Ansible Playbook 설명 및 실제 작동
- PHPz앞으로
- 2023-06-09 20:58:291646검색
1. 개요
- playbook은 ad-hoc과 비교하여 ansible을 사용하는 방식이 완전히 다르며, saltstack의 상태 파일과 유사합니다. Ad-hoc은 영구적으로 사용할 수 없으며 플레이북은 영구적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
- playbook은 하나 이상의 연극으로 구성된 목록입니다. 놀이의 주요 기능은 이전에 그룹으로 그룹화된 호스트에게 Ansible의 작업을 통해 미리 정의된 역할을 부여하는 것입니다.
- 기본적으로 소위 태스크는 Ansible을 호출하는 모듈에 지나지 않습니다. 여러 극을 하나의 플레이북으로 구성하면 미리 정해진 메커니즘에 따라 특정 작업을 완료하기 위해 결합할 수 있습니다.
참조 문서: https://ansible-tran.readthedocs.io/en/latest/docs/playbooks.html
Ansible의 기본 소개 및 환경 배포에 대해서는 내 기사를 참조할 수 있습니다. Ansible 소개 및 실제 동작 시연
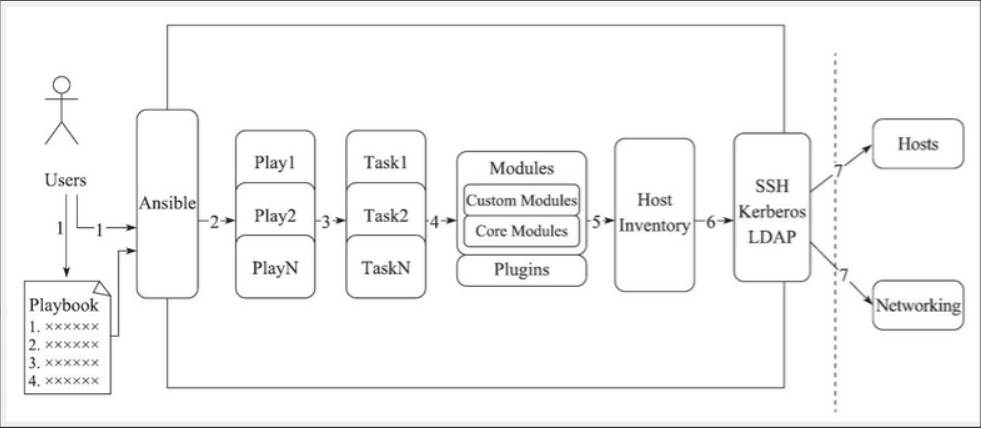
2. 플레이북 핵심 요소
- Hosts실행된 원격 호스트 목록
- 작업 작업 세트
- Varniables내장 변수 또는 사용자 정의 변수는 플레이북에서 호출됩니다.
- Templates템플릿, 즉 구성 파일 등과 같은 템플릿 구문을 사용하는 파일
- Handlers는 notity와 함께 사용됩니다. 특정 조건에 의해 트리거된 작업은 조건이 충족될 때만 실행되고, 그렇지 않으면 실행되지 않습니다.
- Tags 태그는 실행될 특정 작업을 지정합니다. 플레이북의 코드 일부를 선택하고 실행하는 데 사용됩니다.
3. 플레이북 구문(yaml)
- 플레이북은 yaml 구문 형식을 사용하며 접미사는 yaml 또는 yml일 수 있습니다.
- YAML( /ˈjæməl/ )은 XML, C 언어, Python, Perl 및 전자 메일 형식인 RFC2822를 포함한 많은 다른 언어를 참조합니다. Clark Evans는 2001년 5월에 이 언어를 처음 게시했으며 Ingy döt Net 및 Oren Ben-Kiki는 다음과 같습니다. 또한 이 언어의 공동 디자이너이기도 합니다.
- YAML 형식은 JSON과 유사한 파일 형식입니다. 파일 구성 작성에는 YAML이 사용되며, 개발 및 디자인에는 JSON이 주로 사용됩니다.
1) YAML 소개
1. YAML 형식은 다음과 같습니다
- 파일의 첫 번째 줄은 YAML 파일의 시작을 나타내는 "---"(하이픈 3개)로 시작해야 합니다.
- 같은 줄에서 # 뒤의 내용은 쉘, 파이썬, 루비와 유사한 주석을 나타냅니다.
- YAML의 목록 요소는 "-"로 시작하고 뒤에 공백이 옵니다. 다음은 요소 콘텐츠입니다.
- 동일 목록의 요소는 동일한 들여쓰기를 유지해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 오류로 처리됩니다.
- 호스트, 변수, 역할, 작업 등의 플레이 객체는 키 값을 ":"으로 구분하여 표현하며, ":" 뒤에는 공백을 추가해야 합니다.
2. Playbooks yaml 구성 파일 설명
Hosts:运行指定任务的目标主机 remoute_user:在远程主机上执行任务的用户; sudo_user: tasks:任务列表 tasks的具体格式: tasks: - name: TASK_NAME module: arguments notify: HANDLER_NAME handlers: - name: HANDLER_NAME module: arguments ##模块,模块参数: 格式如下: (1)action: module arguments (2) module: arguments 注意:shell和command模块后直接加命令,而不是key=value类的参数列表 handlers:任务,在特定条件下触发;接受到其他任务的通知时被触发;
3. 예시
--- - hosts: web remote_user: root tasks: - name: install nginx##安装模块,需要在被控主机里加上nginx的源 yum: name=nginx state=present - name: copy nginx.conf##复制nginx的配置文件过去,需要在本机的/tmp目录下编辑nginx.conf copy: src=/tmp/nginx.conf dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf backup=yes notify: reload#当nginx.conf发生改变时,通知给相应的handlers tags: reloadnginx#打标签 - name: start nginx service#服务启动模块 service: name=nginx state=started tags: startnginx#打标签 handlers: - name: reload service: name=nginx state=restarted
2) 변수 변수
변수 변수에는 네 가지 정의 방법이 있습니다.
1. Facts: 직접 호출할 수 있습니다.
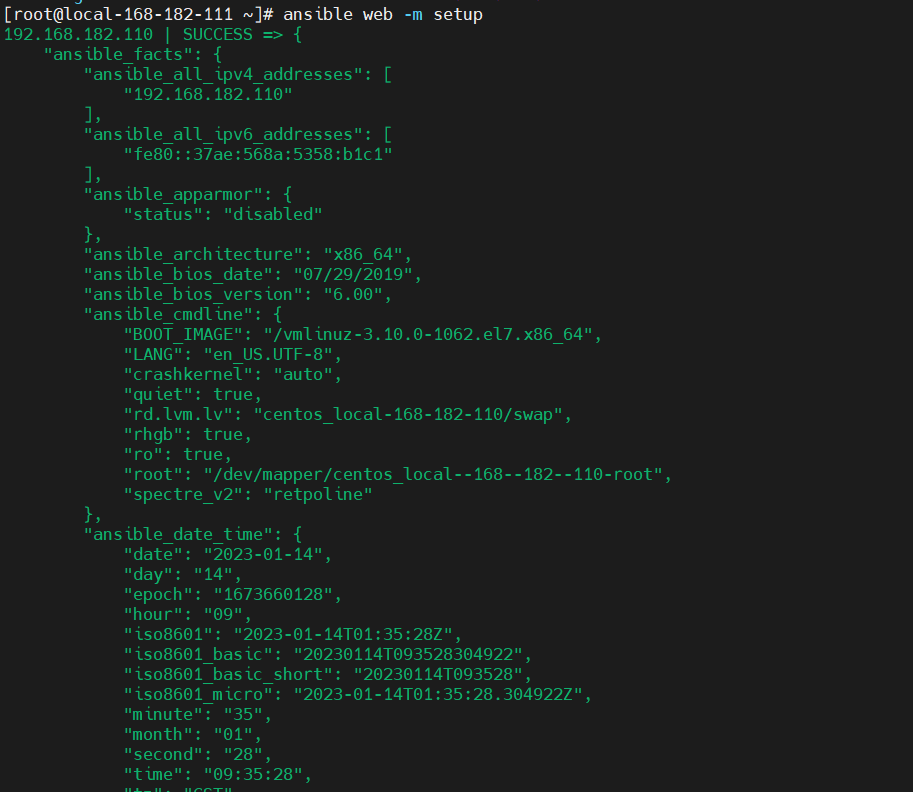
Ansible에는 설정 모듈이 있습니다. 이 모듈은 주로 노드 자체의 시스템 정보, BIOS 정보, 네트워크를 통해 구현됩니다. , 하드 디스크 및 기타 정보. 여기의 변수는 setup 모듈을 사용하여 사실 구성 요소를 직접 호출한 다음 이를 스크립트에 직접 넣어 호출할 수도 있습니다.
ansible web -m setup
常用的几个参数:
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses # ipv4的所有地址 ansible_all_ipv6_addresses # ipv6的所有地址 ansible_date_time # 获取到控制节点时间 ansible_default_ipv4 # 默认的ipv4地址 ansible_distribution # 系统 ansible_distribution_major_version # 系统的大版本 ansible_distribution_version # 系统的版本号 ansible_domain #系统所在的域 ansible_env #系统的环境变量 ansible_hostname #系统的主机名 ansible_fqdn #系统的全名 ansible_machine #系统的架构 ansible_memory_mb #系统的内存信息 ansible_os_family # 系统的家族 ansible_pkg_mgr # 系统的包管理工具 ansible_processor_cores #系统的cpu的核数(每颗) ansible_processor_count #系统cpu的颗数 ansible_processor_vcpus #系统cpu的总个数=cpu的颗数*CPU的核数 ansible_python # 系统上的python
搜索
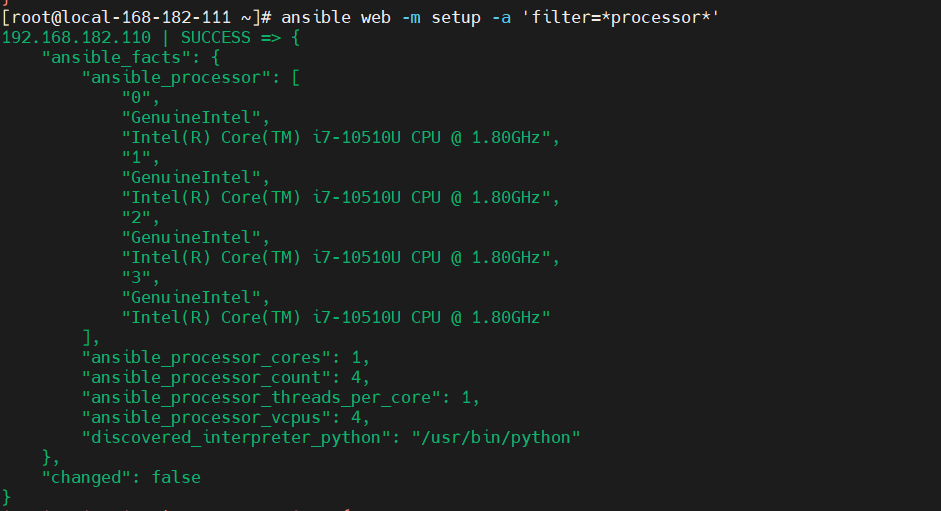
ansible web -m setup -a 'filter=*processor*'
2、用户自定义变量
自定义变量有两种方式
- 通过命令行传入
ansible-playbook命令行中的 -e VARS,--extra-vars VARS,这样就可以直接把自定义的变量传入
使用playbook定义变量,实例如下:
---
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install {{ rpmname }}
yum: name={{ rpmname }} state=present
- name: copy {{ rpmname }}.conf
copy: src=/tmp/{{ rpmname }}.conf dest=/etc/{{ rpmname }}/{{ rpmname }}.conf backup=yes
notify: reload
tags: reload{{ rpmname }}
- name: start {{ rpmname }} service
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=started
tags: start{{ rpmname }}
handlers:
- name: reload
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=restarted使用:
ansible-playbook nginx.yml -e rpmname=keepalived ansible-playbook nginx.yml --extra-vars rpmname=keepalived
- 在playbook中定义变量
##在playbook中定义变量如下: vars: - var1: value1 - var2: value2
使用:
---
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
vars:
- rpmname: keepalived
tasks:
- name: install {{ rpmname }}
yum: name={{ rpmname }} state=present
- name: copy {{ rpmname }}.conf
copy: src=/tmp/{{ rpmname }}.conf dest=/etc/{{ rpmname }}/{{ rpmname }}.conf backup=yes
notify: reload
tags: reload{{ rpmname }}
- name: start {{ rpmname }} service
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=started
tags: start{{ rpmname }}
handlers:
- name: reload
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=restarted3、通过roles传递变量
下面介绍roles会使用roles传递变量,小伙伴可以翻到下面看详解讲解。
4、 Host Inventory
可以在主机清单中定义,方法如下:
#向不同的主机传递不同的变量 IP/HOSTNAME varaiable=value var2=value2 #向组中的主机传递相同的变量 [groupname:vars] variable=value
3)流程控制
1、用when 来表示的条件判断
- hosts: web remote_user: root#代表用root用户执行,默认是root,可以省略 tasks: - name: createfile copy: content="test3" dest=/opt/p1.yml when: a=='3' - name: createfile copy: content="test4" dest=/opt/p1.yml when: a=='4'
如果a"3",就将“test3”,写入到web组下被管控机的/opt/p1.yml中,
如果a"4",就将“test4”,写入到web组下被管控机的/opt/p1.yml中。
执行
# 语法校验 ansible-playbook--syntax-check p1.yml #执行 ansible-playbook -e 'a="3"' p1.yml
2、标签(只执行配置文件中的一个任务)
- hosts: web tasks: - name: installnginx yum: name=nginx - name: copyfile copy: src=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf tags: copyfile - name: start service: name=nginx static=restarted
执行
# 语法校验 ansible-playbook--syntax-check p2.yml #执行 ansible-playbook -t copyfile p2.yml
3、循环 with_items
创建三个用户
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: createruser
user: name={{ item }}
with_items:
- shy1
- shy2
- shy3
- name: creategroup
group: name={{ item }}
with_items:
- group1
- group2
- group3 执行
#语法校验 ansible-playbook--syntax-check p3.yml #执行 ansible-playbook p3.yml
4、循环嵌套(字典)
用户shy1的属组是group1,用户shy2的属组是group2,用户shy3的属组是group3
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: creategroup
group: name={{item}}
with_items:
- group3
- group4
- group5
- name: createuser
user: name={{item.user}} group={{item.group}}
with_items:
- {'user': shy3,'group': group3}
- {'user': shy4,'group': group4}
- {'user': shy5,'group': group5}执行
#语法校验 ansible-playbook--syntax-check p4.yml #执行 ansible-playbook p4.yml
4)模板 templates
- 模板是一个文本文件,嵌套有脚本(使用模板编程语言编写)
- Jinja2是python的一种模板语言,以Django的模板语言为原本
该模板支持:
字符串:使用单引号或双引号;
数字:整数,浮点数;
列表:[item1, item2, ...]
元组:(item1, item2, ...)
字典:{key1:value1, key2:value2, ...}
布尔型:true/false
算术运算:
+, -, *, /, //, %, **
比较操作:
==, !=, >, >=, <, <=
逻辑运算:
and, or, not- 通常模板都是通过引用变量来运用的
【示例】
1、定义模板
usernginx; #设置nginx服务的系统使用用户
worker_processes{{ ansible_processor_vcpus }}; #工作进程数
error_log/var/log/nginx/error.log warn; #nginx的错误日志
pid/var/run/nginx.pid; #nginx启动时候的pid
events {
worker_connections1024; #每个进程允许的最大连接数
}
http { #http请求配置,一个http可以包含多个server
#定义 Content-Type
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_typeapplication/octet-stream;
#日志格式 此处main与access_log中的main对应
#$remote_addr:客户端地址
#$remote_user:http客户端请求nginx认证的用户名,默认不开启认证模块,不会记录
#$timelocal:nginx的时间
#$request:请求method + 路由 + http协议版本
#status:http reponse 状态码
#body_bytes_sent:response body的大小
#$http_referer:referer头信息参数,表示上级页面
#$http_user_agent:user-agent头信息参数,客户端信息
#$http_x_forwarded_for:x-forwarded-for头信息参数
log_formatmain'$http_user_agent' '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#访问日志,后面的main表示使用log_format中的main格式记录到access.log中
access_log/var/log/nginx/access.logmain;
#nginx的一大优势,高效率文件传输
sendfileon;
#tcp_nopush on;
#客户端与服务端的超时时间,单位秒
keepalive_timeout65;
#gzipon;
server { #http服务,一个server可以配置多个location
listen {{ nginxport }}; #服务监听端口
server_namelocalhost; #主机名、域名
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log/var/log/nginx/host.access.logmain;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #页面存放目录
indexindex.html index.htm; #默认页面
}
#error_page404/404.html;
# 将500 502 503 504的错误页面重定向到 /50x.html
error_page 500 502 503 504/50x.html;
location = /50x.html { #匹配error_page指定的页面路径
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #页面存放的目录
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
#proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
#root html;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#fastcgi_indexindex.php;
#fastcgi_paramSCRIPT_FILENAME/scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
#includefastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
#denyall;
#}
}
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}2、定义yaml编排
---
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
vars:
- rpmname: nginx
- nginxport: 8088
tasks:
- name: install {{ rpmname }}
yum: name={{ rpmname }} state=present
- name: copy {{ rpmname }}.conf
copy: src=/tmp/{{ rpmname }}.conf dest=/etc/{{ rpmname }}/{{ rpmname }}.conf backup=yes
notify: reload
tags: reload{{ rpmname }}
- name: start {{ rpmname }} service
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=started
tags: start{{ rpmname }}
handlers:
- name: reload
service: name={{ rpmname }} state=restarted使用
##使用reloadnginx标签,重新加载剧本
copy与template的区别
- copy模块不替代参数,template模块替代参数
- template的参数几乎与copy的参数完全相同
5)handlers(触发事件)
notify:触发 handlers:触发的动作
使用上场景:修改配置文件时
【示例】 正常情况时handlers是不会执行的
- hosts: web tasks: - name: installredis yum: name=redis - name: copyfile template: src=redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf tags: copyfile notify: restart - name: start service: name=redis state=started handlers: - name: restart service: name=redis
执行
ansible-playbook -t copyfile p6.yml
6)roles
1、roles介绍与优势
一般情况下将roles写在/etc/ansible/roles中,也可以写在其他任意位置(写在其他位置要自己手动建立一个roles文件夹)
- 对于以上所有方式有个缺点就是无法实现同时部署web、database、keepalived等不同服务或者不同服务器组合不同的应用就需要写多个yaml文件,很难实现灵活的调用
- roles用于层次性,结构化地组织playbook。roles能够根据层次结果自动装载变量文件、tasks以及handlers等。
- 要使用roles只需要在playbook中使用include指令即可。
- 简单来讲,roles就是通过分别将变量(vars)、文件(files)、任务(tasks)、模块(modules)以及处理器(handlers)放置于单独的目录中,并且可以便捷的include它们地一种机制。
- 角色一般用于基于主机构建服务的场景中,但是也可以用于构建守护进程等场景中。4
2、目录结构
创建目录
mkdir -pv ./{nginx,mysql,httpd}/{files,templates,vars,tasks,handlers,meta,default}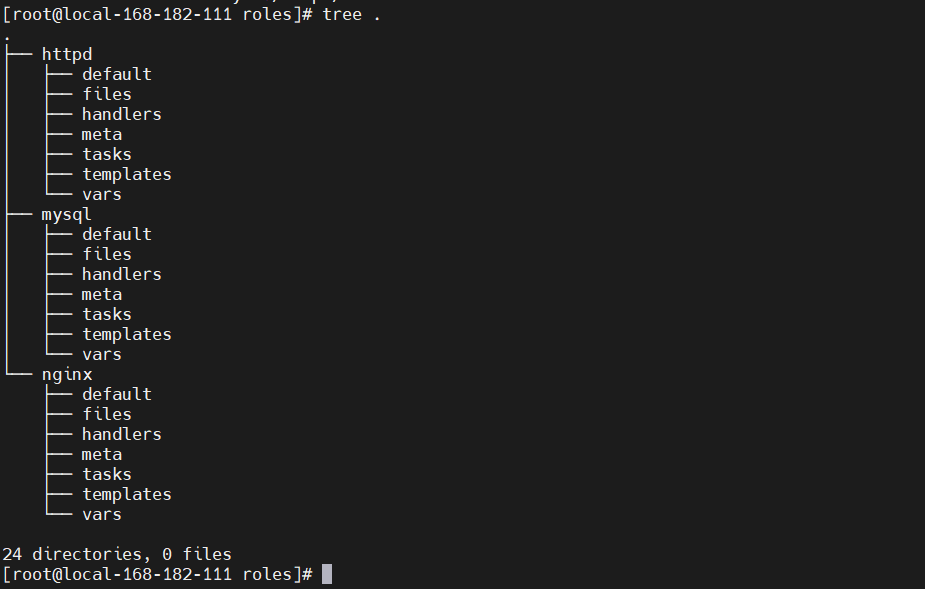
- roles/
- mysql/:mysql服务的yml文件
- httpd/:apached服务的yml文件
- nginx/:nginx服务的yml文件
- files/:存储由copy或者script等模块调用的文件或者脚本;
- tasks/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各个task;其他文件需要由main.yml进行包含调用;
- handlers/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各个handler;其他文件需要由main.yml进行包含调用;
- vars/:此目录至少应该有一个名为main,yml的文件,用于定义各个variable;其他的文件需要由main.yml进行包含调用;
- templates/:存储由templates模块调用的模板文件;
- meta/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,定义当前角色的特殊设定以及依赖关系,其他文件需要由main.yml进行包含调用;
- default/:此目录至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于设定默认变量;
3、实战操作
【1】创建目录
mkdir -pv ./{nginx,mysql,httpd}/{files,templates,vars,tasks,handlers,meta,default}【2】定义配置文件
先下载nginx rpm部署包
# 下载地址:http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/x86_64/RPMS/ wget http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/x86_64/RPMS/nginx-1.18.0-1.el7.ngx.x86_64.rpm -O nginx/files/nginx-1.18.0-1.el7.ngx.x86_64.rpm
- nginx/tasks/main.yml
- name: cp copy: src=nginx-1.18.0-1.el7.ngx.x86_64.rpm dest=/tmp/nginx-1.18.0-1.el7.ngx.x86_64.rpm - name: install yum: name=/tmp/nginx-1.18.0-1.el7.ngx.x86_64.rpm state=latest - name: conf template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf tags: nginxconf notify: new conf to reload - name: start service service: name=nginx state=started enabled=true
- nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
usernginx; #设置nginx服务的系统使用用户
worker_processes{{ ansible_processor_vcpus }}; #工作进程数
error_log/var/log/nginx/error.log warn; #nginx的错误日志
pid/var/run/nginx.pid; #nginx启动时候的pid
events {
worker_connections1024; #每个进程允许的最大连接数
}
http { #http请求配置,一个http可以包含多个server
#定义 Content-Type
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_typeapplication/octet-stream;
#日志格式 此处main与access_log中的main对应
#$remote_addr:客户端地址
#$remote_user:http客户端请求nginx认证的用户名,默认不开启认证模块,不会记录
#$timelocal:nginx的时间
#$request:请求method + 路由 + http协议版本
#status:http reponse 状态码
#body_bytes_sent:response body的大小
#$http_referer:referer头信息参数,表示上级页面
#$http_user_agent:user-agent头信息参数,客户端信息
#$http_x_forwarded_for:x-forwarded-for头信息参数
log_formatmain'$http_user_agent' '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#访问日志,后面的main表示使用log_format中的main格式记录到access.log中
access_log/var/log/nginx/access.logmain;
#nginx的一大优势,高效率文件传输
sendfileon;
#tcp_nopush on;
#客户端与服务端的超时时间,单位秒
keepalive_timeout65;
#gzipon;
server { #http服务,一个server可以配置多个location
listen {{ nginxport }}; #服务监听端口
server_namelocalhost; #主机名、域名
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log/var/log/nginx/host.access.logmain;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #页面存放目录
indexindex.html index.htm; #默认页面
}
#error_page404/404.html;
# 将500 502 503 504的错误页面重定向到 /50x.html
error_page 500 502 503 504/50x.html;
location = /50x.html { #匹配error_page指定的页面路径
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #页面存放的目录
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
#proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
#root html;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
#fastcgi_indexindex.php;
#fastcgi_paramSCRIPT_FILENAME/scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
#includefastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
#denyall;
#}
}
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}- nginx/vars/main.yml
nginxport: 9999
- nginx/handlers/main.yml
- name: new conf to reload service: name=nginx state=restarted
- 定义剧本文件(roles.yml)
- hosts: web remote_user: root roles: - nginx
最后的目录结构如下:
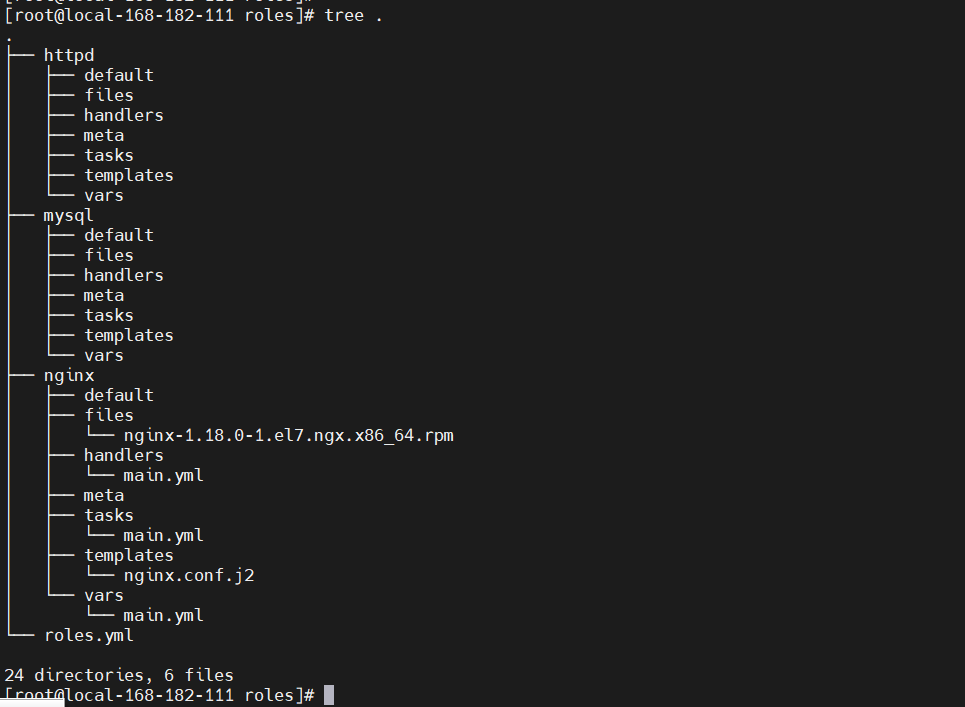
执行
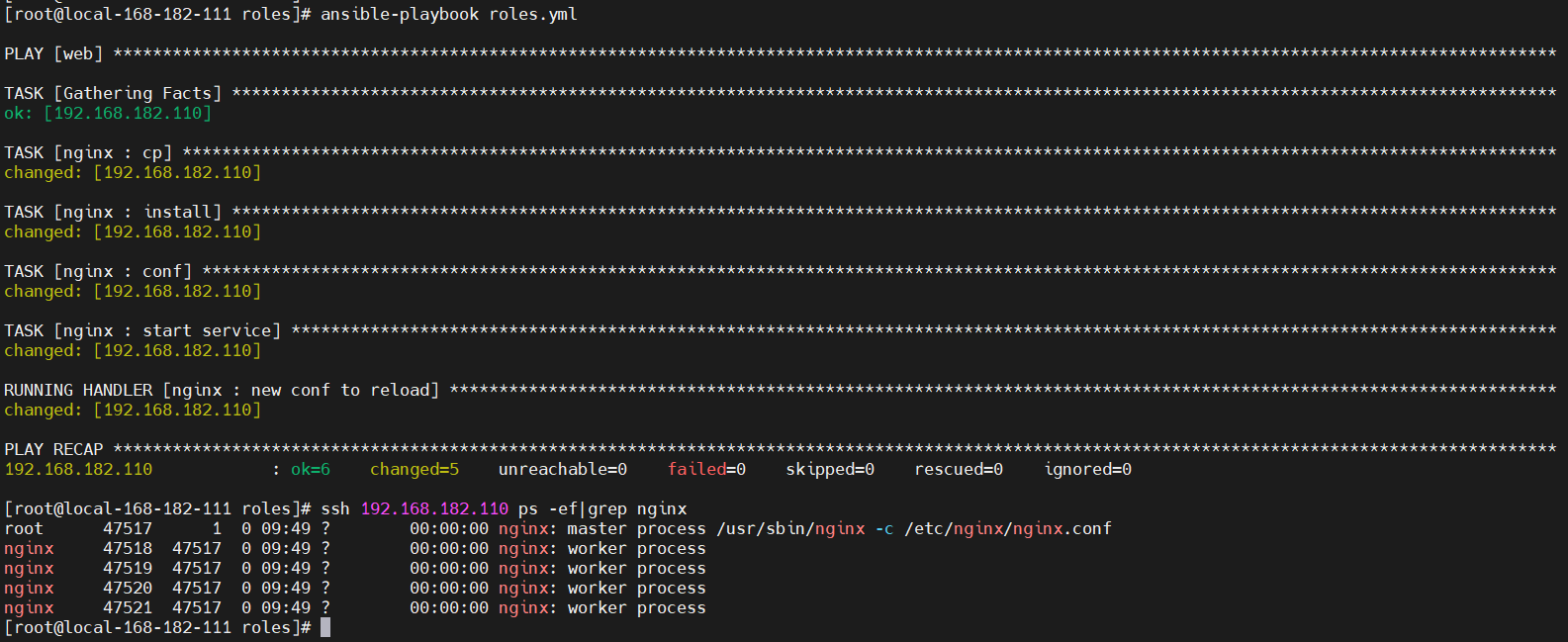
ansible-playbook roles.yml
위 내용은 Ansible Playbook 설명 및 실제 작동의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

