Linux 드라이버의 메모리 응용 기술: 원리 및 방법
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB앞으로
- 2024-02-12 09:45:221266검색
메모리는 Linux 시스템에서 가장 중요한 리소스 중 하나이며 데이터, 코드, 스택 등을 저장하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 메모리 적용 및 해제는 Linux 드라이버 개발에서 가장 기본적인 작업 중 하나입니다. 여기에는 커널 공간과 사용자 공간, 정적 할당과 동적 할당, 연속 메모리와 비연속 메모리 등의 개념이 포함됩니다. 이 기사에서는 kmalloc, vmalloc, get_free_pages, dma_alloc_coherent 및 기타 기능을 포함한 Linux 드라이버의 메모리 응용 기술을 소개하고 사용법과 주의 사항을 설명하는 예를 제공합니다.

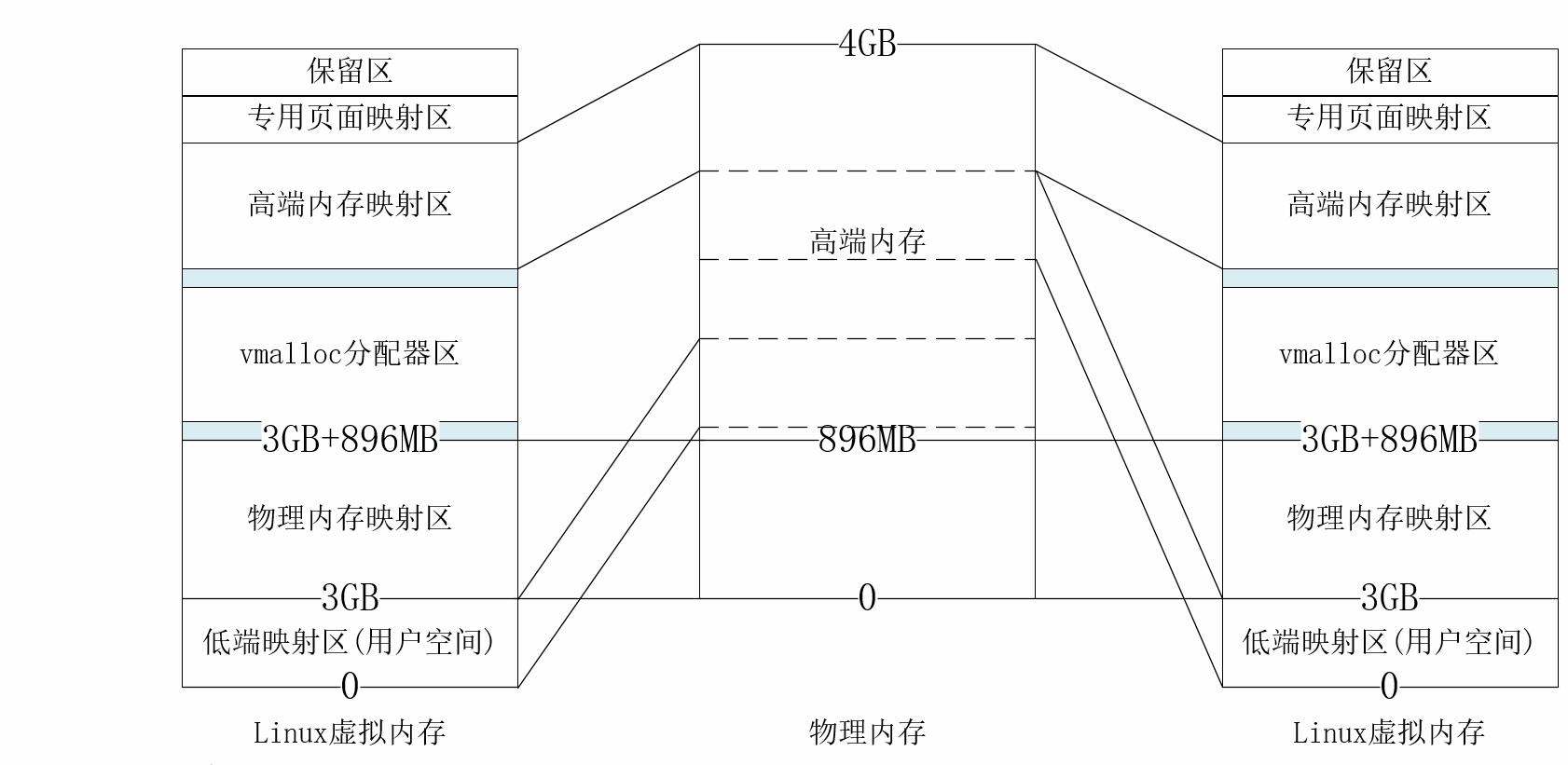
기본부터 시작해 보겠습니다. 아래 그림은 Linux의 메모리 매핑 모델입니다
- 각 프로세스에는 고유한 프로세스 공간이 있습니다. 프로세스 공간 중 0~3G는 사용자 공간이고 3G~4G는 커널 공간입니다
- 각 프로세스의 사용자 공간은 동일한 물리적 메모리 페이지에 있지 않지만 모든 프로세스의 커널 공간은 동일한 물리적 주소에 해당합니다
- vmalloc이 할당한 주소는 고급 메모리일 수도 있고 저가형 메모리일 수도 있습니다
- 0~896MB의 물리적 주소는 물리적 매핑 영역에 선형적으로 매핑됩니다.
“
”
메모리 동적 애플리케이션
애플리케이션 계층과 마찬가지로 커널 프로그램도 메모리를 동적으로 할당해야 합니다. 차이점은 커널 프로세스가 할당된 메모리가 사용자 공간에 있는지 아니면 커널 공간에 있는지 제어할 수 있다는 것입니다. 전자는 메모리를 힙 영역에 할당하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 사용자 공간, 예를 들어 user 프로세스의 사용자 공간의 malloc은 결국 시스템 호출을 통해 커널 공간의 메모리 할당 함수를 콜백하게 되는데 이때 메모리 할당 기능은 사용자 프로세스에 속해 할당할 수 있다. 사용자 프로세스의 힙 영역에 있는 공간을 반환하여 궁극적으로 사용자가 자신의 사용자 공간에서 메모리 할당을 얻습니다. 후자는 커널 공간에만 할당되므로 사용자 프로세스는 해당 공간에 직접 액세스할 수 없습니다. 따라서 커널 프로그램 자체의 메모리 요구 사항을 충족하는 데 주로 사용됩니다. 다음은 Linux 커널 공간 애플리케이션 메모리에 대한 일반적인 API입니다.
kmalloc – kfree
kmalloc이 요청한 메모리는 실제 메모리에서 연속적이므로 실제 물리적 주소와 고정된 오프셋만 있으므로 간단한 변환 관계가 있습니다. 이 API는 주로 페이지 크기보다 작은 메모리를 적용하는 데 사용됩니다. kmalloc의 하단 레이어는 **__get_free_pages를 호출해야 합니다. 매개변수의 메모리 유형을 나타내는 gtp_t 플래그는 이 함수의 약어입니다. 일반적으로 사용되는 메모리 유형에는 GFP_USER, GFP_KERNEL, GFP_ATOMIC**이 있습니다.
- GFP_USER는 사용자 공간 페이지에 메모리를 할당하는 것을 의미하며 차단될 수 있습니다.
- GFP_KERNEL은 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 플래그입니다. 이 플래그를 사용하여 메모리를 적용할 때 일시적으로 만족할 수 없으면 프로세스 차단이 발생하므로 인터럽트 처리와 같은 비프로세스 컨텍스트에서는 사용하면 안 됩니다. 함수, 태스크렛, 커널 타이머. ! ! GFP_ATOMIC
- 은 위의 세 가지 시나리오에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 플래그는 요청된 메모리를 사용할 수 없는 경우 즉시 반환됨을 나타냅니다. 아아아아 동일한 API 시리즈도 사용 가능합니다
__get_free_pages()는 kmalloc()과 마찬가지로 물리적으로 연속적인 메모리입니다. 이 일련의 함수는 기본 버디 알고리즘이 **(2^n)×을 기반으로 하기 때문에 Linux 커널에서 사용 가능한 메모리를 얻는 가장 낮은 수준의 방법입니다. PAGE_SIZE
는 메모리 관리에 사용되므로항상 페이지 단위로 메모리를 할당** 으아아아 동일한 API 시리즈도 사용 가능합니다
unsigned long __get_free_page(gfp_t gfp) unsigned long get_zeroed_page(gfp_t gfp_mask) struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order) void free_page(unsigned long addr)
vmalloc – vfree
vmalloc在虚拟内存空间给出一块连续的内存区,实质上,这片连续的虚拟内存在物理内存中并不一定连续,所以vmalloc申请的虚拟内存和物理内存之间也就没有简单的换算关系,正因如此,vmalloc()通常用于分配远大于__get_free_pages()的内存空间,它的实现需要建立新的页表,此外还会调用使用GFP_KERN的kmalloc,so,一定不要在中断处理函数,tasklet和内核定时器等非进程上下文中使用vmalloc!
/** * vmalloc - allocate virtually contiguous memory * @size: allocation size * Allocate enough pages to cover @size from the page level allocator and map them into contiguous kernel virtual space. */ void *vmalloc(unsigned long size) /** * vfree - release memory allocated by vmalloc() * @addr: memory base address */ void vfree(const void *addr)
同系列的API还有
/** * vmalloc_32 - allocate virtually contiguous memory (32bit addressable) * @size: allocation size * Allocate enough 32bit PA addressable pages to cover @size from the page level allocator and map them into contiguous kernel virtual space. */ void *vmalloc_32(unsigned long size)
slab缓存
我们知道,页是内存映射的基本单位,但内核中很多频繁创建的对象所需内存都不到一页,此时如果仍然按照页映射的方式,频繁的进行分配和释放就会造成资源的浪费,同时也会降低系统性能。为了解决的这样的问题,内核引入了slab机制,使对象在前后两次被使用时被分配在同一块内存或同一类内存空间,且保留了基本的数据结构,就可以大大提高效率。kmalloc的底层即是使用slab算法管理分配的内存的。注意,slab依然是以页为单位进行映射,只是映射之后分割这些页为相同的更小的单元,从而节省了内存。slab分配的单元不能小于32B或大于128K。
/** * kmem_cache_create - 创建slab缓存对象 * @name:slab缓存区名字, * @size:slab分配的缓存区的每一个单元的大小 * @align:缓存区内存的对齐方式,一般给0 * @flags:控制分配的位掩码, * %SLAB_POISON - Poison the slab with a known test pattern (a5a5a5a5) to catch references to uninitialised memory. * %SLAB_RED_ZONE - Insert `Red' zones around the allocated memory to check for buffer overruns. * %SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN - Align the objects in this cache to a hardware cacheline. This can be beneficial if you're counting cycles as closely as davem. * %SLAB_CACHE_DMA - Use GFP_DMA memory * %SLAB_STORE_USER - Store the last owner for bug hunting *define SLAB_PANIC - Panic if kmem_cache_create() fails */ struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache_create(const char *name, size_t size, size_t align,unsigned long flags, void (*ctor)(void *)) /** * kmem_cache_alloc - Allocate an object from this cache. * @cachep: The cache to allocate from. * @flags: See kmalloc(). * The flags are only relevant if the cache has no available objects. */ void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags) /** * kmem_cache_free - Deallocate an object * @cachep: The cache the allocation was from. * @objp: The previously allocated object. * Free an object which was previously allocated from this cache. */ void kmem_cache_free(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp) void kmem_cache_destroy(struct kmem_cache *s)
范例
//创建slab对象
struct kmem_cache_t *xj_sbcache;
xj_sbcache = kmem_cache_create("xjslab",sizeof(struct xj_unit_t),0,SLAB_CACHE_DMA|SLAB_PANIC,NULL,NULL);
//分配slab缓存
struct xj_unit_t *xj_unit;
xj_unit = kmem_cache_alloc(xj_sbcache,GFP_KERNEL);
/* 使用slab缓存 */
/* 释放slab缓存 */
kmem_cache_free(xj_sbcache, xj_unit);
/* 销毁slab缓存 */
kmem_cache_destroy(xj_sbcache);
内存池
除了slab机制,内核还提供了传统的内存池机制来管理小块内存的分配。内存池主要是用来解决可能出现的内存不足的情况,因为一个内存池在创建的时候就已经分配好了一内存,当我们用mempool_alloc向一个已经创建好的内存池申请申请内存时,该函数首先会尝试回调内存池创建时的分配内存函数,如果已经没有内存可以分配,他就会使用内存池创建时预先分配的内存,这样就可以避免因为无内存分配而陷入休眠,当然,如果预分配的内存也已经使用完毕,还是会陷入休眠。slab机制的目的是提高内存使用率以及内存管理效率,内存池的目的是避免内存的分配失败。下面是内核中提供的关于内存池的API
/** * mempool_create - create a memory pool * @min_nr: the minimum number of elements guaranteed to be allocated for this pool. * @alloc_fn: user-defined element-allocation function. * @free_fn: user-defined element-freeing function. * @pool_data: optional private data available to the user-defined functions. * * this function creates and allocates a guaranteed size, preallocated memory pool. The pool can be used from the mempool_alloc() and mempool_free() functions. * This function might sleep. Both the alloc_fn() and the free_fn() functions might sleep - as long as the mempool_alloc() function is not called from IRQ contexts. */ mempool_t *mempool_create(int min_nr, mempool_alloc_t *alloc_fn, mempool_free_t *free_fn, void *pool_data) /** * mempool_alloc - allocate an element from a specific memory pool * @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create(). * @gfp_mask: the usual allocation bitmask. * this function only sleeps if the alloc_fn() function sleeps or returns NULL. Note that due to preallocation, this function never* fails when called from process contexts. (it might fail if called from an IRQ context.) */ void * mempool_alloc(mempool_t *pool, gfp_t gfp_mask) /** * mempool_free - return an element to the pool. * @element: pool element pointer. * @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create(). * * this function only sleeps if the free_fn() function sleeps. */ void mempool_free(void *element, mempool_t *pool) /** * mempool_destroy - deallocate a memory pool * @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create(). * * Free all reserved elements in @pool and @pool itself. This function only sleeps if the free_fn() function sleeps. */ void mempool_destroy(mempool_t *pool)
通过本文,我们了解了Linux驱动中的内存申请技术,它们各有优缺点和适用场景。我们应该根据实际需求选择合适的函数,并遵循一些基本原则,如匹配申请和释放函数,检查返回值是否为空,避免内存泄漏等。内存申请技术是Linux驱动开发中不可或缺的一部分,它可以保证驱动程序的正常运行和数据交换,也可以提升驱动程序的性能和稳定性。希望本文能够对你有所帮助和启发。
위 내용은 Linux 드라이버의 메모리 응용 기술: 원리 및 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!