클릭을 사용하여 완벽한 Python 명령줄 프로그램 만들기
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB앞으로
- 2023-04-18 14:55:031343검색

Python 프로그래머의 주요 업무는 명령줄 프로그램, 즉 터미널에서 직접 실행되는 스크립트를 작성하는 것입니다. 프로젝트 규모가 커짐에 따라 매번 소스 코드를 수정하는 대신 다양한 매개변수를 제공하여 다양한 문제를 해결할 수 있는 효과적인 명령줄 인터페이스를 만들고 싶습니다.
이 목표를 달성하기 위해 네 가지 원칙을 요약했는데, 이것이 모든 사람에게 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.
- 명령줄 매개변수는 기본값을 제공해야 합니다.
- 누락된 매개변수, 잘못된 데이터를 포함하여 가능한 모든 매개변수 오류를 처리합니다. 유형, 찾을 수 없음 파일 등
- 매개변수의 의미와 설정 방법을 설명하는 좋은 문서 작성
- 진행률 표시줄을 사용하여 장기 실행 작업 표시
간단한 예
이러한 규칙을 적용해 봅시다 구체적인 사례: 메시지 암호화 및 해독을 위해 Caesar 암호 스크립트를 사용합니다.
다음과 같이 암호화 함수를 작성한다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 이제 메시지를 암호화하고 해독하는 스크립트를 만들어 보겠습니다.
스크립트를 통해 사용자는 모드(암호화 또는 암호 해독), 키를 선택할 수 있습니다. 전자의 기본값은 암호화이고, 후자의 기본값은 1입니다. 이는 모두 명령줄 매개변수를 통해 달성됩니다.
def encrypt(plaintext, key):
cyphertext = ''
for character in plaintext:
if character.isalpha():
number = ord(character)
number += key
if character.isupper():
if number > ord('Z'):
number -= 26
elif number < ord('A'):
number += 26
elif character.islower():
if number > ord('z'):
number -= 26
elif number < ord('a'):
number += 26
character = chr(number)
cyphertext += character
return cyphertext초보자용 방법: sys.argv
스크립트는 먼저 명령줄 매개변수의 값을 가져와야 합니다. 가장 간단한 sys.argv를 사용하여 먼저 구현해 보겠습니다.
sys.argv는 스크립트를 실행할 때 사용자가 입력한 모든 매개변수(스크립트 이름 자체 포함)가 포함된 목록입니다.
터미널에 다음 명령을 입력하세요.
> python caesar_script.py --key 23 --decrypt my secret message pb vhfuhw phvvdjh
sys.argv 목록에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
['caesar_script.py', '--key', '23', '--decrypt', 'my', 'secret', 'message']
매개변수 값을 얻으려면 매개변수 목록을 순회하여 '--key'를 찾아야 합니다. (또는 '-k')를 사용하여 키 값을 얻고 '--decrypt' 가져오기 모드를 찾습니다.
import sys
from caesar_encryption import encryp
def caesar():
key = 1
is_error = False
for index, arg in enumerate(sys.argv):
if arg in ['--key', '-k'] and len(sys.argv) > index + 1:
key = int(sys.argv[index + 1])
del sys.argv[index]
del sys.argv[index]
break
for index, arg in enumerate(sys.argv):
if arg in ['--encrypt', '-e']:
del sys.argv[index]
break
if arg in ['--decrypt', '-d']:
key = -key
del sys.argv[index]
break
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
is_error = True
else:
for arg in sys.argv:
if arg.startswith('-'):
is_error = True
if is_error:
print(f'Usage: python {sys.argv[0]} [ --key <key> ] [ --encrypt|decrypt ] <text>')
else:
print(encrypt(' '.join(sys.argv[1:]), key))
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar()코드는 처음에 제시한 원칙을 따릅니다.
기본 키 값과 기본 모드가 있습니다.
기본 오류 처리(제공된 입력 텍스트가 없거나 알 수 없는 매개변수)
매개변수 오류가 있거나 매개변수가 없는 경우 스크립트를 호출할 때 간결한 프롬프트 메시지를 인쇄하세요
> python caesar_script_using_sys_argv.py Usage: python caesar.py [ --key <key> ] [ --encrypt|decrypt ] <text>
하지만 이 버전의 스크립트는 꽤 길고(암호화 기능을 제외한 39줄), 코드도 매우 보기 흉합니다.
명령줄 인수를 구문 분석하는 더 좋은 방법이 있나요?
Enter argparse
argparse는 명령줄 인수를 구문 분석하기 위한 Python 표준 라이브러리 모듈입니다.
argparse를 사용하여 명령줄 인수를 구문 분석하도록 스크립트를 수정하세요.
import argparse
from caesar_encryption import encrypt
def caesar():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group()
group.add_argument('-e', '--encrypt', action='store_true')
group.add_argument('-d', '--decrypt', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('text', nargs='*')
parser.add_argument('-k', '--key', type=int, default=1)
args = parser.parse_args()
text_string = ' '.join(args.text)
key = args.key
if args.decrypt:
key = -key
cyphertext = encrypt(text_string, key)
print(cyphertext)
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar()코드는 여전히 우리가 제안한 원칙을 준수하며 명령줄 인수를 수동으로 구문 분석하는 것보다 더 정확한 문서화와 대화형 오류 처리를 제공합니다.
> python caesar_script_using_argparse.py --encode My message usage: caesar_script_using_argparse.py [-h] [-e | -d] [-k KEY] [text [text ...]] caesar_script_using_argparse.py: error: unrecognized arguments: --encode > python caesar_script_using_argparse.py --help usage: caesar_script_using_argparse.py [-h] [-e | -d] [-k KEY] [text [text ...]]positional arguments: text optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit -e, --encrypt -d, --decrypt -k KEY, --key KEY
스크립트의 7~13행은 명령줄 인수를 정의하지만 그다지 우아하지는 않습니다. 너무 장황하고 절차적이므로 보다 간결하고 선언적인 방식으로 수행할 수 있습니다.
더 나은 명령줄 인터페이스를 만들려면 클릭을 사용하세요
다행히 명령줄 인터페이스를 만들기 위한 타사 라이브러리 클릭이 있습니다. 이 라이브러리는 argparse보다 더 많은 기능을 제공할 뿐만 아니라 더 아름다운 코드 스타일도 제공합니다. argparse를 click으로 바꾸고 스크립트 최적화를 계속하세요.
import click
from caesar_encryption import encrypt
@click.command()
@click.argument('text', nargs=-1)
@click.option('--decrypt/--encrypt', '-d/-e')
@click.option('--key', '-k', default=1)
def caesar(text, decrypt, key):
text_string = ' '.join(text)
if decrypt:
key = -key
cyphertext = encrypt(text_string, key)
click.echo(cyphertext)
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar()명령줄 인수와 옵션은 데코레이터에서 선언되므로 함수에 대한 인수로 직접 액세스할 수 있습니다.
위 코드를 주의 깊게 분석해 보겠습니다.
nargs는 명령줄 인수로 수신되는 값의 수를 정의합니다. 기본값은 1이며, nargs=-1은 임의 개수의 단어를 제공할 수 있도록 허용합니다.
--encrypt/--decrypt는 궁극적으로 부울 값으로 프로그램에 전달되는 상호 배타적인 옵션을 정의합니다.
click.echo는 클릭 라이브러리에서 제공하는 기본 기능입니다. 기능은 인쇄와 유사하지만 콘솔에 인쇄되는 텍스트 색상을 조정하는 등 더욱 강력한 기능을 제공합니다.
로컬 파일에서 입력 읽기
명령줄 인수로 받은 값은 암호화되는 일급 비밀 메시지이므로 사용자가 터미널에 직접 일반 텍스트를 입력하라는 요청을 받으면 보안 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
더 안전한 방법은 숨겨진 힌트를 사용하거나 로컬 파일에서 텍스트를 읽는 것입니다. 이는 긴 텍스트에 더 실용적입니다.
출력에도 동일한 아이디어가 적용됩니다. 사용자는 이를 파일에 저장하거나 터미널에서 인쇄할 수 있습니다. 계속해서 스크립트를 최적화해 보겠습니다.
import click
from caesar_encryption import encrypt
@click.command()
@click.option(
'--input_file',
type=click.File('r'),
help='File in which there is the text you want to encrypt/decrypt.'
'If not provided, a prompt will allow you to type the input text.',
)
@click.option(
'--output_file',
type=click.File('w'),
help='File in which the encrypted / decrypted text will be written.'
'If not provided, the output text will just be printed.',
)
@click.option(
'--decrypt/--encrypt',
'-d/-e',
help='Whether you want to encrypt the input text or decrypt it.'
)
@click.option(
'--key',
'-k',
default=1,
help='The numeric key to use for the caesar encryption / decryption.'
)
def caesar(input_file, output_file, decrypt, key):
if input_file:
text = input_file.read()
else:
text = click.prompt('Enter a text', hide_input=not decrypt)
if decrypt:
key = -key
cyphertext = encrypt(text, key)
if output_file:
output_file.write(cyphertext)
else:
click.echo(cyphertext)
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar()스크립트가 복잡해짐에 따라 매개변수의 기능을 자세히 설명하기 위해 매개변수 문서(click.option 데코레이터의 도움말 매개변수를 정의하여 구현)를 생성합니다.
> python caesar_script_v2.py --help Usage: caesar_script_v2.py [OPTIONS] Options: --input_file FILENAMEFile in which there is the text you want to encrypt/decrypt. If not provided, a prompt will allow you to type the input text. --output_file FILENAME File in which the encrypted/decrypted text will be written. If not provided, the output text will just be printed. -d, --decrypt / -e, --encryptWhether you want to encrypt the input text or decrypt it. -k, --key INTEGERThe numeric key to use for the caesar encryption / decryption. --help Show this message and exit.
두 개의 새로운 매개변수 input_file과 output_file이 있으며 유형은 click.File입니다. 클릭하면 올바른 모드에서 파일이 열리고 발생할 수 있는 오류를 처리합니다. 예를 들어 파일을 찾을 수 없습니다.
> python caesar_script_v2.py --decrypt --input_file wrong_file.txt Usage: caesar_script_v2.py [OPTIONS] Error: Invalid value for "--input_file": Could not open file: wrong_file.txt: No such file or directory
input_file이 제공되지 않으면 click.prompt를 사용하여 사용자가 텍스트를 직접 입력할 수 있도록 명령줄에 프롬프트 창을 만듭니다. 프롬프트는 암호화를 위해 숨겨집니다. 방법. 효과는 다음과 같습니다:
> python caesar_script_v2.py --encrypt --key 2 Enter a text: ************** yyy.ukectc.eqo
假设你是一名黑客:想要解密一个用凯撒加密过的密文,但你不知道秘钥是什么。最简单的策略就是用所有可能的秘钥调用解密函数 25 次,阅读解密结果,看看哪个是合理的。但你很聪明,而且也很懒,所以你想让整个过程自动化。确定解密后的 25 个文本哪个最可能是原始文本的方法之一,就是统计所有这些文本中的英文单词的个数。这可以使用 PyEnchant 模块实现:
import click
import enchant
from caesar_encryption import encrypt
@click.command()
@click.option(
'--input_file',
type=click.File('r'),
required=True,
)
@click.option(
'--output_file',
type=click.File('w'),
required=True,
)
def caesar_breaker(input_file, output_file):
cyphertext = input_file.read()
english_dictionnary = enchant.Dict("en_US")
max_number_of_english_words = 0
for key in range(26):
plaintext = encrypt(cyphertext, -key)
number_of_english_words = 0
for word in plaintext.split(' '):
if word and english_dictionnary.check(word):
number_of_english_words += 1
if number_of_english_words > max_number_of_english_words:
max_number_of_english_words = number_of_english_words
best_plaintext = plaintext
best_key = key
click.echo(f'The most likely encryption key is {best_key}. It gives the following plaintext:nn{best_plaintext[:1000]}...')
output_file.write(best_plaintext)
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar_breaker()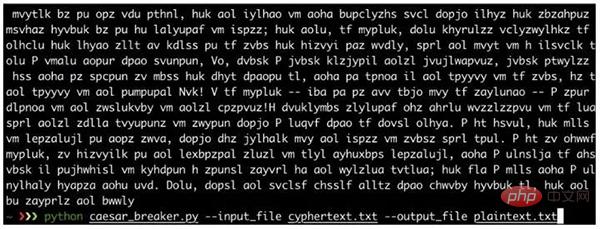
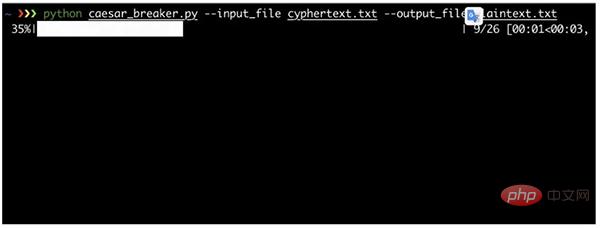
使用进度条
示例中的文本包含10^4个单词,因此该脚本需要大约5秒才能解密。这很正常,因为它需要检查所有25个秘钥,每个秘钥都要检查10^4个单词是否出现在英文字典中。
假设你要解密的文本包括10^5个单词,那么就要花费50秒才能输出结果,用户可能会非常着急。因此我建议这种任务一定要显示进度条。特别是,显示进度条还非常容易实现。下面是个显示进度条的例子:
import click
import enchant
from tqdm import tqdm
from caesar_encryption import encrypt
@click.command()
@click.option(
'--input_file',
type=click.File('r'),
required=True,
)
@click.option(
'--output_file',
type=click.File('w'),
required=True,
)
def caesar_breaker(input_file, output_file):
cyphertext = input_file.read()
english_dictionnary = enchant.Dict("en_US")
best_number_of_english_words = 0
for key in tqdm(range(26)):
plaintext = encrypt(cyphertext, -key)
number_of_english_words = 0
for word in plaintext.split(' '):
if word and english_dictionnary.check(word):
number_of_english_words += 1
if number_of_english_words > best_number_of_english_words:
best_number_of_english_words = number_of_english_words
best_plaintext = plaintext
best_key = key
click.echo(f'The most likely encryption key is {best_key}. It gives the following plaintext:nn{best_plaintext[:1000]}...')
output_file.write(best_plaintext)
if __name__ == '__main__':
caesar_breaker()这里使用了tqdm库,tqdm.tqdm类可以将任何可迭代对象转化为一个进度条。click也提供了类似的接口来创建进度条(click.progress_bar),但我觉得它不如tqdm好用。
위 내용은 클릭을 사용하여 완벽한 Python 명령줄 프로그램 만들기의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

