Tencent Cloud에 PHP를 설치하는 방법
- 藏色散人원래의
- 2021-11-30 10:54:202550검색
Tencent Cloud에 PHP를 설치하는 방법: 1. Tencent Cloud에 등록하고 서버를 임대합니다. 2. putty.exe를 사용하여 원격으로 로그인합니다. 3. 서버에 aphache 및 php와 같은 소프트웨어를 설치합니다. 파일.

이 기사의 운영 환경: CentOS 7.2 시스템, PHP 버전 7.1.2, DELL G3 컴퓨터
Tencent Cloud에 PHP를 설치하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
Tencent Cloud는 처음부터 PHP 운영 환경을 구축합니다
1. 먼저 Tencent Cloud에 등록하고 서버를 임대해야 합니다. 저는 CentOS 7.2 64비트를 선택했습니다. 이때 이 호스트의 공용 IP와 인트라넷 IP가 제공됩니다. 이 호스트의 비밀번호입니다.
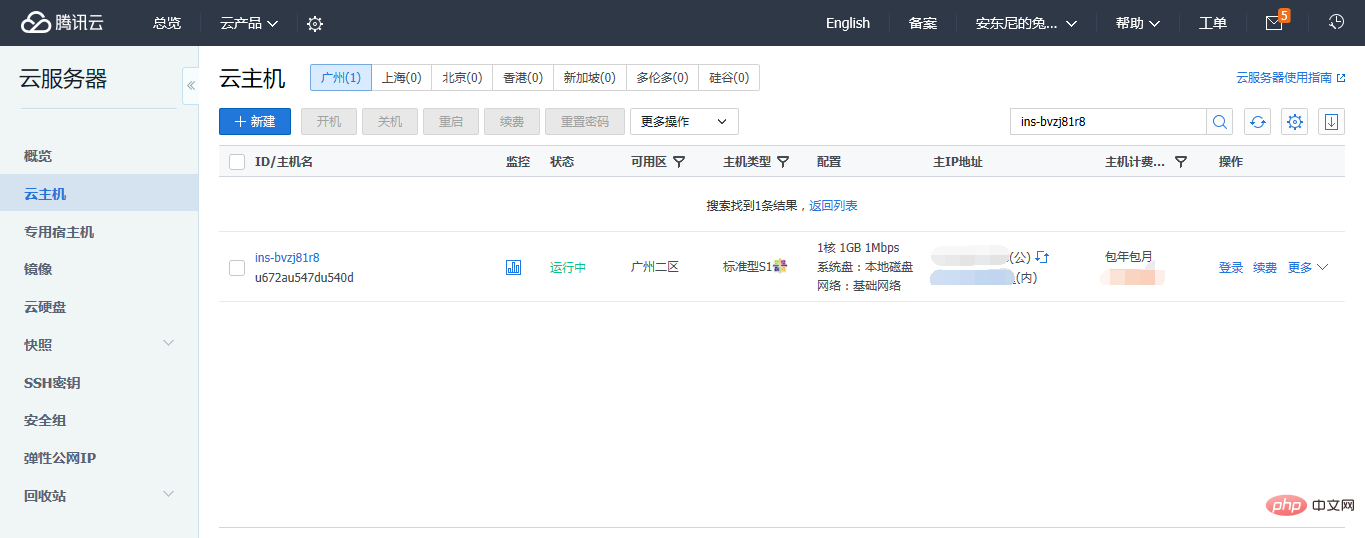
2. Tencent Cloud 웹페이지의 로그인 버튼을 사용해 로그인하거나, Putty를 사용해 로그인할 수 있습니다. 아래에서는 원격 작업에 Putty를 사용합니다.
1. 최신 퍼티를 다운로드할 수 있습니다. 다운로드는 압축 패키지입니다.
psftp.exe는 파일 전송에 사용됩니다.
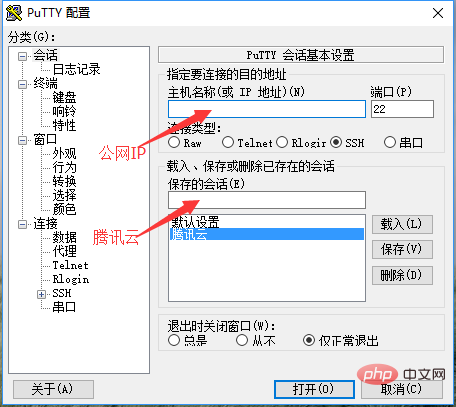
2 . ssh를 사용하여 연결하는 것이 더 안전하며 기본 포트는 22입니다. 클릭하면 로드됩니다. 이때 사용자 이름과 비밀번호를 입력하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 올바르게 입력하면 로그인이 성공한 것입니다.
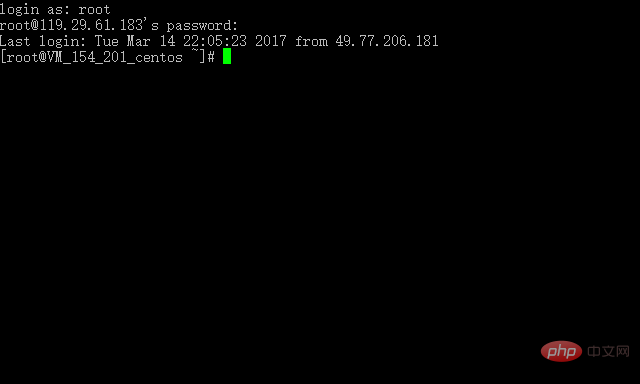
3. 서버에 aphache, php 및 기타 소프트웨어를 설치해야 하므로 서버에 파일을 업로드하는 것을 잊지 않을 수 있습니다. 편리하고 직관적인 wincp를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
1. Baidu Winscp를 성공적으로 설치한 후 서버의 공용 IP, 사용자 이름 및 비밀번호를 입력하면 그림과 같이 성공적으로 로그인할 수 있습니다.
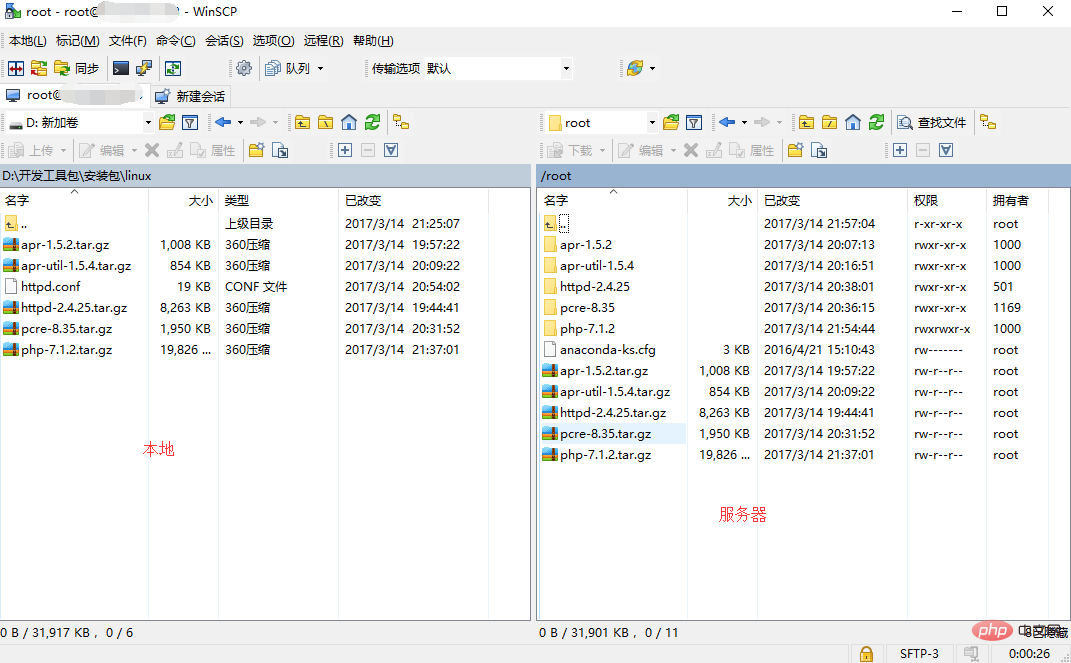
도구가 준비되면 환경 구축을 시작할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 http://www.cnblogs.com/lufangtao/archive/2012/12/30/2839679.html을 참조하세요. 이 기사는 매우 철저합니다.
1. 먼저 Apache를 설치하고 공식 웹사이트에서 Linux 설치 패키지를 다운로드합니다: http://httpd.apache.org/download.cgi
Apache를 설치하기 전에 APR 및 APR-util, prce
를 설치해야 합니다. APR 및 APR-util 다운로드 주소: http://apr.apache.org/download.cgi?Preferred=http%3A%2F%2Fmirrors.hust.edu.cn%2Fapache%2F
prce 다운로드 주소: http:/ /jaist.dl.sourceforge.NET/project/pcre/pcre/8.35/pcre-8.35.tar.gz
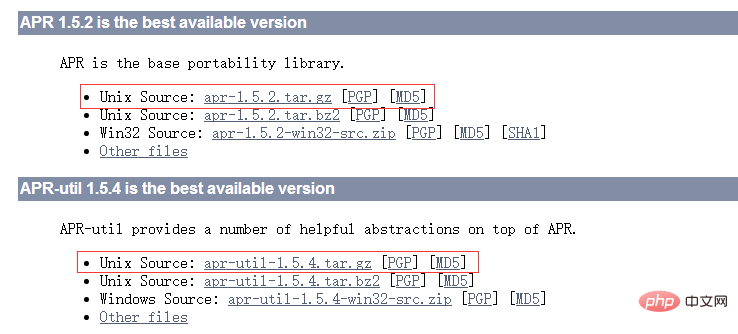
4개의 압축 파일을 모두 다운로드합니다.

2.wincp를 사용하여 4개의 파일을 모두 다운로드합니다. 서버에 업로드한 후 압축을 푼다:
tar -zxvf httpd-2.4.25.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apr-1.5.2.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apr-util-1.5.4.tar .gz
tar -zxvf pcre-8.35.tar.gz
3. Gcc 설치: yum install gcc
C++ 컴파일러 설치: yum install gcc-c++
4 APR 설치:
압축 해제된 APR 폴더를 입력하세요. cd apr-1.5.2
설치 전 확인: ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/apr
컴파일: make
설치: make install
5 apr-util 설치:
Enter 압축을 푼 apr. -util 폴더: cd apr-util-1.5.4
설치 전 확인: ./confiure --prefix=/usr/local/apr-util --with-apr=/usr/local/ apr
컴파일: make
설치: make install
6. pcre 설치:
압축 해제된 pcre 폴더 입력: cd pcre-8.35
설치 전 확인: ./configure --prefix=/usr/ local/pcre
컴파일: make
설치: make install
7. 아파치 설치:
압축 해제된 아파치 폴더 입력: cd httpd-2.4.25
설치 전 확인: ./configure --prefix =/usr/local/apache2 --enable-module =공유 --with-apr=/usr/local/apr/ --with-apr-util=/usr/local/apr-util/ --with-pcre= /usr/local/pcre
컴파일: make
설치: make install
8. 시작, 다시 시작 및 중지, 먼저 설치가 완료된 후 /usr/local/apache2/bin
./apachectl -k start
./apachectl -k restart
디렉터리로 전환합니다../apachectl -k stop
9. 구성 파일: (가장 기본적인 구성 충족)
#
# This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
# See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information.# In particular, see
# <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html># for a discussion of each configuration directive.
#
# Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding
# what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure# consult the online docs. You have been warned.
#
# Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many
# of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the
# server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin
# with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so "logs/access_log"# with ServerRoot set to "/usr/local/apache2" will be interpreted by the
# server as "/usr/local/apache2/logs/access_log", whereas "/logs/access_log" # will be interpreted as '/logs/access_log'.
#
# ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's# configuration, error, and log files are kept.
#
# Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point
# ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the
# Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the
# same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at
# least PidFile.
#
ServerRoot "/usr/local/apache2"#
# Mutex: Allows you to set the mutex mechanism and mutex file directory
# for inpidual mutexes, or change the global defaults
#
# Uncomment and change the directory if mutexes are file-based and the default# mutex file directory is not on a local disk or is not appropriate for some
# other reason.
#
# Mutex default:logs
#
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost># directive.
#
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
# prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses.
#
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80Listen 80#
# Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support
#
# To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you
# have to place corresponding `LoadModule' lines at this location so the# directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used.
# Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l') do not need# to be loaded here.
#
# Example:
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
LoadModule authn_file_module modules/mod_authn_file.so
#LoadModule authn_dbm_module modules/mod_authn_dbm.so
#LoadModule authn_anon_module modules/mod_authn_anon.so
#LoadModule authn_dbd_module modules/mod_authn_dbd.so
#LoadModule authn_socache_module modules/mod_authn_socache.so
LoadModule authn_core_module modules/mod_authn_core.so
LoadModule authz_host_module modules/mod_authz_host.so
LoadModule authz_groupfile_module modules/mod_authz_groupfile.so
LoadModule authz_user_module modules/mod_authz_user.so
#LoadModule authz_dbm_module modules/mod_authz_dbm.so
#LoadModule authz_owner_module modules/mod_authz_owner.so
#LoadModule authz_dbd_module modules/mod_authz_dbd.so
LoadModule authz_core_module modules/mod_authz_core.so
LoadModule access_compat_module modules/mod_access_compat.so
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
#LoadModule auth_form_module modules/mod_auth_form.so
#LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so
#LoadModule allowmethods_module modules/mod_allowmethods.so
#LoadModule file_cache_module modules/mod_file_cache.so
#LoadModule cache_module modules/mod_cache.so
#LoadModule cache_disk_module modules/mod_cache_disk.so
#LoadModule cache_socache_module modules/mod_cache_socache.so
#LoadModule socache_shmcb_module modules/mod_socache_shmcb.so
#LoadModule socache_dbm_module modules/mod_socache_dbm.so
#LoadModule socache_memcache_module modules/mod_socache_memcache.so
#LoadModule watchdog_module modules/mod_watchdog.so
#LoadModule macro_module modules/mod_macro.so
#LoadModule dbd_module modules/mod_dbd.so
#LoadModule dumpio_module modules/mod_dumpio.so
#LoadModule buffer_module modules/mod_buffer.so
#LoadModule ratelimit_module modules/mod_ratelimit.so
LoadModule reqtimeout_module modules/mod_reqtimeout.so
#LoadModule ext_filter_module modules/mod_ext_filter.so
#LoadModule request_module modules/mod_request.so
#LoadModule include_module modules/mod_include.so
LoadModule filter_module modules/mod_filter.so
#LoadModule substitute_module modules/mod_substitute.so
#LoadModule sed_module modules/mod_sed.so
LoadModule mime_module modules/mod_mime.so
LoadModule log_config_module modules/mod_log_config.so
#LoadModule log_debug_module modules/mod_log_debug.so
#LoadModule logio_module modules/mod_logio.so
LoadModule env_module modules/mod_env.so
#LoadModule expires_module modules/mod_expires.so
LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.so
#LoadModule unique_id_module modules/mod_unique_id.so
LoadModule setenvif_module modules/mod_setenvif.so
LoadModule version_module modules/mod_version.so
#LoadModule remoteip_module modules/mod_remoteip.so
#LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
#LoadModule proxy_connect_module modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
#LoadModule proxy_ftp_module modules/mod_proxy_ftp.so
#LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
#LoadModule proxy_fcgi_module modules/mod_proxy_fcgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_scgi_module modules/mod_proxy_scgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_fdpass_module modules/mod_proxy_fdpass.so
#LoadModule proxy_wstunnel_module modules/mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
#LoadModule proxy_ajp_module modules/mod_proxy_ajp.so
#LoadModule proxy_balancer_module modules/mod_proxy_balancer.so
#LoadModule proxy_express_module modules/mod_proxy_express.so
#LoadModule proxy_hcheck_module modules/mod_proxy_hcheck.so
#LoadModule session_module modules/mod_session.so
#LoadModule session_cookie_module modules/mod_session_cookie.so
#LoadModule session_dbd_module modules/mod_session_dbd.so
#LoadModule slotmem_shm_module modules/mod_slotmem_shm.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_byrequests_module modules/mod_lbmethod_byrequests.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bytraffic_module modules/mod_lbmethod_bytraffic.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bybusyness_module modules/mod_lbmethod_bybusyness.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_heartbeat_module modules/mod_lbmethod_heartbeat.so
LoadModule unixd_module modules/mod_unixd.so
#LoadModule dav_module modules/mod_dav.so
LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so
LoadModule autoindex_module modules/mod_autoindex.so
#LoadModule info_module modules/mod_info.so
#LoadModule cgid_module modules/mod_cgid.so
#LoadModule dav_fs_module modules/mod_dav_fs.so
#LoadModule vhost_alias_module modules/mod_vhost_alias.so
#LoadModule negotiation_module modules/mod_negotiation.so
LoadModule dir_module modules/mod_dir.so
#LoadModule actions_module modules/mod_actions.so
#LoadModule speling_module modules/mod_speling.so
#LoadModule userdir_module modules/mod_userdir.so
LoadModule alias_module modules/mod_alias.so
#LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so<IfModule unixd_module>#
# If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run
# httpd as root initially and it will switch.
#
# User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as.
# It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for# running httpd, as with most system services.
#
User daemon
Group daemon</IfModule># 'Main' server configuration
#
# The directives in this section set up the values used by the 'main'# server, which responds to any requests that aren't handled by a
# <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for# any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file.
#
# All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers,
# in which case these default settings will be overridden for the
# virtual host being defined.
#
#
# ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be
# e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such
# as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com
#
ServerAdmin you@example.com
#
# ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself.
# This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify
# it explicitly to prevent problems during startup.
#
# If your host doesn't have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here.#
ServerName localhost:80#
# Deny access to the entirety of your server's filesystem. You must# explicitly permit access to web content directories in other
# <Directory> blocks below.
#<Directory />
AllowOverride none
Require all denied</Directory>#
# Note that from this point forward you must specifically allow
# particular features to be enabled - so if something's not working as# you might expect, make sure that you have specifically enabled it
# below.
#
#
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
DocumentRoot "/usr/local/apache2/htdocs"
<Directory "/usr/local/apache2/htdocs">
#
# Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All",
# or any combination of:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#
# Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All"
# doesn't give it to you. #
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords:
# AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
#
AllowOverride None
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
Require all granted</Directory>#
# DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory
# is requested.
#<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.html
DirectoryIndex index.html index.php</IfModule>#
# The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being
# viewed by Web clients.
#<Files ".ht*">
Require all denied</Files>#
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost># container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost># container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here.#
ErrorLog "logs/error_log"#
# LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log.
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
#
LogLevel warn<IfModule log_config_module>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common <IfModule logio_module>
# You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" %I %O" combinedio </IfModule>
#
# The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format).
# If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost>
# container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do*
# define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be
# logged therein and *not* in this file.
#
CustomLog "logs/access_log" common
#
# If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information
# (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive.
#
#CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined</IfModule>
<IfModule alias_module>
#
# Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to
# exist in your server's namespace, but do not anymore. The client
# will make a new request for the document at its new location.
# Example:
# Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar
#
# Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to
# access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot.
# Example:
# Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path
#
# If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will
# require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely
# need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to
# the filesystem path.
#
# ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts.
# ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that
# documents in the target directory are treated as applications and
# run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the
# client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias
# directives as to Alias.
#
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/usr/local/apache2/cgi-bin/"
</IfModule>
<IfModule cgid_module>
#
# ScriptSock: On threaded servers, designate the path to the UNIX
# socket used to communicate with the CGI daemon of mod_cgid.
#
#Scriptsock cgisock</IfModule>#
# "/usr/local/apache2/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased
# CGI directory exists, if you have that configured.
#<Directory "/usr/local/apache2/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted</Directory>
<IfModule headers_module>
#
# Avoid passing HTTP_PROXY environment to CGI's on this or any proxied
# backend servers which have lingering "httpoxy" defects.
# 'Proxy' request header is undefined by the IETF, not listed by IANA
#
RequestHeader unset Proxy early</IfModule>
<IfModule mime_module>
#
# TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from
# filename extension to MIME-type.
#
TypesConfig conf/mime.types
#
# AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration
# file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types.
#
#AddType application/x-gzip .tgz
#
# AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress
# information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this.
#
#AddEncoding x-compress .Z
#AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you
# probably should define those extensions to indicate media types:
#
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php
AddType application/x-httpd-php-source .php5
#
# AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers":
# actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server
# or added with the Action directive (see below)
#
# To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories:
# (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.)
#
#AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
# For type maps (negotiated resources):
#AddHandler type-map var
#
# Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client.
#
# To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI):
# (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.)
#
#AddType text/html .shtml
#AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml</IfModule>#
# The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the
# contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile
# directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located.
#
#MIMEMagicFile conf/magic
#
# Customizable error responses come in three flavors:
# 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects
#
# Some examples:
#ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo."#ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html
#ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl"#ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html#
#
# MaxRanges: Maximum number of Ranges in a request before
# returning the entire resource, or one of the special
# values 'default', 'none' or 'unlimited'.
# Default setting is to accept 200 Ranges.
#MaxRanges unlimited
#
# EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it,
# memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver
# files. This usually improves server performance, but must
# be turned off when serving from networked-mounted
# filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise
# broken on your system.
# Defaults: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off
#
#EnableMMAP off
#EnableSendfile on
# Supplemental configuration
#
# The configuration files in the conf/extra/ directory can be
# included to add extra features or to modify the default configuration of
# the server, or you may simply copy their contents here and change as
# necessary.
# Server-pool management (MPM specific)
#Include conf/extra/httpd-mpm.conf
# Multi-language error messages
#Include conf/extra/httpd-multilang-errordoc.conf
# Fancy directory listings
#Include conf/extra/httpd-autoindex.conf
# Language settings
#Include conf/extra/httpd-languages.conf
# User home directories
#Include conf/extra/httpd-userdir.conf
# Real-time info on requests and configuration
#Include conf/extra/httpd-info.conf
# Virtual hosts
#Include conf/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf
# Local access to the Apache HTTP Server Manual
#Include conf/extra/httpd-manual.conf
# Distributed authoring and versioning (WebDAV)
#Include conf/extra/httpd-dav.conf
# Various default settings
#Include conf/extra/httpd-default.conf
# Configure mod_proxy_html to understand HTML4/XHTML1<IfModule proxy_html_module>Include conf/extra/proxy-html.conf</IfModule># Secure (SSL/TLS) connections
#Include conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
#
# Note: The following must must be present to support
# starting without SSL on platforms with no /dev/random equivalent
# but a statically compiled-in mod_ssl.
#<IfModule ssl_module>SSLRandomSeed startup builtin
SSLRandomSeed connect builtin</IfModule>
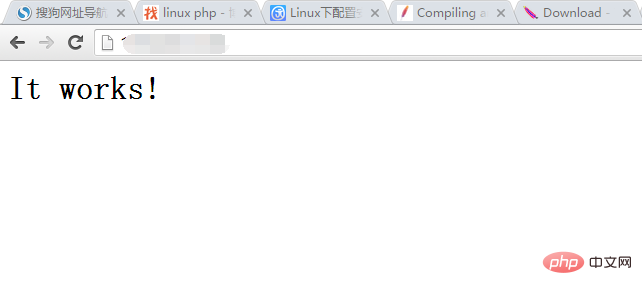
10. 테스트:
브라우저에 http://public을 입력하면 네트워크 IP가 다음과 같이 표시되며 구성은 다음과 같습니다. 성공했습니다.
5. php
설치 1. 공식 웹사이트에서 PHP 압축 패키지를 다운로드하고 서버에 업로드하여 압축을 푼다: http://www.php.net/downloads.php
2、建立目标文件夹mkdir /usr/local/php,等下php安装到该目录下。
3、安装前校验: ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php --with-apxs2=/usr/local/apache/bin/apxs
可能会提示出现错误:configure: error: xml2-config not found. Please check your libxml2 installation。运行yum install libxml2,然后再运行yum install libxml2-devel安装完毕后,重新运行上面的./configure命令。
4、编译:make
5、编译测试:make test
6、编译安装:make install
7、在apache的htdocs下建立一个php文件test.php,里面的内容如下:
<?php
phpinfo(); ?>
重启apache服务器,在浏览器中输入:http://公网IP/test.php,结果如下:
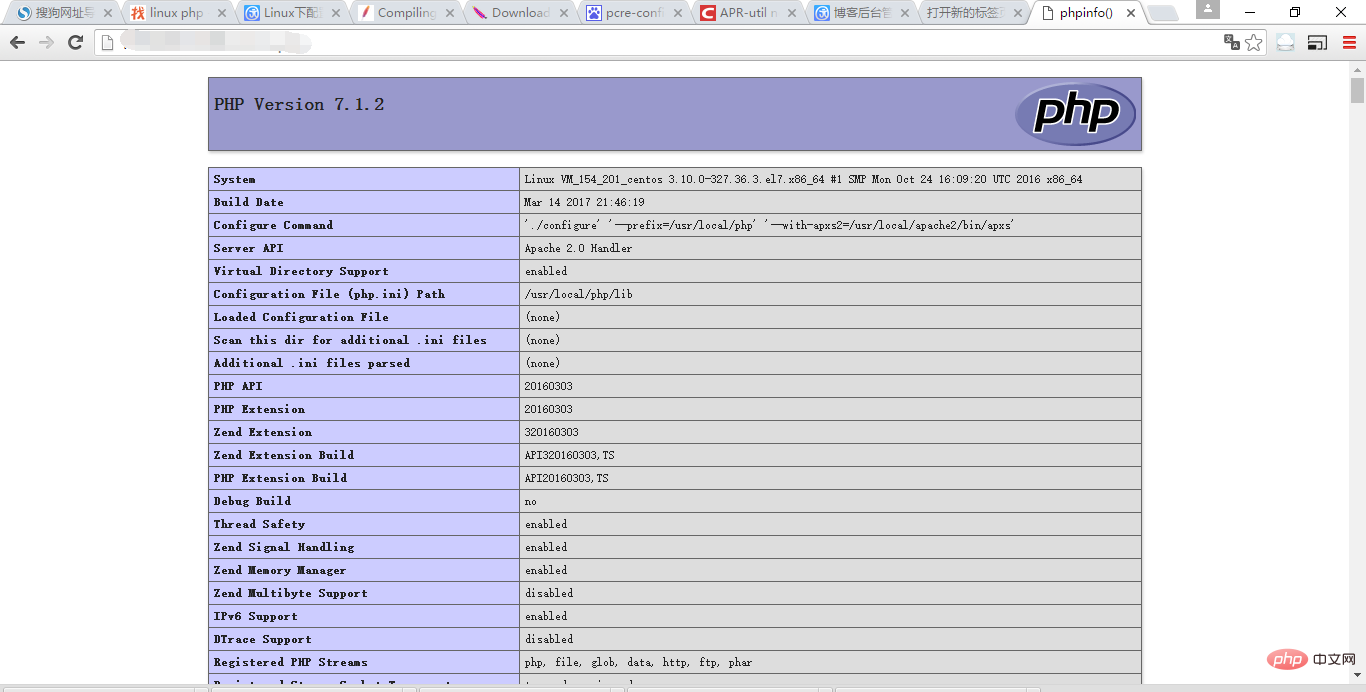
php配置成功!
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
위 내용은 Tencent Cloud에 PHP를 설치하는 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

