JS 조합 디자인 패턴에 대한 자세한 설명
- 小云云원래의
- 2018-02-23 14:06:021693검색
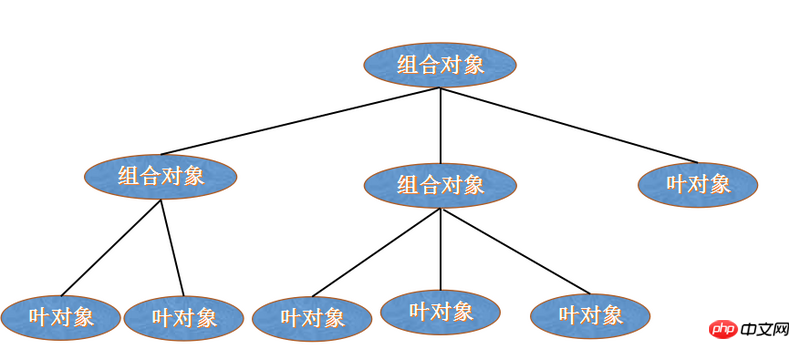
구성 모드는 개체를 트리 구조로 결합하여 "부분-전체" 계층을 나타냅니다. 조합 모드를 사용하면 단일 개체와 결합된 개체를 일관되게 사용할 수 있습니다.
트리 구조 문제에서 단순한 요소와 복잡한 요소의 개념이 모호해졌습니다. 클라이언트 프로그램은 복잡한 요소를 단순한 요소처럼 처리할 수 있으므로 클라이언트 프로그램을 복잡한 요소의 내부 구조에서 분리합니다. 이는 개발자가 유사한 기능을 가진 여러 개체를 분류하고 표준화된 디자인을 개선하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 계층적 데이터 구조의 예가 많아 조합 패턴이 매우 유용합니다. 계층적 데이터 구조의 일반적인 예는 컴퓨터를 사용할 때마다 접하게 되는 파일 시스템입니다. 파일 시스템은 디렉터리와 파일로 구성됩니다. 각 디렉터리에는 콘텐츠가 포함될 수 있습니다. 디렉터리의 내용은 파일일 수도 있고 디렉터리일 수도 있습니다. 이런 방식으로 컴퓨터의 파일 시스템은 재귀적 구조로 구성됩니다. 이러한 데이터 구조를 설명하려면 복합 패턴을 사용할 수 있습니다.
역할 관련
특징
구성 패턴의 계층에는 리프 개체와 복합 개체라는 두 가지 유형의 개체가 있습니다. 이는 재귀적인 정의이지만 복합 개체가 유용한 이유이기도 합니다. 다른 객체로 구성되어 있지만 리프 객체에는 더 이상 하위 객체가 포함되지 않습니다.
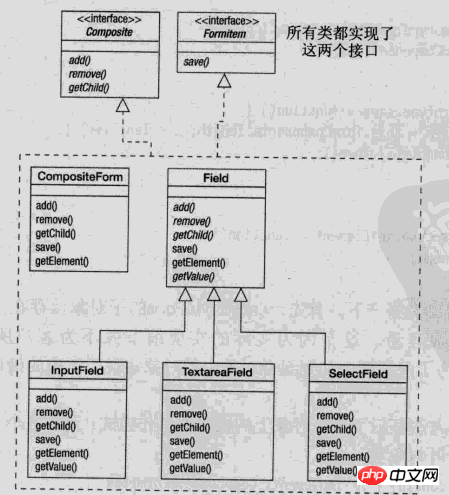
javascript 디자인 패턴의 다이어그램을 빌려 조합 패턴
 인터페이스는 적절한 경우 모든 클래스에 공통된 인터페이스의 기본 동작을 구현하는 컴포지션의 개체 선언 인터페이스입니다. Component 하위 구성 요소에 액세스하고 관리하기 위한 인터페이스를 선언합니다.
인터페이스는 적절한 경우 모든 클래스에 공통된 인터페이스의 기본 동작을 구현하는 컴포지션의 개체 선언 인터페이스입니다. Component 하위 구성 요소에 액세스하고 관리하기 위한 인터페이스를 선언합니다.
Field는 리프 노드 개체를 조합하여 나타냅니다. 리프 노드에는 자식 노드가 없으며 추상 클래스로 설계할 수 있습니다.
- Composite는 자식 노드의 동작을 정의합니다. 하위 컴포넌트를 저장하기 위해 추가(추가), 삭제(제거) 등 하위 컴포넌트와 관련된 작업을 Component 인터페이스에 구현합니다.
- Interface
-
/* Interfaces. */ var Composite = new Interface('Composite', ['add', 'remove', 'getChild']); var FormItem = new Interface('FormItem', ['save']);
결합된 개체 클래스
/* CompositeForm class. */ var CompositeForm = function(id, method, action) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.formComponents = []; this.element = document.createElement('form'); this.element.id = id; this.element.method = method || 'POST'; this.element.action = action || '#'; }; CompositeForm.prototype.add = function(child) { Interface.ensureImplements(child, Composite, FormItem); this.formComponents.push(child); this.element.appendChild(child.getElement()); }; CompositeForm.prototype.remove = function(child) { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { if(this.formComponents[i] === child) { this.formComponents.splice(i, 1); // Remove one element from the array at // position i. break; } } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getChild = function(i) { return this.formComponents[i]; }; CompositeForm.prototype.save = function() { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { this.formComponents[i].save(); } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; };Leaf 개체 클래스 - 잎 개체는 간단한 클래스일 수도 있고, 나뭇잎의 다양한 범주를 구성하기 위해 추상 클래스로 설계될 수도 있습니다. 여기에 채택된 추상 클래스 디자인은 다양한 범주의 나뭇잎
/* Field class, abstract. */ var Field = function(id) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.id = id; this.element; }; Field.prototype.add = function() {}; Field.prototype.remove = function() {}; Field.prototype.getChild = function() {}; Field.prototype.save = function() { setCookie(this.id, this.getValue); }; Field.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; }; Field.prototype.getValue = function() { throw new Error('Unsupported operation on the class Field.'); }; - InputField 클래스
/* InputField class. */ var InputField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.input = document.createElement('input'); this.input.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.input); }; extend(InputField, Field); // Inherit from Field. InputField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.input.value; }; - TextareaField 클래스
/* TextareaField class. */ var TextareaField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.textarea = document.createElement('textarea'); this.textarea.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.textarea); }; extend(TextareaField, Field); // Inherit from Field. TextareaField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.textarea.value; };
SelectField 클래스 -
/* SelectField class. */ var SelectField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.select = document.createElement('select'); this.select.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.select); }; extend(SelectField, Field); // Inherit from Field. SelectField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.select.options[this.select.selectedIndex].value; };사용 -
/* Usage. */ var contactForm = new CompositeForm('contact-form', 'POST', 'contact.php'); contactForm.add(new InputField('first-name', 'First Name')); contactForm.add(new InputField('last-name', 'Last Name')); contactForm.add(new InputField('address', 'Address')); contactForm.add(new InputField('city', 'City')); contactForm.add(new SelectField('state', 'State', stateArray)); // var stateArray =[{'al', 'Alabama'}, ...] contactForm.add(new InputField('zip', 'Zip')); contactForm.add(new TextareaField('comments', 'Comments')); addEvent(window, 'unload', contactForm.save);조합 모드는 많은 인원에게 적합합니다. 객체 작업의 분류 작업을 통해 작업 객체는 계층적 관계를 가지게 되므로 객체 간의 결합이 약화됩니다. 이 모드는 코드를 더욱 모듈화하고, 더욱 뚜렷하고, 유지 관리하기 쉽게 만듭니다.
관련 권장 사항: - 자세한 설명 js 브리지 디자인 패턴
위 내용은 JS 조합 디자인 패턴에 대한 자세한 설명의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!