Python이 블록체인을 구축하는 방법
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB앞으로
- 2023-05-12 17:55:061819검색
Blockchain
블록체인은 컴퓨터 네트워크의 노드 간에 데이터를 공유하는 원장(분산 데이터베이스)입니다. 데이터베이스로서 블록체인은 정보를 전자 형식으로 저장합니다. 블록체인의 혁신은 (신뢰할 수 있는 제3자가 필요 없이) 데이터 기록의 보안, 신뢰성 및 신뢰성을 보장한다는 것입니다.
블록체인과 일반 데이터베이스의 차이점은 데이터 구조입니다. 블록체인은 block 형태로 정보를 수집합니다. block的方式收集信息。
block
block是一种能永久记录加密货币交易数据(或其他用途)的一种数据结构。类似于链表。一个block记录了一些火所有尚未被验证的最新交易。验证数据后,block将关闭,之后会创建一个新的block来输入和验证新的交易。因此,一旦写入,永久不能更改和删除。
block是区块链中存储和加密信息的地方block由长数字标识,其中包括先前加密块的加密交易信息和新的交易信息在创建之前,
block以及其中的信息必须由网络验证
以下是一个简单的例子:
block = {
'index': 1,
'timestamp': 1506057125.900785,
'transactions': [
{
'sender': "8527147fe1f5426f9dd545de4b27ee00",
'recipient': "a77f5cdfa2934df3954a5c7c7da5df1f",
'amount': 5,
}
],
'proof': 324984774000,
'previous_hash': "2cf24dba5fb0a30e26e83b2ac5b9e29e1b161e5c1fa7425e73043362938b9824"
}目标
区块链的目标是允许数字信息被记录和分发,但不能编辑。通过这种方式,区块链成为了不可变分类账或无法更改、删除和销毁的交易记录的基础。
去中心化
想象一下,一家公司拥有10000台服务器,用于维护一个包含所有客户信息的数据库。公司的所有服务器都在一个仓库中,可以完全控制每台服务器。这就提供了单点故障。如果那个地方停电了怎么办?如果他的网络连接被切断了怎么办?在任何情况下,数据都会丢失或损坏。
构建
区块链类
我们将创建一个BlockChain类,构造函数创建一个空列表来存储区块链,再创建一个空列表来存储交易。创建block_chain.py
# block_chain.py
class Blockchain:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.chain = []
self.current_transactions = []
def new_block(self):
# Creates a new Block and adds it to the chain
pass
def new_transaction(self):
# Adds a new transaction to the list of transactions
pass
@staticmethod
def hash(block):
# Hashes a Block
pass
@property
def last_block(self):
# Returns the last Block in the chain
pass添加交易
我们需要一种将交易添加到区块的方法。new_transaction负责这个
class Blockchain(object):
...
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount) -> int:
self.current_transactions.append({
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
})
return self.last_block['index'] + 1在 new_transaction 将交易添加到列表后,它返回交易将被添加到的块的索引——下一个要挖掘的块。这将在以后对提交交易的用户有用。
创建新blocks
当我们的区块链被实例化时,我们需要为它播种一个创世块——一个没有前辈的块。我们还需要向我们的创世块添加一个“证明”,这是挖掘的结果(或工作量证明)。除了在我们的构造函数中创建创世块之外,我们还将充实 new_block()、new_transaction() 和 hash() 的方法:
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
class Blockchain:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.chain = []
self.current_transactions = []
# Create the genesis block
self.new_block(previous_hash=1, proof=100)
def new_block(self, proof, previous_hash=None) -> dict:
block = {
'index': len(self.chain) + 1,
'timestamp': time(),
'transactions': self.current_transactions,
'proof': proof,
'previous_hash': previous_hash or self.hash(self.chain[-1]),
}
self.current_transactions = []
self.chain.append(block)
return block
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount) -> int:
self.current_transactions.append(
{
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
}
)
return self.last_block['index'] + 1
@property
def last_block(self) -> dict:
# Returns the last Block in the chain
return self.chain[-1]
@staticmethod
def hash(block) -> str:
block_string = json.dumps(block, sort_keys=True).encode()
return hashlib.sha256(block_string).hexdigest()到这里,我们几乎完成了代表我们的区块链。但此时,你一定想知道新区块是如何创建、锻造或开采的。
POW
工作量证明算法 (PoW) 是在区块链上创建或挖掘新块的方式,它的目标是发现一个解决问题的数字。这个数字必须很难找到但很容易被网络上的任何人验证。PoW广泛用于加密货币挖掘,用于验证交易和挖掘新代币。由于PoW,比特币和其他加密货币交易可以以安全的方式进行点对点处理,而无需受信任的第三方。
让我们实现一个类似的算法:
class Blockchain(object):
def proof_of_work(self, last_proof) -> int:
proof = 0
while self.valid_proof(last_proof, proof) is False:
proof += 1
return proof
@staticmethod
def valid_proof(last_proof, proof) -> bool:
guess = f'{last_proof}{proof}'.encode()
guess_hash = hashlib.sha256(guess).hexdigest()
return guess_hash[:4] == '0000'API
为了使区块链能够交互,我们需要一个将其置于web服务器上。这里我们是用Flask框架。
如果没有安装,需要安装flask
pip install flask
我们的服务器将在我们的区块链网络中形成单一节点,在同级目录下创建一个app.py
block은 암호화폐 거래 데이터(또는 기타 목적)를 영구적으로 기록할 수 있는 데이터 구조입니다. 연결리스트와 유사합니다. 블록은 아직 확인되지 않은 모든 최신 거래를 기록합니다. 데이터를 확인한 후 블록이 닫히고 새로운 블록이 생성되어 새로운 거래를 입력하고 확인할 수 있습니다. 따라서 한번 작성한 내용은 영구적으로 변경하거나 삭제할 수 없습니다.
블록은 정보가 블록체인
블록에 저장되고 암호화되는 곳입니다. code> 이전에 암호화된 블록의 암호화된 거래 정보와 새로운 거래 정보가 포함된 긴 숫자로 식별됩니다
블록과 그에 포함된 정보는 반드시 네트워크 검증에 의해 결정됩니다
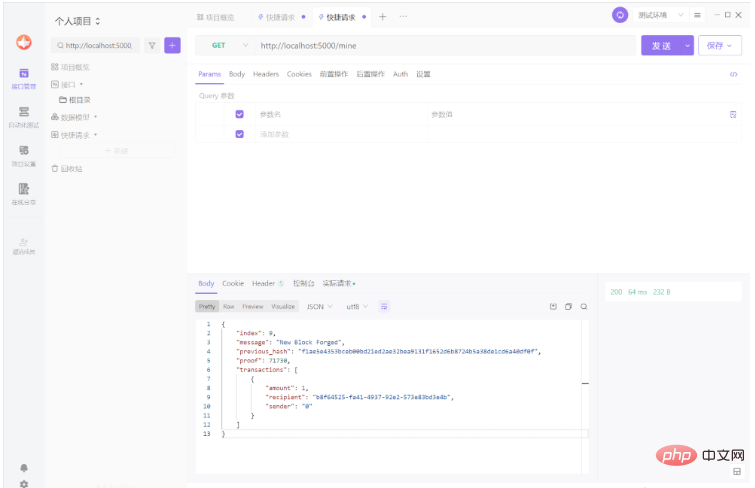 다음은 간단한 예입니다:
다음은 간단한 예입니다: from uuid import uuid4
from time import time
from textwrap import dedent
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
from block_chain import Blockchain
# 实例化应用
app = Flask(__name__)
# 创建随机节点名称
node_identifier = str(uuid4()).replace('_', '')
# 实例化block_chain类
block_chain = Blockchain()
# 创建/mine端点
@app.route('/mine', methods=['GET'])
def mine():
block_chain.new_transaction(
sender="0",
recipient=node_identifier,
amount=1,
)
last_block = block_chain.last_block
last_proof = last_block['proof']
proof = block_chain.proof_of_work(last_proof)
previous_hash = block_chain.hash(last_block)
block = block_chain.new_block(proof, previous_hash)
response = {
'message': "New Block Forged",
'index': block['index'],
'transactions': block['transactions'],
'proof': block['proof'],
'previous_hash': block['previous_hash'],
}
return jsonify(response), 200
@app.route('/transactions/new', methods=['POST'])
def new_transaction():
return "We'll add a new transaction"
@app.route('/chain', methods=['GET'])
def full_chain():
response = {
'chain': block_chain.chain,
'length': len(block_chain.chain),
}
return jsonify(response), 200
# 修改端口号
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)Goal 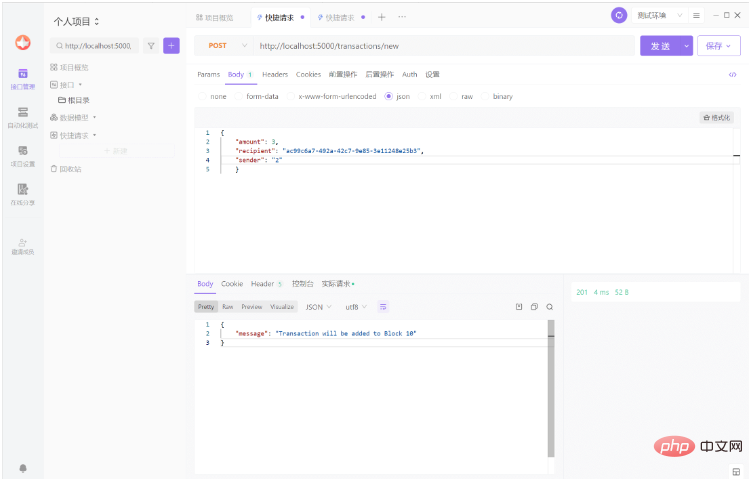
BlockChain 클래스를 생성하고, 생성자는 블록체인을 저장할 빈 목록을 만든 다음, 거래를 저장할 빈 목록을 만듭니다. block_chain.py 생성🎜...
from urllib.parse import urlparse
...
class Blockchain:
def __init__(self) -> None:
...
self.nodes = set()
...
def register_node(self, address) -> None:
parsed_url = urlparse(address)
self.nodes.add(parsed_url.netloc)🎜트랜잭션 추가🎜🎜블록에 트랜잭션을 추가할 수 있는 방법이 필요합니다. new_transaction이 이 🎜...
import requests
class Blockchain:
...
def valid_chain(self, chain):
last_block = chain[0]
current_index = 1
while current_index < len(chain):
block = chain[current_index]
print(f'{last_block}')
print(f'{block}')
print("\n-----------\n")
# Check that the hash of the block is correct
if block['previous_hash'] != self.hash(last_block):
return False
# Check that the Proof of Work is correct
if not self.valid_proof(last_block['proof'], block['proof']):
return False
last_block = block
current_index += 1
return True
def resolve_conflicts(self):
"""
This is our Consensus Algorithm, it resolves conflicts
by replacing our chain with the longest one in the network.
:return: <bool> True if our chain was replaced, False if not
"""
neighbours = self.nodes
new_chain = None
# We're only looking for chains longer than ours
max_length = len(self.chain)
# Grab and verify the chains from all the nodes in our network
for node in neighbours:
response = requests.get(f'http://{node}/chain')
if response.status_code == 200:
length = response.json()['length']
chain = response.json()['chain']
# Check if the length is longer and the chain is valid
if length > max_length and self.valid_chain(chain):
max_length = length
new_chain = chain
# Replace our chain if we discovered a new, valid chain longer than ours
if new_chain:
self.chain = new_chain
return True
return False🎜new_transaction이 목록에 트랜잭션을 추가한 후 트랜잭션이 추가될 블록의 인덱스(다음 블록)를 반환합니다. 채굴됩니다. 이는 나중에 거래를 제출한 사용자에게 유용할 것입니다. 🎜🎜새 블록 생성🎜🎜블록체인이 인스턴스화되면 이전 블록이 없는 블록인 제네시스 블록으로 시드해야 합니다. 또한 채굴(또는 작업 증명)의 결과인 "증명"을 제네시스 블록에 추가해야 합니다. 생성자에서 제네시스 블록을 생성하는 것 외에도 new_block(), new_transaction() 및 hash() 메서드를 구체화할 것입니다. 🎜@app.route('/nodes/register', methods=['POST'])
def register_nodes():
values = request.get_json()
nodes = values.get('nodes')
if nodes is None:
return "Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes", 400
for node in nodes:
blockchain.register_node(node)
response = {
'message': 'New nodes have been added',
'total_nodes': list(blockchain.nodes),
}
return jsonify(response), 201
@app.route('/nodes/resolve', methods=['GET'])
def consensus():
replaced = blockchain.resolve_conflicts()
if replaced:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain was replaced',
'new_chain': blockchain.chain
}
else:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain is authoritative',
'chain': blockchain.chain
}
return jsonify(response), 200🎜이 시점에서 블록체인 표현이 거의 완료되었습니다. 하지만 이 시점에서 여러분은 어떻게 새로운 블록이 생성되고, 위조되고, 채굴되는지 궁금할 것입니다. 🎜🎜POW🎜🎜작업 증명(PoW)은 문제를 해결하는 숫자를 찾는 것을 목표로 블록체인에서 새로운 블록을 생성하거나 채굴하는 방법입니다. 이 번호는 찾기 어렵지만 웹에서 누구나 쉽게 확인할 수 있어야 합니다. PoW는 거래를 검증하고 새로운 코인을 채굴하기 위해 암호화폐 채굴에 널리 사용됩니다. PoW 덕분에 비트코인 및 기타 암호화폐 거래는 신뢰할 수 있는 제3자 없이도 안전한 방식으로 P2P로 처리될 수 있습니다. 🎜🎜유사한 알고리즘을 구현해 보겠습니다. 🎜rrreee🎜API🎜🎜블록체인이 상호 작용하려면 이를 호스팅할 웹 서버가 필요합니다. 여기서는 Flask 프레임워크를 사용하고 있습니다. 🎜🎜설치되어 있지 않은 경우 flask를 설치해야 합니다.🎜🎜🎜pip installFlask🎜🎜🎜우리 서버는 블록체인 네트워크에서 단일 노드를 형성하고 동일한 디렉토리에 를 생성합니다. >app.py:🎜rrreee🎜그런 다음🎜🎜🎜flask run🎜🎜🎜api 소프트웨어를 통해 요청을 보냅니다(이번에는 api fox 사용):🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜🎜새 노드 등록🎜 🎜블록체인의 핵심은 분산되어야 한다는 것입니다. 네트워크에 여러 노드를 갖고 싶다면 합의 알고리즘을 사용해야 합니다. 합의 알고리즘을 구현하기 전에 노드가 네트워크의 이웃 노드를 알 수 있는 방법이 필요합니다. 네트워크의 각 노드는 네트워크에 있는 다른 노드의 레지스트리를 유지해야 합니다. 따라서 더 많은 엔드포인트가 필요합니다. 🎜rrreee🎜Conferences🎜🎜충돌은 한 노드가 다른 노드와 다른 체인을 가질 때 발생합니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 우리는 가장 긴 유효 체인이 권한이라는 규칙을 개발할 것입니다. 이 알고리즘을 사용하여 네트워크 내 노드 간의 합의를 달성합니다. 🎜...
import requests
class Blockchain:
...
def valid_chain(self, chain):
last_block = chain[0]
current_index = 1
while current_index < len(chain):
block = chain[current_index]
print(f'{last_block}')
print(f'{block}')
print("\n-----------\n")
# Check that the hash of the block is correct
if block['previous_hash'] != self.hash(last_block):
return False
# Check that the Proof of Work is correct
if not self.valid_proof(last_block['proof'], block['proof']):
return False
last_block = block
current_index += 1
return True
def resolve_conflicts(self):
"""
This is our Consensus Algorithm, it resolves conflicts
by replacing our chain with the longest one in the network.
:return: <bool> True if our chain was replaced, False if not
"""
neighbours = self.nodes
new_chain = None
# We're only looking for chains longer than ours
max_length = len(self.chain)
# Grab and verify the chains from all the nodes in our network
for node in neighbours:
response = requests.get(f'http://{node}/chain')
if response.status_code == 200:
length = response.json()['length']
chain = response.json()['chain']
# Check if the length is longer and the chain is valid
if length > max_length and self.valid_chain(chain):
max_length = length
new_chain = chain
# Replace our chain if we discovered a new, valid chain longer than ours
if new_chain:
self.chain = new_chain
return True
return False第一个方法 valid_chain() 负责通过遍历每个块并验证哈希和证明来检查链是否有效。resolve_conflicts() 是一种循环遍历我们所有相邻节点、下载它们的链并使用上述方法验证它们的方法。如果找到一个有效的链,其长度大于我们的,我们将替换我们的。
让我们将两个端点注册到我们的 API,一个用于添加相邻节点,另一个用于解决冲突:
@app.route('/nodes/register', methods=['POST'])
def register_nodes():
values = request.get_json()
nodes = values.get('nodes')
if nodes is None:
return "Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes", 400
for node in nodes:
blockchain.register_node(node)
response = {
'message': 'New nodes have been added',
'total_nodes': list(blockchain.nodes),
}
return jsonify(response), 201
@app.route('/nodes/resolve', methods=['GET'])
def consensus():
replaced = blockchain.resolve_conflicts()
if replaced:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain was replaced',
'new_chain': blockchain.chain
}
else:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain is authoritative',
'chain': blockchain.chain
}
return jsonify(response), 200在这一点上,如果你愿意,你可以拿一台不同的机器,并在你的网络上启动不同的节点。或者在同一台机器上使用不同的端口启动进程。比如创建两个端口5000和6000来进行尝试。
위 내용은 Python이 블록체인을 구축하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

