Python 지점 간 간단한 구현
- 巴扎黑원래의
- 2017-09-15 10:48:391658검색
이 글은 간단한 점대점 p2p 채팅을 구현하기 위한 파이썬을 위주로 자세하게 소개하고 있습니다. 관심 있는 친구들은 참고해 보세요.
Peer-to-point 채팅은 먼저 멀티스레드 네트워크 프로그래밍을 기반으로 하며, 둘째, 각 Connection은 고유한 속성을 가진 객체로 저장되어 Connection 목록에 추가됩니다. 각 Connection 객체가 보내는 정보에는 세 가지 주요 내용(from, to, message)이 포함되어야 합니다. 서버는 연결 목록을 탐색하여 to의 연결 개체를 기반으로 대상 개체를 찾아 정보를 대상으로 보냅니다. 대상은 정보를 얻은 후 해당 정보를 보낸 사람이 누구인지 알고 ID 번호에 따라 응답합니다. 이 구현은 계속 개선될 것이며 이후의 새로운 기능은 내 개인 Github 홈페이지에 표시될 것입니다.
서버 측 구현:
#coding:utf-8
'''
file:server.py
date:2017/9/10 12:43
author:lockey
email:lockey@123.com
platform:win7.x86_64 pycharm python3
desc:p2p communication serverside
'''
import socketserver,json
import subprocess
connLst = []
## 连接列表,用来保存一个连接的信息(代号 地址和端口 连接对象)
class Connector(object):#连接对象类
def __init__(self,account,password,addrPort,conObj):
self.account = account
self.password = password
self.addrPort = addrPort
self.conObj = conObj
class MyServer(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
print("got connection from",self.client_address)
register = False
while True:
conn = self.request
data = conn.recv(1024)
if not data:
continue
dataobj = json.loads(data.decode('utf-8'))
#如果连接客户端发送过来的信息格式是一个列表且注册标识为False时进行用户注册
if type(dataobj) == list and not register:
account = dataobj[0]
password = dataobj[1]
conObj = Connector(account,password,self.client_address,self.request)
connLst.append(conObj)
register = True
continue
print(connLst)
#如果目标客户端在发送数据给目标客服端
if len(connLst) > 1 and type(dataobj) == dict:
sendok = False
for obj in connLst:
if dataobj['to'] == obj.account:
obj.conObj.sendall(data)
sendok = True
if sendok == False:
print('no target valid!')
else:
conn.sendall('nobody recevied!'.encode('utf-8'))
continue
if __name__ == '__main__':
server = socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(('192.168.1.4',8022),MyServer)
print('waiting for connection...')
server.serve_forever()클라이언트 측 구현:
#coding:utf-8
'''
file:client.py.py
date:2017/9/10 11:01
author:lockey
email:lockey@123.com
platform:win7.x86_64 pycharm python3
desc:p2p communication clientside
'''
from socket import *
import threading,sys,json,re
HOST = '192.168.1.4' ##
PORT=8022
BUFSIZ = 1024 ##缓冲区大小 1K
ADDR = (HOST,PORT)
tcpCliSock = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
tcpCliSock.connect(ADDR)
userAccount = None
def register():
myre = r"^[_a-zA-Z]\w{0,}"
#正则验证用户名是否合乎规范
accout = input('Please input your account: ')
if not re.findall(myre, accout):
print('Account illegal!')
return None
password1 = input('Please input your password: ')
password2 = input('Please confirm your password: ')
if not (password1 and password1 == password2):
print('Password not illegal!')
return None
global userAccount
userAccount = accout
return (accout,password1)
class inputdata(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
while True:
sendto = input('to>>:')
msg = input('msg>>:')
dataObj = {'to':sendto,'msg':msg,'froms':userAccount}
datastr = json.dumps(dataObj)
tcpCliSock.send(datastr.encode('utf-8'))
class getdata(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
while True:
data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ)
dataObj = json.loads(data.decode('utf-8'))
print('{} -> {}'.format(dataObj['froms'],dataObj['msg']))
def main():
while True:
regInfo = register()
if regInfo:
datastr = json.dumps(regInfo)
tcpCliSock.send(datastr.encode('utf-8'))
break
myinputd = inputdata()
mygetdata = getdata()
myinputd.start()
mygetdata.start()
myinputd.join()
mygetdata.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()실행 결과의 예:
서버 측 결과:
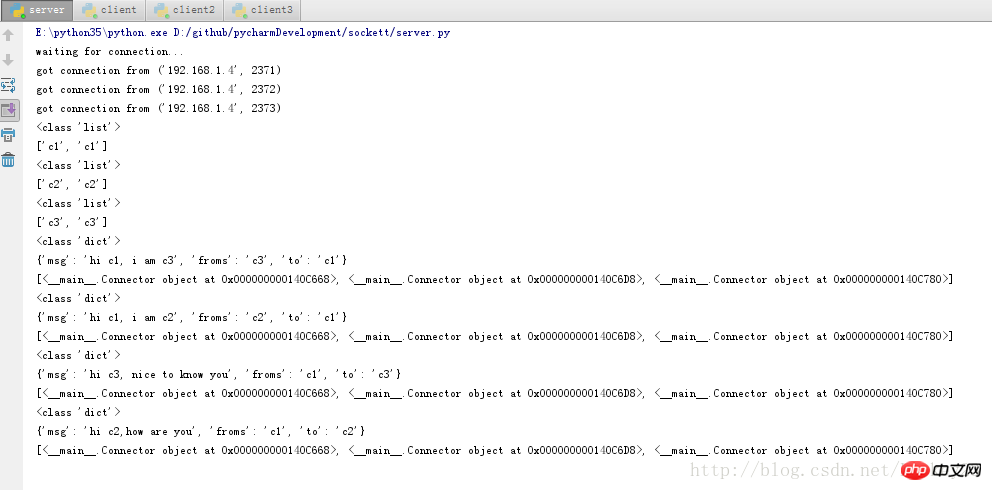
클라이언트 1:

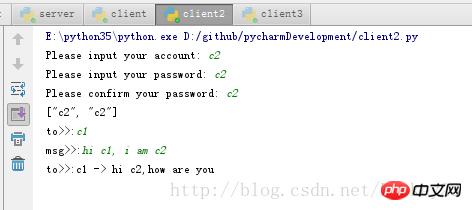
클라이언트 2:
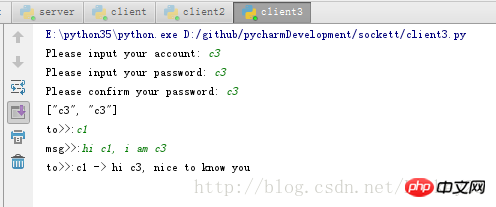
클라이언트 3:
위 내용은 Python 지점 간 간단한 구현의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
성명:
본 글의 내용은 네티즌들의 자발적인 기여로 작성되었으며, 저작권은 원저작자에게 있습니다. 본 사이트는 이에 상응하는 법적 책임을 지지 않습니다. 표절이나 침해가 의심되는 콘텐츠를 발견한 경우 admin@php.cn으로 문의하세요.
이전 기사:파이썬과 루비 비교다음 기사:파이썬과 루비 비교

