Java FutureTask 소스코드 분석 및 사용내역
- PHPz앞으로
- 2023-04-23 23:37:051207검색
FutureTask가 무엇인지 이해하시나요?
FutureTask는 취소 가능한 비동기 계산입니다.
FutureTask는 Future의 기본 구현을 제공하며 계산을 시작 및 취소하고 계산 완료 여부를 쿼리하고 계산 결과를 얻을 수 있는 메서드를 호출할 수 있습니다. FutureTask提供了对Future的基本实现,可以调用方法去开始和取消一个计算,可以查询计算是否完成,并且获取计算结果。
FutureTask只能在计算完成后获取到计算结果,一旦计算完成,将不能重启或者取消,除非调用runAndReset方法。
FutureTask除了实现了Future接口以外,还实现了Runnable接口,因此FutureTask是可以交由线程池的Executor执行,也可以直接使用一个异步线程调用执行(futureTask.run())。
FutureTask 是如何实现的呢?
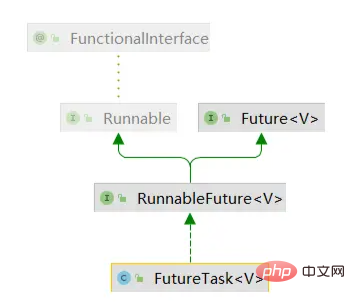
首先,我们看一下FutureTask类的继承结构,如下图,它实现的是RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture继承自Future和函数式接口Runnable,所以说FutureTask本质就是一个可运行的Future。
Future 接口约定了一些异步计算类必须要实现的功能,源码如下:
package java.util.concurrent;
public interface Future<V> {
/**
* 尝试取消任务的执行,并返回取消结果。
* 参数mayInterruptIfRunning:是否中断线程。
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
/**
* 判断任务是否被取消(正常结束之前被被取消返回true)
*/
boolean isCancelled();
/**
* 判断当前任务是否执行完毕,包括正常执行完毕、执行异常或者任务取消。
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* 获取任务执行结果,任务结束之前会阻塞。
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* 在指定时间内尝试获取执行结果。若超时则抛出超时异常TimeoutException
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}Runnable 接口我们都很熟悉,他就是一个函数式接口,我们常用其创建一个线程。
package java.lang;
?
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
? ?
? ?public abstract void run();
}FutureTask就是一个将要被执行的任务,它包含了以上接口具体的实现,FutureTask内部定义了任务的状态state和一些状态的常量,它的内部核心是一个Callable callable,我们通过构造函数可以传入callable或者是runnable,最后都会内部转为callable,因为我们需要获取异步任务的执行结果,只有通过Callable创建的线程才会返回结果。
我们可以通过此时的状态判断Future中isCancelled(),isDone()的返回结果。
以下为FutureTask源码,内含核心源码分析注释
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
/**
* 任务的运行状态
*/
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成
private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 正常
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的
private Callable<V> callable;
/**
* 返回结果
*/
private Object outcome;
private volatile Thread runner;
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
...
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW;
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW;
}
public boolean isCancelled() {
return state >= CANCELLED;
}
public boolean isDone() {
return state != NEW;
}
/*
* 取消任务实现
* 如果任务还没有启动就调用了cancel(true),任务将永远不会被执行。
* 如果任务已经启动,参数mayInterruptIfRunning将决定任务是否应该中断执行该任务的线程,以尝试中断该任务。
* 如果任务任务已经取消、已经完成或者其他原因不能取消,尝试将失败。
*/
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。并且判断时间是否超时
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成,若超时抛出超时等待异常。
*/
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
/*
* 等待获取结果
* 获取当前状态,判断是否执行完成。
* 如果任务没有执行完成,就阻塞等待完成。
*/
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
/**
* 根据状态判断返回结果还是异常
*/
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
protected void done() { }
/**
* 设置结果借助CAS确认状态是否完成状态
*/
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/**
* 设置异常,当运行完成出现异常,设置异常状态
*/
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
/*
* 执行callable获取结果,或者异常
* 判断状态是不是启动过的,如果是新建才可以执行run方法
*/
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
runner = null;
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
/**
* 重新执行
*/
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
boolean ran = false;
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
c.call(); // don't set result
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
setException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
runner = null;
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
return ran && s == NEW;
}
/*
* 处理可能取消的中断
*/
private void handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(int s) {
if (s == INTERRUPTING)
while (state == INTERRUPTING)
Thread.yield();
}
static final class WaitNode {
volatile Thread thread;
volatile WaitNode next;
WaitNode() { thread = Thread.currentThread(); }
}
/**
* 移除并唤醒所有等待线程,执行done,置空callable
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
/**
* 等待完成
* 首先判断是否超时
* 处理中断的,然后处理异常状态的,处理完成的...
*/
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
/**
* 去除等待
*/
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null;
retry:
for (;;) { // restart on removeWaiter race
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
s = q.next;
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) {
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) // check for race
continue retry;
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q, s))
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long runnerOffset;
private static final long waitersOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = FutureTask.class;
stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("state"));
runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));
waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}FutureTask 运行流程
一般来说,我们可以认为FutureTask具有以下三种状态:
未启动:新建的FutureTask,在run()没执行之前,FutureTask处于未启动状态。
private static final int NEW = 0; // 新建
已启动:FutureTask对象的run方法启动并执行的过程中,FutureTask处于已启动状态。
已完成:FutureTask正常执行结束,或者FutureTask
계산이 완료되면 runAndReset 메서드를 호출하지 않는 한 다시 시작하거나 취소할 수 없습니다.
Future 인터페이스 구현 외에도 FutureTask는 Runnable 인터페이스도 구현하므로 FutureTask는 스레드 풀의 Executor에 의해 실행되거나 비동기 스레드 호출을 사용하여 직접 실행될 수 있습니다( futureTask.run( )).
먼저 아래와 같이 FutureTask 클래스의 상속 구조를 살펴보겠습니다. 이는 RunnableFuture 인터페이스와 RunnableFuture를 구현합니다. Future 및 Functional 인터페이스 Runnable에서 상속되므로 FutureTask는 본질적으로 실행 가능한 Future입니다.
 🎜🎜🎜Future 인터페이스 규칙 우리 모두는
🎜🎜🎜Future 인터페이스 규칙 우리 모두는 Runnable 인터페이스에 익숙합니다. 이는 기능적 인터페이스이며 스레드를 생성하는 데 자주 사용됩니다. 🎜private static final int COMPLETING = 1; // 完成 private static final int NORMAL = 2; // 完成后正常设置结果 private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; // 完成后异常设置异常 private static final int CANCELLED = 4; // 执行取消 private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; // 中断中 private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; // 中断的🎜FutureTask는 실행될 작업입니다. 여기에는 위 인터페이스의 특정 구현이 포함되어 있습니다. FutureTask는 내부적으로 작업 상태와 일부 상태 상수를 정의하며 생성자를 통해 전달할 수 있습니다. callable 또는 runnable을 입력하면 결국 내부적으로 callable로 변환됩니다. 왜냐하면 비동기 작업의 실행 결과를 얻어야 하고 Callable을 통해 생성된 스레드만 결과를 반환하기 때문입니다. 🎜🎜Future에서
isCancelled()와 isDone()의 반환 결과를 현재 상태를 통해 판단할 수 있습니다. 🎜🎜🎜다음은 핵심 소스 코드 분석 주석을 포함한 FutureTask 소스 코드입니다🎜🎜FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
new Thread(task).stat();
Integer result = task.get();🎜FutureTask 실행 프로세스🎜🎜🎜일반적으로 FutureTask를 다음 세 가지 상태로 생각할 수 있습니다. 🎜🎜🎜🎜시작되지 않음: 🎜 New FutureTask, run()이 실행되기 전에는 FutureTask가 시작되지 않습니다. 🎜FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return sum();
}
});
Executors.newCachedThreadPool().submit(task);
Integer result = task.get();🎜🎜Started🎜: FutureTask 객체의 run 메소드가 시작되어 실행되면 FutureTask가 시작된 상태가 됩니다. 🎜🎜🎜Completed: 🎜FutureTask가 정상적으로 종료되거나, FutureTask의 실행이 취소되거나(FutureTask 개체의 Cancel 메서드), FutureTask 개체의 run 메서드가 예외를 발생시키고 중단된 상태로 종료됩니다. 🎜rrreee🎜FutureTask 사용🎜🎜🎜하나 사용(새 스레드 호출 직접 생성): 🎜🎜rrreee🎜🎜두 개 사용(스레드 풀과 함께 사용)🎜🎜rrreee위 내용은 Java FutureTask 소스코드 분석 및 사용내역의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
관련 기사
더보기- MySQL에 연결할 때 Android 앱에서 \'java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\'가 발생하는 이유는 무엇입니까?
- Joda Time을 사용하여 Java에서 두 날짜의 차이를 계산하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- PEM 인코딩 파일에서 RSA 개인 키를 추출하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- AbstractTableModel 및 SwingWorker를 사용하여 스윙 테이블에 데이터베이스 데이터를 효율적으로 표시하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- Spring MVC 애플리케이션에서 UTF-8 인코딩 문제를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?

