pytorch + visdom 자체 구축 이미지 데이터 세트를 처리하는 CNN 방법
- 不言원래의
- 2018-06-04 16:19:004141검색
이 글은 자체 구축한 이미지 데이터 세트를 처리하기 위한 pytorch + visdom CNN 방법을 주로 소개합니다. 이제 특정 참조 가치가 있으므로 필요한 친구들이 참조할 수 있습니다.
Environment
시스템: win10
cpu: i7-6700HQ
gpu: gtx965m
python: 3.6
pytorch: 0.3
데이터 다운로드
Sasank Chilamkurthy의 튜토리얼에서 출처 : 다운로드 링크;
다운로드하여 압축을 풀고 프로젝트 루트 디렉터리에 넣으세요:

데이터 세트는 개미와 벌을 분류하는 데 사용됩니다. 각 클래스에는 약 120개의 훈련 이미지와 75개의 검증 이미지가 있습니다.
데이터 가져오기
torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(root,transforms) 모듈을 사용하여 이미지를 텐서로 변환할 수 있습니다.
첫 번째 변환 정의:
ata_transforms = {
'train': transforms.Compose([
# 随机切成224x224 大小图片 统一图片格式
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
# 图像翻转
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
# totensor 归一化(0,255) >> (0,1) normalize channel=(channel-mean)/std
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
]),
"val" : transforms.Compose([
# 图片大小缩放 统一图片格式
transforms.Resize(256),
# 以中心裁剪
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
}
데이터 가져오기 및 로드:
data_dir = './hymenoptera_data'
# trans data
image_datasets = {x: datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, x), data_transforms[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
# load data
data_loaders = {x: DataLoader(image_datasets[x], batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) for x in ['train', 'val']}
data_sizes = {x: len(image_datasets[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
class_names = image_datasets['train'].classes
print(data_sizes, class_names){'train': 244, 'val': 153} ['ants', 'bees']훈련 세트 244개, 테스트 세트 153개.
visdom은 텐서 입력을 지원하므로 numpy로 변경할 필요가 없습니다. 텐서 계산을 직접 사용할 수 있습니다. 이전 기사의 cifar10 사양 변경:
inputs, classes = next(iter(data_loaders['val'])) out = torchvision.utils.make_grid(inputs) inp = torch.transpose(out, 0, 2) mean = torch.FloatTensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) std = torch.FloatTensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) inp = std * inp + mean inp = torch.transpose(inp, 0, 2) viz.images(inp)
loss, 최적화 기능: 
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, n_class):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.cnn = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(in_dim, 16, 7), # 224 >> 218
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # 218 >> 109
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5), # 105
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 5), # 101
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # 101 >> 50
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, 1, 1), #
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.MaxPool2d(3), # 50 >> 16
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(128*16*16, 120),
nn.BatchNorm1d(120),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(120, n_class))
def forward(self, x):
out = self.cnn(x)
out = self.fc(out.view(-1, 128*16*16))
return out
# 输入3层rgb ,输出 分类 2
model = CNN(3, 2)매개변수:
line = viz.line(Y=np.arange(10)) loss_f = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=LR, momentum=0.9) scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)10 에포크를 실행하고 살펴보세요.
rreee
Run 20 살펴보기:
BATCH_SIZE = 4 LR = 0.001 EPOCHS = 10정확도는 상대적으로 낮습니다: 단 74.5%우리는 모델에서 resnet18을 사용하여 10개의 에포크를 실행합니다.
[9/10] train_loss:0.650|train_acc:0.639|test_loss:0.621|test_acc0.706 [10/10] train_loss:0.645|train_acc:0.627|test_loss:0.654|test_acc0.686 Training complete in 1m 16s Best val Acc: 0.712418
[19/20] train_loss:0.592|train_acc:0.701|test_loss:0.563|test_acc0.712 [20/20] train_loss:0.564|train_acc:0.721|test_loss:0.571|test_acc0.706 Training complete in 2m 30s Best val Acc: 0.745098
 원하는 경우 효과도 매우 평균입니다. 짧은 시간에 훈련시키면 효과가 매우 좋을 것입니다. 좋은 모델의 경우 훈련된 상태를 다운로드하여 다음을 기준으로 훈련할 수 있습니다.
원하는 경우 효과도 매우 평균입니다. 짧은 시간에 훈련시키면 효과가 매우 좋을 것입니다. 좋은 모델의 경우 훈련된 상태를 다운로드하여 다음을 기준으로 훈련할 수 있습니다.
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(True) num_ftrs = model.fc.in_features model.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2)
[9/10] train_loss:0.621|train_acc:0.652|test_loss:0.588|test_acc0.667 [10/10] train_loss:0.610|train_acc:0.680|test_loss:0.561|test_acc0.667 Training complete in 1m 24s Best val Acc: 0.686275
10 에포크는 95% 정확도에 직접 도달할 수 있습니다. 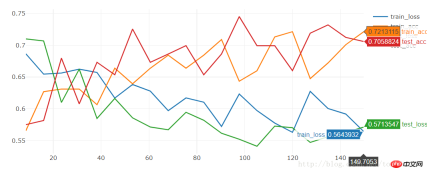
관련 추천:
pytorch + visdom은 간단한 분류 문제를 처리합니다
위 내용은 pytorch + visdom 자체 구축 이미지 데이터 세트를 처리하는 CNN 방법의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
성명:
본 글의 내용은 네티즌들의 자발적인 기여로 작성되었으며, 저작권은 원저작자에게 있습니다. 본 사이트는 이에 상응하는 법적 책임을 지지 않습니다. 표절이나 침해가 의심되는 콘텐츠를 발견한 경우 admin@php.cn으로 문의하세요.

