루프 스케줄링을 위한 C 프로그램
- 王林앞으로
- 2023-09-25 17:09:02989검색
우리는 해당 버스트 시간과 시간 퀀텀이 있는 n개의 프로세스가 제공되며 작업은 평균 대기 시간과 평균 처리 시간을 찾아 결과를 표시하는 것입니다.
라운드 로빈 스케줄링이란 무엇입니까?
라운드 로빈은 시간 공유 시스템을 위해 특별히 설계된 CPU 스케줄링 알고리즘입니다. 이는 라운드 로빈 프로세스에서 양자 시간 크기로 제한되는 한 가지 변경 사항이 있는 FCFS 스케줄링 알고리즘과 비슷합니다. 시간의 작은 단위는 Time Quantum 또는 Time Slice로 알려져 있습니다. 시간 할당량의 범위는 10~100밀리초입니다. CPU는 준비된 큐를 주어진 시간 조각으로 프로세스를 실행하기 위한 순환 큐로 처리합니다. 프로세스에 고정된 시간을 할당하기 때문에 선제적인 접근 방식을 따릅니다. 유일한 단점은 컨텍스트 전환의 오버헤드입니다.
우리가 계산해야 하는 것은 무엇입니까?
완료 시간은 프로세스가 실행을 완료하는 데 필요한 시간입니다
처리 시간은 프로세스 제출 및 완료
처리 시간 = 프로세스 완료 – 프로세스 제출
대기 시간은 처리 시간과 버스트 시간의 차이입니다.
대기 시간 = 처리 시간 – 버스트 시간
예
3개의 프로세스 P1, P2 및 P3이 제공되며 해당 버스트 시간은 24, 3 및 3
| Process | Burst Time |
|---|---|
| P1 | 24 |
| P2 | 3 |
| P3 | 3 |
시간 퀀텀이 4밀리초이므로 프로세스 P1은 처음 4밀리초를 얻지만 실행을 완료하려면 20밀리초가 더 필요하지만 CPU는 첫 번째 퀀텀 이후에 이를 선점하고 CPU는 다음 프로세스 P2에 할당됩니다. 표에 표시된 것처럼 프로세스 P2는 실행을 완료하는 데 3밀리초만 필요하므로 CPU는 4밀리초 대신 3밀리초의 시간 할당에만 할당됩니다.
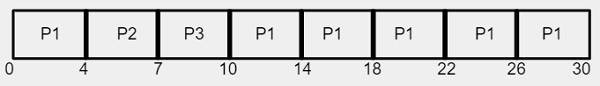
간트 차트를 사용하면 평균 대기 시간은 다음과 같이 계산됩니다. 아래 −
평균 대기 시간 = 17/3 = 5.66밀리초
Algorithm
Start
Step 1-> In function int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i]
return 1
Step 2-> In function int waitingtime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int wt[], int quantum)
Declare rem_bt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rem_bt[i] = bt[i]
Set t = 0
Loop While (1)
Set done = true
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
If rem_bt[i] > 0 then,
Set done = false
If rem_bt[i] > quantum then,
Set t = t + quantum
Set rem_bt[i] = rem_bt[i] - quantum
Else
Set t = t + rem_bt[i]
Set wt[i] = t - bt[i]
Set rem_bt[i] = 0
If done == true then,
Break
Step 3->In function int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[], int quantum)
Declare and initialize wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call function waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum)
Call function turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat)
Print "Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time "
Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print the value i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]
Print "Average waiting time = total_wt / n
Print "Average turnaround time =total_tat / n
Step 4-> In function int main()
Delcare and initialize processes[] = { 1, 2, 3}
Declare and initialize n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0]
Declare and initialize burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12}
Set quantum = 2
Call function findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum)Example
实例演示
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to calculate turn around time
int turnarroundtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int tat[]) {
// calculating turnaround time by adding
// bt[i] + wt[i]
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++)
tat[i] = bt[i] + wt[i];
return 1;
}
// Function to find the waiting time for all
// processes
int waitingtime(int processes[], int n,
int bt[], int wt[], int quantum) {
// Make a copy of burst times bt[] to store remaining
// burst times.
int rem_bt[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
rem_bt[i] = bt[i];
int t = 0; // Current time
// Keep traversing processes in round robin manner
// until all of them are not done.
while (1) {
bool done = true;
// Traverse all processes one by one repeatedly
for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
// If burst time of a process is greater than 0
// then only need to process further
if (rem_bt[i] > 0) {
done = false; // There is a pending process
if (rem_bt[i] > quantum) {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t += quantum;
// Decrease the burst_time of current process
// by quantum
rem_bt[i] -= quantum;
}
// If burst time is smaller than or equal to
// quantum. Last cycle for this process
else {
// Increase the value of t i.e. shows
// how much time a process has been processed
t = t + rem_bt[i];
// Waiting time is current time minus time
// used by this process
wt[i] = t - bt[i];
// As the process gets fully executed
// make its remaining burst time = 0
rem_bt[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// If all processes are done
if (done == true)
break;
}
return 1;
}
// Function to calculate average time
int findavgTime(int processes[], int n, int bt[],
int quantum) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all processes
waitingtime(processes, n, bt, wt, quantum);
// Function to find turn around time for all processes
turnarroundtime(processes, n, bt, wt, tat);
// Display processes along with all details
printf("Processes Burst Time Waiting Time turnaround time</p><p>");
// Calculate total waiting time and total turn
// around time
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
printf("\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d</p><p>",i+1, bt[i], wt[i], tat[i]);
}
printf("Average waiting time = %f", (float)total_wt / (float)n);
printf("</p><p>Average turnaround time = %f</p><p>", (float)total_tat / (float)n);
return 1;
}
// main function
int main() {
// process id's
int processes[] = { 1, 2, 3};
int n = sizeof processes / sizeof processes[0];
// Burst time of all processes
int burst_time[] = {8, 6, 12};
// Time quantum
int quantum = 2;
findavgTime(processes, n, burst_time, quantum);
return 0;
}输ude
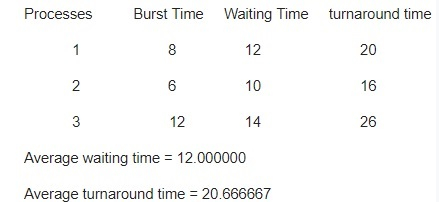
위 내용은 루프 스케줄링을 위한 C 프로그램의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

