Java ThreadPoolExecutor의 거부 정책을 구현하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB앞으로
- 2023-05-08 15:34:08913검색
스레드 풀의 기본 원리
스레드 풀의 원리는 다음과 같습니다.
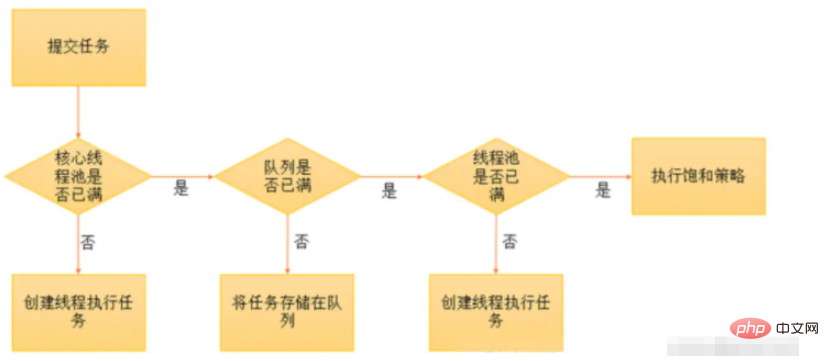
설명:
현재 실행 중인 스레드 수가 corePoolSize보다 작으면 새 스레드를 생성하여 수행합니다. 작업.
실행 중인 스레드가 corePoolSize보다 크거나 같으면 작업이 대기열에 추가됩니다.
작업 대기열이 가득 차면 비corePool에 새 스레드가 생성되어 작업을 처리합니다.
새 스레드를 생성하면 현재 실행 중인 스레드가 maximumPoolSize를 초과하게 되고 작업이 거부되며 RejectedExecutionHandler.rejectedExecution() 메서드가 호출됩니다.
스레드 풀 거부 정책
스레드 풀은 CallerRunsPolicy, AbortPolicy, DiscardPolicy, DiscardOldestPolicy
AbortPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor의 기본 거부 정책은 AbortPolicy가 직접 예외를 발생시키는 것입니다. 특정 구현은 다음과 같습니다.
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
public AbortPolicy() { }
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}설명: 이 전략은 매우 간단하고 조악하며 RejectedExecutionException 예외를 직접 발생시키고 후속 작업을 실행하지 않습니다.
예제 설명:
public class ThreadPoolTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//异步执行
for(int i=0; i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("添加第"+i+"个任务");
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new TestThread("线程"+i));
}
}
}
public class TestThread implements Runnable
{
private String name;
public TestThread(String name){
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run()
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread name:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",执行:"+name);
}
}실행 결과:
스레드 "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException의 예외: 작업 com.skywares.fw.juc.thread.TestThread@55f96302가 java.util.concurrent에서 거부되었습니다. ThreadPoolExecutor@3d4eac69[실행 중, 풀 크기 = 5, 활성 스레드 = 5, 대기 중인 작업 = 1, 완료된 작업 = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2047)
at java. util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:823)
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1369)
com.skywares.fw.juc.thread.ThreadPoolTest.main(ThreadPoolTest. java:26)
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-5, 실행: 스레드 5
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2, 실행: 스레드 1
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-4, 실행: 스레드 4
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-3, 실행: 스레드 3
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 0
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-5, 실행: 스레드 2
AbortPolicy 전략을 사용하면 7번째 태스크까지 태스크가 실행될 때 바로 오류가 보고되어 후속 비즈니스 로직이 실행되지 않는다는 것을 실행 결과를 통해 알 수 있습니다.
CallerRunsPolicy
CallerRunsPolicy는 작업이 거부된 후 거부된 작업을 실행하기 위해 실행 함수를 호출하는 상위 스레드를 사용합니다.
관련 예
public class ThreadPoolTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//异步执行
for(int i=0; i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println("添加第"+i+"个任务");
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new TestThread("线程"+i));
}
}
}실행 결과:
0번째 작업 추가
1번째 작업 추가
2번째 작업 추가
3번째 작업 추가
4번째 작업 추가
5번째 작업 추가
6번째 작업 추가
스레드 이름: main, 실행: thread 6
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-3, 실행: 스레드 3
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 0
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-4, 실행: 스레드 4
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2, 실행: 스레드 1
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-5, 실행: 스레드 5
7번째 작업 추가
8번째 작업 추가
스레드 이름: main, 실행: thread 8
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 7
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-3, 실행: 스레드 2
추가 9번째 작업
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 9
실행 결과를 보면 7번째 작업이 실행되면 스레드 풀 거부 정책으로 인해 이 작업이 메인 스레드가 실행되고 스레드 풀이 자유로워지면 계속해서 실행되는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 다른 작업을 실행합니다. 따라서 이 전략은 메인 스레드를 차단할 수 있습니다.
DiscardPolicy
이 거부 정책은 비교적 간단합니다. 스레드 풀에서 거부된 작업은 예외를 발생시키거나 실행하지 않고 직접 삭제됩니다.
Example
위 코드를 수정하고 거부 정책을 DiscardPolicy
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());실행 결과로 변경합니다.
invoke dealStock 성공실행 결과를 보면 6개의 작업만 실행되었고 나머지 작업은 포기되었습니다. DiscardOldestPolicyDiscardOldestPolicy 작업 추가를 거부하면 대기열에 처음 추가된 작업이 삭제되고 새 작업이 추가됩니다. 설명 예시goodsId: 휴대폰
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 0
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-4, 실행: 스레드 4
스레드 이름: pool-1- thread-5, 실행: 스레드 5
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-3, 실행: 스레드 3
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2, 실행: 스레드 1
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread- 1. 실행 : Thread 2
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
2,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
실행 결과:
0번째 작업 추가1번째 작업 추가
2번째 작업 추가
3번째 작업 추가
4번째 작업 추가
5번째 작업 추가
거래 호출재고 성공
goodsId: 휴대폰
스레드 이름: pool -1-thread-2, 실행: 스레드 3
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 0
스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1, 실행: 스레드 2
스레드 이름: pool-1 -thread-2, 실행: 스레드 1
自定义拒绝策略
当线程池提供的拒绝策略无法满足要求时,我们可以采用自定义的拒绝策略,只需要实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口即可
public class CustRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler
{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor)
{
new Thread(r,"线程:"+new Random().nextInt(10)).start();
}
}
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
2,
10,
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(2),
new CustRejectedExecutionHandler());执行结果:
thread name:客户线程:6,执行:线程5
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程0
thread name:客户线程:8,执行:线程4
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程3
thread name:pool-1-thread-1,执行:线程1
thread name:pool-1-thread-2,执行:线程2
从执行的结果来看,被拒绝的任务都在客户的新线程中执行。
小结
AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,后续的任务不会执行
CallerRunsPolicy:子任务执行的时间过长,可能会阻塞主线程。
DiscardPolicy:不抛异常,任务直接丢弃
DiscardOldestPolicy;丢弃最先加入队列的任务
위 내용은 Java ThreadPoolExecutor의 거부 정책을 구현하는 방법은 무엇입니까?의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

