배열을 사용하여 Java에서 순환 대기열 구현
- 王林앞으로
- 2019-11-30 16:51:473080검색

아이디어 분석:
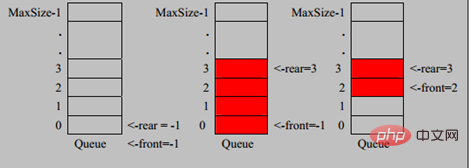
1의 의미를 조정합니다. 이는 큐의 첫 번째 요소를 가리킵니다. 즉, arr[front]는 큐의 첫 번째 요소입니다.
Theinitial value of front = 0
2. Rear 변수 의미가 조정되었습니다. Rear는 대기열의 마지막 요소 다음 위치를 가리킵니다. 관례적으로 공간을 확보하기를 원하기 때문입니다.
rear의 초기 값 = 0#🎜🎜 #
3 큐가 가득 찼을 때 조건은 (rear + 1) % maxSize == front [full] 4 입니다. 큐가 비어 있을 때의 조건은 Rear ==입니다. frontempty 5 이렇게 분석해보면 큐에 있는 유효한 데이터 개수(rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize // Rear = 1 front = 0#🎜 🎜#6. 원형 큐인 Get에서 수정할 수 있습니다.
java 관련 동영상 튜토리얼 공유:
java 학습 동영상import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把
System.out.println("测试数组模拟环形队列的案例~~~");
// 创建一个环形队列
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(4); //说明设置4, 其队列的有效数据最大是3
char key = ' '; // 接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//
boolean loop = true;
// 输出一个菜单
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);// 接收一个字符
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g': // 取出数据
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h': // 查看队列头的数据
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': // 退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~");
}
}
class CircleArray {
private int maxSize; // 表示数组的最大容量
//front 变量的含义做一个调整: front 就指向队列的第一个元素, 也就是说 arr[front] 就是队列的第一个元素
//front 的初始值 = 0
private int front;
//rear 变量的含义做一个调整:rear 指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置. 因为希望空出一个空间做为约定.
//rear 的初始值 = 0
private int rear; // 队列尾
private int[] arr; // 该数据用于存放数据, 模拟队列
public CircleArray(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
// 判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
// 添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
// 判断队列是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据~");
return;
}
//直接将数据加入
arr[rear] = n;
//将 rear 后移, 这里必须考虑取模
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
// 获取队列的数据, 出队列
public int getQueue() {
// 判断队列是否空
if (isEmpty()) {
// 通过抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
// 这里需要分析出 front是指向队列的第一个元素
// 1. 先把 front 对应的值保留到一个临时变量
// 2. 将 front 后移, 考虑取模
// 3. 将临时保存的变量返回
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
// 显示队列的所有数据
public void showQueue() {
// 遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列空的,没有数据~~");
return;
}
// 思路:从front开始遍历,遍历多少个元素
for (int i = front; i < front + size() ; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// 求出当前队列有效数据的个数
public int size() {
// rear = 2
// front = 1
// maxSize = 3
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
// 显示队列的头数据, 注意不是取出数据
public int headQueue() {
// 判断
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空的,没有数据~~");
}
return arr[front];
}
} 관련 기사 튜토리얼 공유: java빠른 시작
위 내용은 배열을 사용하여 Java에서 순환 대기열 구현의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
성명:
이 기사는 csdn.net에서 복제됩니다. 침해가 있는 경우 admin@php.cn으로 문의하시기 바랍니다. 삭제
이전 기사:JVM에서 마스터해야 하는 일부 매개변수다음 기사:JVM에서 마스터해야 하는 일부 매개변수

