
String filename = editname.getText().toString();
String filedetail = editdetail.getText().toString();
SDFileHelper sdHelper = new SDFileHelper(mContext);
try
{
sdHelper.savaFileToSD(filename, filedetail);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btnread:
String detail = "";
SDFileHelper sdHelper2 = new SDFileHelper(mContext);
try
{
String filename2 = editname.getText().toString();
detail = sdHelper2.readFromSD(filename2);
}
catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), detail, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}assets:
<!-- 在SDCard中创建与删除文件权限 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS"/> <!-- 往SDCard写入数据权限 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
코드 다운로드:
- FileDemo.zip: 파일데모를 다운로드하세요. zip
- FileDemo2.zip: Download FileDemo2.zip
이 섹션 요약:
좋아, Android 데이터 저장 및 액세스에 대한 첫 번째 섹션은 여기까지입니다. - 파일 읽기 및 쓰기 당신은 이 글을 공부하고 있습니다 문제가 발생하거나 실수가 있다고 생각되면 언제든지 제기해 주시면 감사하겠습니다~