PHP 배경 및 모바일 APP 인터페이스 개발 예제 코드
- 小云云원래의
- 2018-05-29 10:44:277322검색
이 기사는 모든 사람에게 도움이 되기를 바라며 주로 PHP 백엔드 및 모바일 APP 인터페이스 개발의 예제 코드를 공유합니다.
1. 모바일 APP(클라이언트) 프로그램 인터페이스
여기에서는 PC에서 C++ 프로그램을 사용하여 HTTP 프로토콜 데이터의 POST를 시뮬레이션합니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace std;
#define DEST_IP "10.209.177.22"
#define DEST_PORT 80
#define MAX_DATA_SIZE 1024
int main()
{
int ret;
int sockfd;
struct sockaddr_in dest_addr;
memset(&dest_addr, 0x00, sizeof(sockaddr_in));
dest_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
dest_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(DEST_IP);
dest_addr.sin_port = htons(DEST_PORT);
cout << "dest addr IP:" << inet_ntoa(dest_addr.sin_addr) << endl;
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (sockfd < 0) {
cout << "create socket fail!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
ret = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&dest_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
if (ret != 0) {
cout << "connect server fail!" << endl;
close(sockfd);
exit(1);
} else {
cout << "connect server success!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
int sendlen, recvlen;
char sendbuf[MAX_DATA_SIZE] = {0};
char recvbuf[MAX_DATA_SIZE] = {0};
string body("user=hello&password=123456");
int content_length = body.length();
snprintf(sendbuf, sizeof(sendbuf) - 1,
"POST /api.php HTTP/1.1\r\n"
"Host: 10.209.177.22\r\n"
"Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\r\n"
"Content-Length: %d\r\n",
content_length
);
strcat(sendbuf, "\r\n");
strcat(sendbuf, body.c_str());
sendlen = send(sockfd, sendbuf, sizeof(sendbuf), 0);
if (sendlen < 0) {
cout << "send fail" << endl;
close(sockfd);
exit(1);
}
if ((recvlen = recv(sockfd, recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf), 0)) == -1) {
cout << "recv fail" << endl;
close(sockfd);
exit(1);
} else {
cout << recvbuf << endl;
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}2. 백엔드 PHP 테스트 프로그램
<?php
$input = file_get_contents("php://input");
var_dump($input);
if ($_POST['user'] == "hello" && $_POST['password'] == "123456") {
echo "welcome hello";
} else {
echo "welcome guest";
}
?>3. 구현 효과
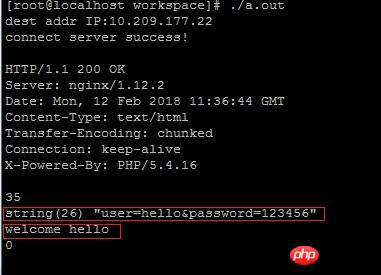
위 그림에서 클라이언트 C++ 프로그램은 POST 데이터를 백그라운드로 보낸 후 Nginx+PHP를 통해 POST 데이터를 얻습니다. 아래 처음 두 가지 방법 :
방법 1. 가장 일반적인 방법은 $_POST['fieldname'];
참고: Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded로 제출된 데이터만 수신할 수 있습니다.
설명: 양식의 데이터 POST입니다.
방법 2, file_get_contents("php://input");
설명:
POST의 원본 데이터를 읽는 것을 허용합니다.
$HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA와 비교할 때 메모리에 대한 부담이 적고 특별한 php.ini 설정이 필요하지 않습니다.
php://input은 enctype="multipart/form-data"와 함께 사용할 수 없습니다.
설명:
Content-Type이 지정되지 않은 POST 데이터의 경우 file_get_contents("php://input")를 사용하여 원본 데이터를 얻을 수 있습니다.
실제로 이 방법은 PHP를 사용하여 모든 POST 데이터를 수신하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 콘텐츠 유형에 관계없이 바이너리 파일 스트림을 포함하는 것도 허용됩니다.
그러므로 2번 방법을 사용하는 것이 가장 안전한 방법입니다.
방법 3, $GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA'];
참고:
항상 원본 POST 데이터가 포함된 $HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA 변수를 생성하세요.
이 변수는 인식할 수 없는 MIME 유형의 데이터가 발견될 때만 생성됩니다.
$HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA는 enctype="multipart/form-data" 양식 데이터에 사용할 수 없습니다.
게시된 데이터가 PHP에서 인식되지 않으면 $GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA']를 사용하여
text/xml 또는
설명:
$GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA']는 POST의 원본 데이터를 저장합니다.
$_POST 또는 $_REQUEST는 PHP에서 형식화된 데이터를 키=>값 형식으로 저장합니다.
그러나 POST 데이터를 $GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA']에 저장할지 여부는 Content-Type 설정에 따라 다릅니다. 즉, 데이터를 POST할 때 Content-Type을 명시적으로 지정해야 합니다: application/x-www-form-urlencoded , POST 데이터는 $GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA']에 저장됩니다.
파일을 업로드하려면 POST enctype="multipart/form-data"를 사용하세요. PHP 백엔드 코드 예:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<body>
<form method="post" action="" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" id="file" />
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form>
<?php
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($_FILES);
if ($_FILES["file"]["error"] > 0) {
echo "Error: " . $_FILES["file"]["error"] . "<br>";
} else {
$file = fopen($_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"], "r");
while (!feof($file)) {
echo fgetc($file);
}
fclose($file);
}
?>
</body>
</html>관련 권장 사항:
PHP로 APP 인터페이스를 개발할 때 주의해야 할 문제는 무엇입니까?
위 내용은 PHP 배경 및 모바일 APP 인터페이스 개발 예제 코드의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

