Springboot가 Redisson을 기반으로 Redis 분산 재진입 잠금 소스 코드 분석을 구현하는 방법
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB앞으로
- 2023-06-02 23:21:421236검색
1. 소개
우리는 분산 잠금을 구현하기 위해 Redis를 사용하고 있으며 처음에는 일반적으로 SET 리소스 이름 anystring NX EX max-lock-time을 사용합니다. 잠금을 해제하려면 Lua 스크립트를 사용하여 원자성을 보장하세요. 이 수동 구현은 더 까다롭습니다. 또한 Redis 공식 웹사이트에는 Java 버전이 이를 구현하기 위해 Redisson을 사용한다고 명시되어 있습니다. 편집자님도 공식 홈페이지를 보다가 천천히 알아보시고, 클로즈업해서 기록해두셨는데요. 공식 웹사이트에서 Springboot를 소스 코드 해석에 통합하는 것까지 단일 노드를 예로 들어 보겠습니다. SET resource-name anystring NX EX max-lock-time进行加锁,使用Lua脚本保证原子性进行实现释放锁。这样手动实现比较麻烦,对此Redis官网也明确说Java版使用Redisson来实现。小编也是看了官网慢慢的摸索清楚,特写此记录一下。从官网到整合Springboot到源码解读,以单节点为例。
二、为什么使用Redisson
1. 我们打开官网
redis中文官网
2. 我们可以看到官方让我们去使用其他

3. 打开官方推荐
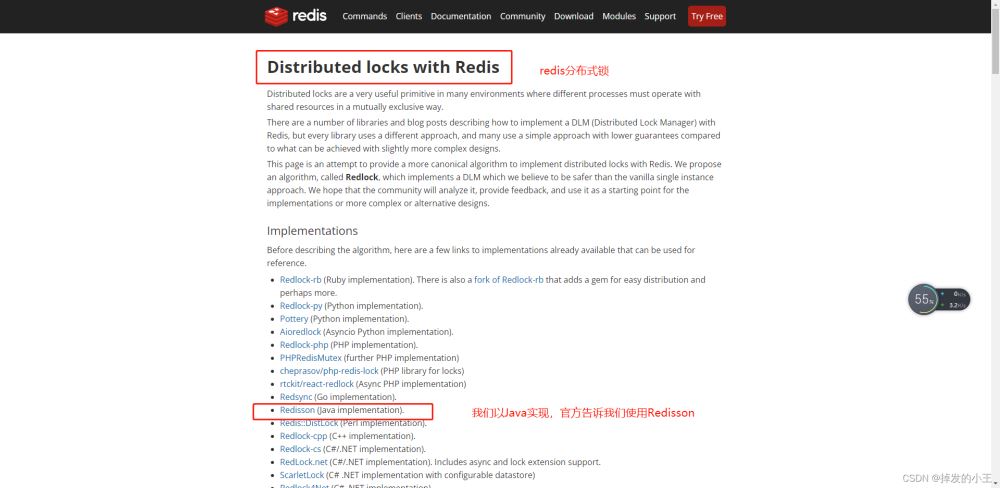
4. 找到文档
Redisson地址
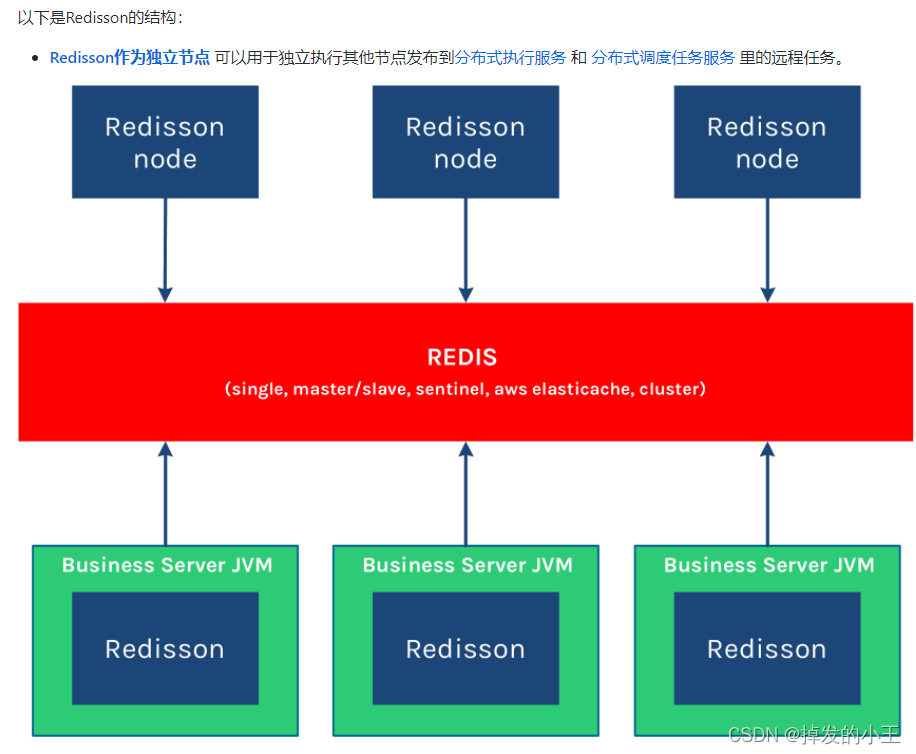
5. Redisson结构
三、Springboot整合Redisson
1. 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--redis分布式锁-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.12.0</version>
</dependency>2. 以官网为例查看如何配置
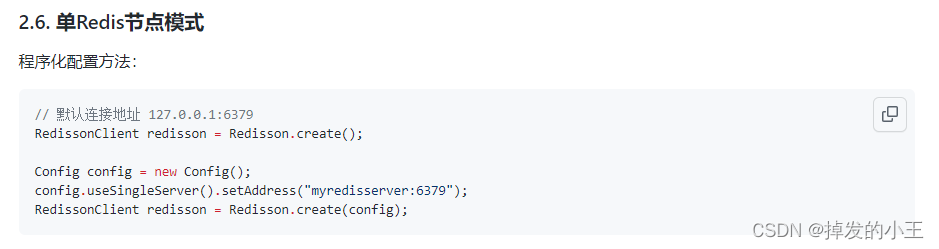
3. 编写配置类
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author wangzhenjun
* @date 2022/2/9 9:57
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedissonConfig {
/**
* 所有对redisson的使用都是通过RedissonClient来操作的
* @return
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
public RedissonClient redisson(){
// 1. 创建配置
Config config = new Config();
// 一定要加redis://
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.17.130:6379");
// 2. 根据config创建出redissonClient实例
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
}4. 官网测试加锁例子
5. 根据官网简单Controller接口编写
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
// 1.获取一把锁,只要锁名字一样,就是同一把锁
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("my-lock");
// 2. 加锁
lock.lock();// 阻塞试等待 默认加的都是30s
// 带参数情况
// lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 10s自动解锁,自动解锁时间一定要大于业务的执行时间。
try {
System.out.println("加锁成功" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 3. 解锁
System.out.println("解锁成功:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello";
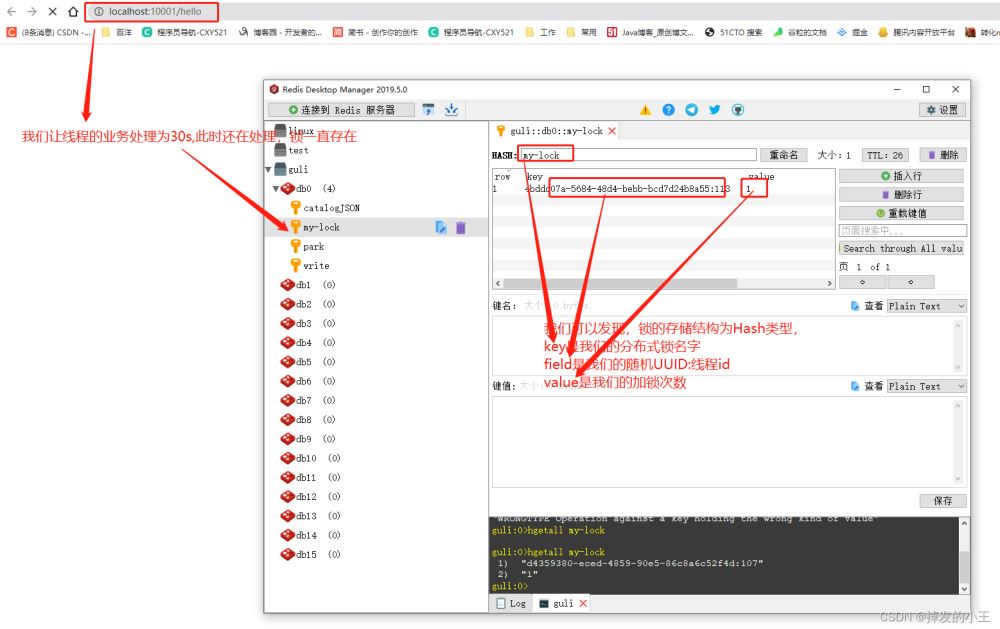
}6. 测试
四、lock.lock()源码分析
1. 打开RedissonLock实现类
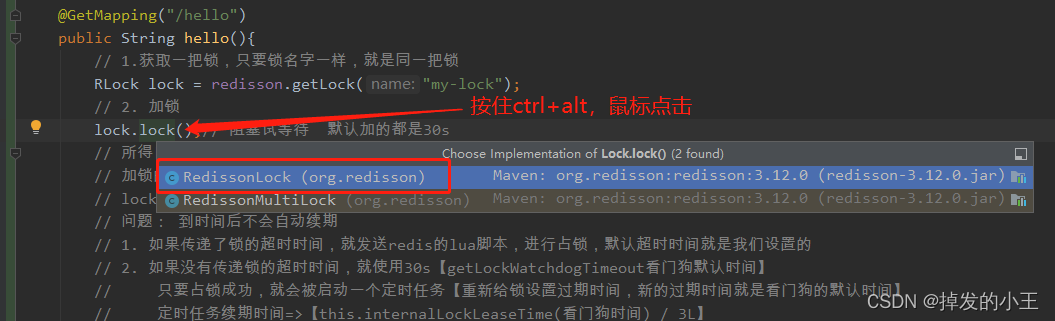
2. 找到实现方法
@Override
public void lock() {
try {
// 我们发现不穿过期时间源码默认过期时间为-1
lock(-1, null, false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}3. 按住Ctrl进去lock方法
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取线程的id,占有锁的时候field的值为UUID:线程号id
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 尝试获得锁
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired 获得锁,返回
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 这里说明获取锁失败,就通过线程id订阅这个锁
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
if (interruptibly) {
commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future);
} else {
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
}
try {
// 这里进行自旋,不断尝试获取锁
while (true) {
// 继续尝试获取锁
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired 获取成功
if (ttl == null) {
// 直接返回,挑出自旋
break;
}
// waiting for message 继续等待获得锁
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquire();
} else {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
// 取消订阅
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
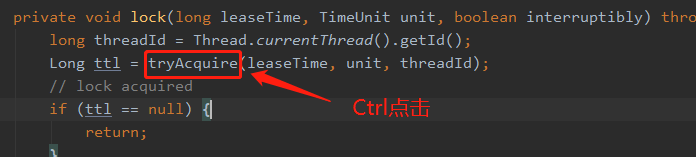
}4. 进去尝试获取锁方法
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 直接进入异步方法
return get(tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 这里进行判断如果没有设置参数leaseTime = -1
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 此方法进行获得锁,过期时间为看门狗的默认时间
// private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;看门狗默认过期时间为30s
// 加锁和过期时间要保证原子性,这个方法后面肯定调用执行了Lua脚本,我们下面在看
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 开启一个定时任务进行不断刷新过期时间
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired 获得锁
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 刷新过期时间方法,我们下一步详细说一下
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;5. 查看tryLockInnerAsync()方法
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 首先判断锁是否存在
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
// 存在则获取锁
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 然后设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// hexists查看哈希表的指定字段是否存在,存在锁并且是当前线程持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// hincrby自增一
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 锁的值大于1,说明是可重入锁,重置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 锁已存在,且不是本线程,则返回过期时间ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}6. 进入4留下的定时任务scheduleExpirationRenewal()方法
一步步往下找源码:scheduleExpirationRenewal --->renewExpiration
根据下面源码,定时任务刷新时间为:internalLockLeaseTime / 3,是看门狗的1/3,即为10s刷新一次
private void renewExpiration() {
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself
renewExpiration();
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}五、lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)源码分析
1. 打开实现类
@Override
public void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) {
try {
// 这里的过期时间为我们输入的10
lock(leaseTime, unit, false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}2. 方法lock()实现展示,同三.3源码
3. 直接来到尝试获得锁tryAcquireAsync()方法
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 这里进行判断如果没有设置参数leaseTime = -1,此时我们为10
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// 来到此方法
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 此处省略后面内容,前面以详细说明。。。。
}4. 打开tryLockInnerAsync()方法
我们不难发现和没有传过期时间的方法一样,只不过leaseTime的值变了。
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 首先判断锁是否存在
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
// 存在则获取锁
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 然后设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// hexists查看哈希表的指定字段是否存在,存在锁并且是当前线程持有锁
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
// hincrby自增一
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
// 锁的值大于1,说明是可重入锁,重置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 锁已存在,且不是本线程,则返回过期时间ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}六、lock.unlock()源码分析
1. 打开方法实现
@Override
public void unlock() {
try {
// 点击进入释放锁方法
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
// Future<Void> future = unlockAsync();
// future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// if (future.isSuccess()) {
// return;
// }
// if (future.cause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
// throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)future.cause();
// }
// throw commandExecutor.convertException(future);
}2. 打开unlockAsync()方法
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<Void>();
// 解锁方法,后面展开说
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
// 完成
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
// 取消到期续订
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
// 将这个未来标记为失败并通知所有人
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
// 状态为空,说明解锁的线程和当前锁不是同一个线程
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
result.trySuccess(null);
});
return result;
}3. 打开unlockInnerAsync()
1. 공식 웹사이트를 엽니다.
🎜redis 중국 공식 웹사이트🎜2. 공식 사이트에서 다른 사이트도 사용할 수 있도록 허용하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
🎜 🎜3. 공식 권장 사항 열기🎜
🎜3. 공식 권장 사항 열기🎜 🎜
🎜4. 문서 찾기
🎜Redisson 주소🎜🎜 🎜🎜5. Redisson 구조🎜🎜
🎜🎜5. Redisson 구조🎜🎜 🎜🎜3. Springboot는 Redisson을 통합합니다🎜
🎜🎜3. Springboot는 Redisson을 통합합니다🎜1. 종속성 가져오기 h4>protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 判断释放锁的线程和已存在锁的线程是不是同一个线程,不是返回空
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
// 释放锁后,加锁次数减一
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
// 判断剩余数量是否大于0
"if (counter > 0) then " +
// 大于0 ,则刷新过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
// 释放锁,删除key并发布锁释放的消息
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
} 2. 구성 방법을 보려면 공식 웹사이트를 예로 들어보세요
🎜 🎜
🎜3. 구성 클래스 작성
rrreee4. 공식 웹사이트 테스트 잠금 예시🎜 🎜
🎜5. 공식 웹사이트의 간단한 컨트롤러 인터페이스에 따라 작성되었습니다.
rrreee6. 테스트
🎜 🎜🎜4. Lock.lock() 소스 코드 분석🎜
🎜🎜4. Lock.lock() 소스 코드 분석🎜1 . RedissonLock 구현 클래스 열기
🎜 🎜
🎜 2. 구현 방법 찾기
rrreee3. Ctrl 키를 누른 채 잠금 방법 입력
rrreee4. 들어가서 잠금 방법을 얻으십시오.
🎜 🎜rrreee
🎜rrreee5. tryLockInnerAsync( ) 메소드 보기
rrreee6. 4에 남은 예약된 작업의 ScheduleExpirationRenewal() 메소드 입력
🎜찾기 단계별 소스 코드: ScheduleExpirationRenewal --->renewExpiration🎜🎜아래 소스 코드에 따르면 예약된 작업 새로 고침 시간은 내부LockLeaseTime / 3이며 이는 Watchdog의 1/3, 즉 1회마다 새로 고쳐집니다. 10초🎜rrreee🎜5. Lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) 소스 코드 분석🎜🎜1. 구현 클래스 열기🎜rrreee🎜2 메소드 lock()는 3.3과 동일합니다. 소스 코드 🎜🎜3. 잠금 tryAcquireAsync() 메서드를 얻으려면 직접 이동하세요. 🎜rrreee🎜4. tryLockInnerAsync() 메서드를 엽니다.🎜🎜 어렵지 않습니다. LeaseTime의 값이 변경된 점을 제외하면 만료 시간을 통과하지 않는 메서드와 동일한 것을 알 수 있습니다. 🎜rrreee🎜6. Lock.unlock() 소스 코드 분석🎜🎜1. 메소드 구현 열기🎜rrreee🎜2. unlockAsync() 메소드 열기🎜rrreee🎜3. /코드>메서드 🎜rrreee
 🎜
🎜5. 공식 웹사이트의 간단한 컨트롤러 인터페이스에 따라 작성되었습니다.
rrreee6. 테스트
🎜 🎜🎜4. Lock.lock() 소스 코드 분석🎜
🎜🎜4. Lock.lock() 소스 코드 분석🎜1 . RedissonLock 구현 클래스 열기
🎜 🎜
🎜2. 구현 방법 찾기
rrreee3. Ctrl 키를 누른 채 잠금 방법 입력
rrreee4. 들어가서 잠금 방법을 얻으십시오.
🎜 🎜rrreee
🎜rrreee5. tryLockInnerAsync( ) 메소드 보기
rrreee6. 4에 남은 예약된 작업의 ScheduleExpirationRenewal() 메소드 입력
🎜찾기 단계별 소스 코드: ScheduleExpirationRenewal --->renewExpiration🎜🎜아래 소스 코드에 따르면 예약된 작업 새로 고침 시간은 내부LockLeaseTime / 3이며 이는 Watchdog의 1/3, 즉 1회마다 새로 고쳐집니다. 10초🎜rrreee🎜5. Lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) 소스 코드 분석🎜🎜1. 구현 클래스 열기🎜rrreee🎜2 메소드lock()는 3.3과 동일합니다. 소스 코드 🎜🎜3. 잠금 tryAcquireAsync() 메서드를 얻으려면 직접 이동하세요. 🎜rrreee🎜4. tryLockInnerAsync() 메서드를 엽니다.🎜🎜 어렵지 않습니다. LeaseTime의 값이 변경된 점을 제외하면 만료 시간을 통과하지 않는 메서드와 동일한 것을 알 수 있습니다. 🎜rrreee🎜6. Lock.unlock() 소스 코드 분석🎜🎜1. 메소드 구현 열기🎜rrreee🎜2. unlockAsync() 메소드 열기🎜rrreee🎜3. /코드>메서드 🎜rrreee위 내용은 Springboot가 Redisson을 기반으로 Redis 분산 재진입 잠금 소스 코드 분석을 구현하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

