JAVAEE에 대한 자세한 소개—스프링
- PHP中文网원래의
- 2017-06-21 09:53:142105검색
1. 스프링 소개
1. 3티어 아키텍처에서 스프링의 위치
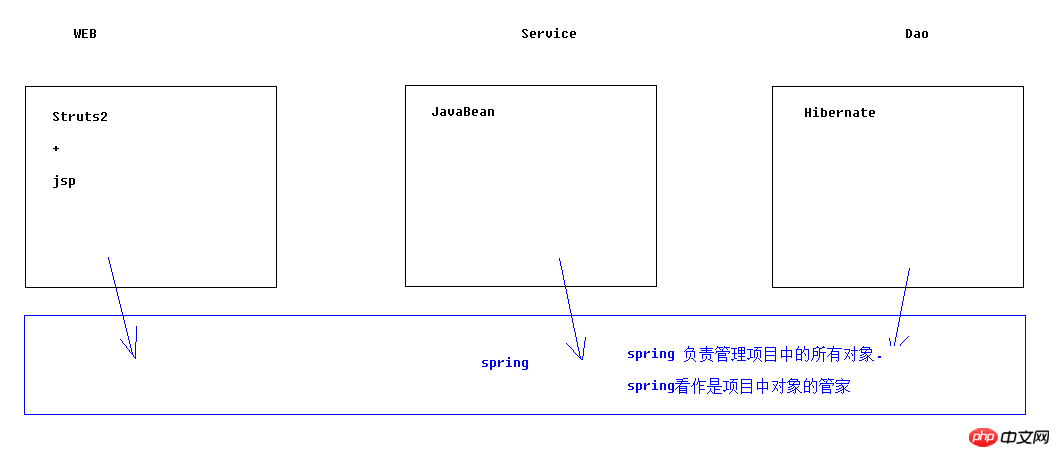
2. 스프링 원스톱 프레임워크
바로 스프링 프레임워크의 성격이 컨테이너이기 때문이다.
컨테이너에 어떤 객체가 설치되어 있든 어떤 기능을 하는지 그래서 원스톱샵이 될 수 있습니다.
다른 프레임워크를 배제할 뿐만 아니라 다른 프레임워크가 객체를 관리하는 데에도 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
Aop 지원, ioc 아이디어 , spring jdbc, aop 트랜잭션, junit 테스트 지원
두 번째, spring 구성
1. 가이드 패키지
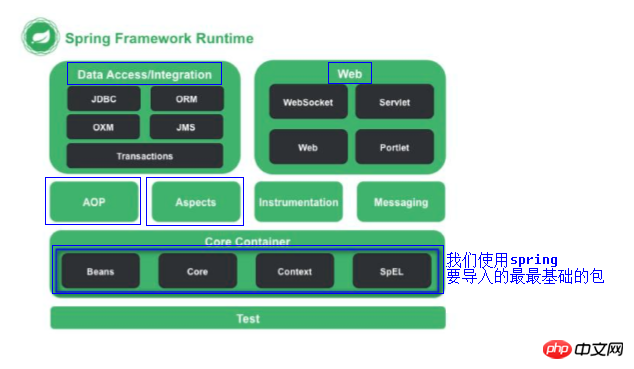
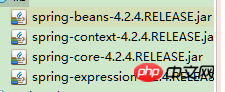
로그 패키지: com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging-1.1.1 .jar
선택 사항: com.springsource.org.apache.log4j-1.2 .15.jar (이전 버전을 가져와야 하며 가져오기를 하면 실행이 보장됩니다)
2. 객체 생성
public class User {private String name;private Integer age; public String getName() {return name;
}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;
}public Integer getAge() {return age;
}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;
}
}
3. 컨테이너에 구성 등록 객체 쓰기
모든 위치(src에 넣는 것이 좋습니다)
구성 파일의 이름은 임의적입니다(applicationContext.xml 권장)
가져오기 제약 조건:
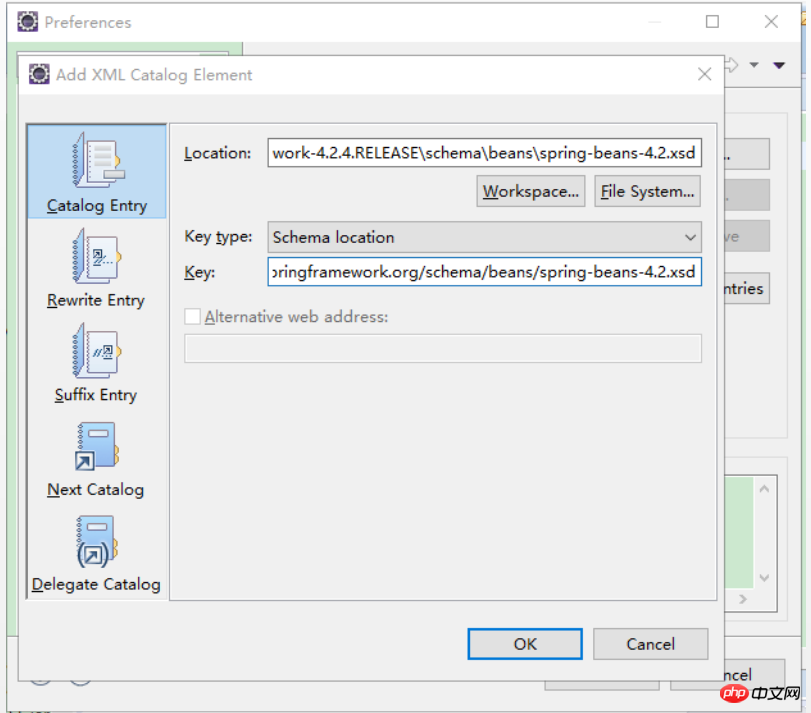
그런 다음 applicationContext를 편집합니다.
xsi 추가가 완료되었습니다. 마지막으로 추가를 다시 클릭하고 새 네임스페이스를 지정합니다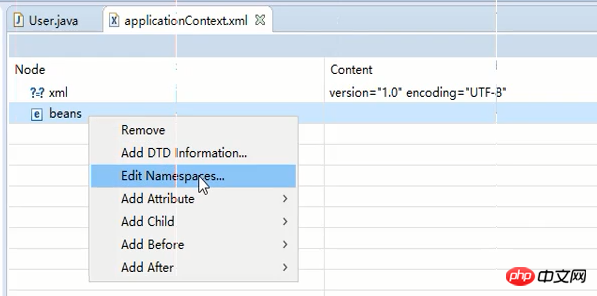
그런 다음 방금 가져온 xsd를 선택합니다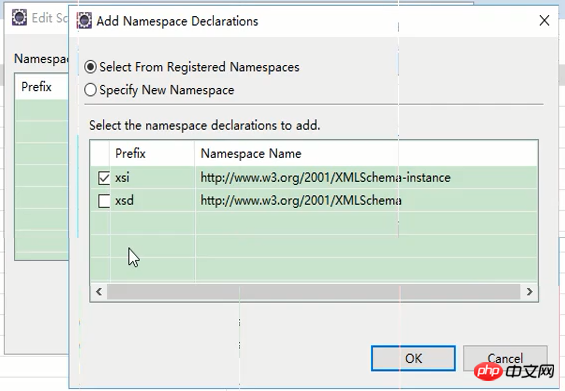
확인을 클릭하여 방금 페이지로 돌아갑니다. 그리고 네임스페이스 이름을 설정하고(위치 힌트 단락의 첫 번째 절반을 직접 복사할 수 있음) 접두사를 비워두세요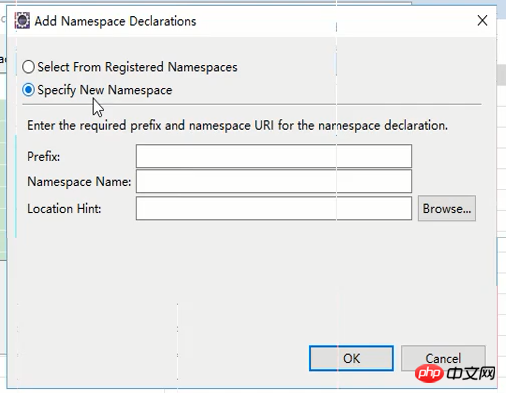
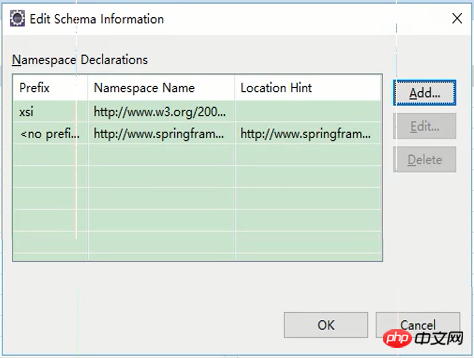
확인을 클릭하면 다음 인터페이스가 표시되어 가져오기가 성공했음을 나타냅니다. 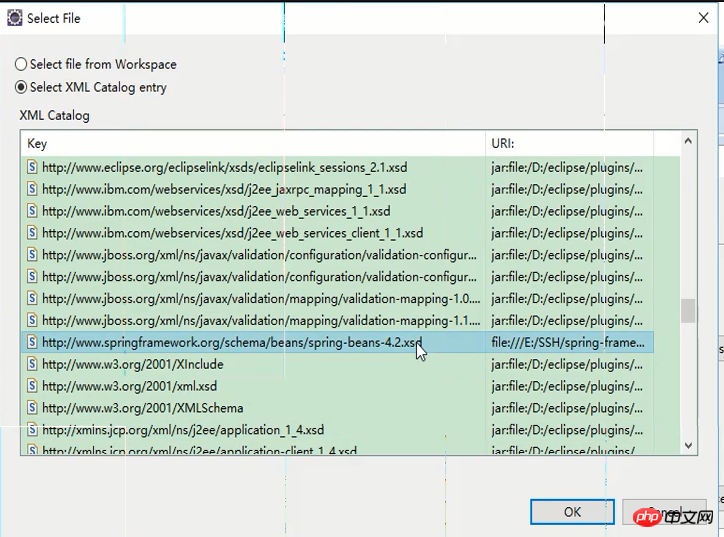
applicationContext.xml 작성: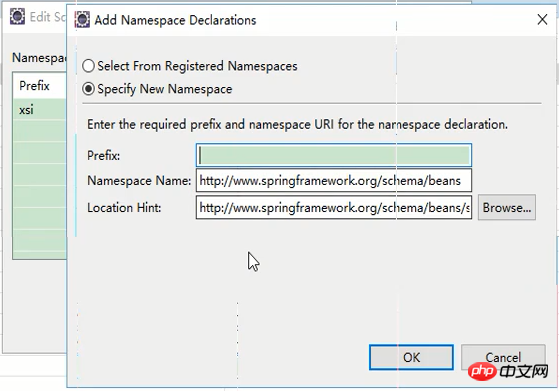
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans "><!-- 将User对象交给spring容器管理 --><bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ></bean></beans>
 4. 코드 테스트
4. 코드 테스트
@Testpublic void fun1(){ //1 创建容器对象ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//2 向容器"要"user对象User u = (User) ac.getBean("user");//3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u);
}
3, 스프링 개념
1. 생각
1.2 di

 BeanFactory 인터페이스 구현 클래스의 컨테이너가 특징입니다. 물건을 얻을 때마다.
BeanFactory 인터페이스 구현 클래스의 컨테이너가 특징입니다. 물건을 얻을 때마다.
2.2 ApplicationContext
컨테이너에 구성된 모든 객체는 컨테이너가 시작될 때마다 생성되며 더 많은 기능을 제공합니다.
클래스 경로에서 구성 파일을 로드합니다: ClassPath 1. Bean 요소
<!-- 将User对象交给spring容器管理 --><!-- Bean元素:使用该元素描述需要spring容器管理的对象
class属性:被管理对象的完整类名.
name属性:给被管理的对象起个名字.获得对象时根据该名称获得对象.
可以重复.可以使用特殊字符.
id属性: 与name属性一模一样.
名称不可重复.不能使用特殊字符.
结论: 尽量使用name属性. --><bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ></bean>
2.Bean元素进阶
2.1 scope属性
singleton(默认值):单例对象.被标识为单例的对象在spring容器中只会存在一个实例
prototype:多例原型.被标识为多例的对象,每次再获得才会创建.每次创建都是新的对象.整合struts2时,ActionBean必须配置为多例的.
request:web环境下.对象与request生命周期一致.
session:web环境下,对象与session生命周期一致.
2.2 生命周期属性
init-method:配置一个方法作为生命周期初始化方法.spring会在对象创建之后立即调用.
destory-method:配置一个方法作为生命周期的销毁方法.spring容器在关闭并销毁所有容器中的对象之前调用.
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean>
3.spring创建对象的方式
<!-- 创建方式1:空参构造创建(重点) --><bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean> <!-- 创建方式2:静态工厂创建 (了解)
调用UserFactory的createUser方法创建名为user2的对象.放入容器 --><bean name="user2"
class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory"
factory-method="createUser" ></bean><!-- 创建方式3:实例工厂创建 (了解)
调用UserFactory对象的createUser2方法创建名为user3的对象.放入容器 --><bean name="user3"
factory-bean="userFactory"factory-method="createUser2" ></bean><bean name="userFactory"
class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory" ></bean>4.spring的分模块配置
<!-- 导入其他spring配置文件 --><import resource="cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"/>
五、spring属性注入
1.注入方式
1.1 set方法注入(重中之重)
<!-- set方式注入: --><bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ><!--值类型注入: 为User对象中名为name的属性注入tom作为值 --><property name="name" value="tom" ></property><property name="age" value="18" ></property><!-- 引用类型注入: 为car属性注入下方配置的car对象 --><property name="car" ref="car" ></property></bean><!-- 将car对象配置到容器中 --><bean name="car" class="cn.itcast.bean.Car" ><property name="name" value="兰博基尼" ></property><property name="color" value="黄色" ></property></bean>
1.2 构造函数注入(重点)
<!-- 构造函数注入 --><bean name="user2" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ><!-- name属性: 构造函数的参数名 --><!-- index属性: 构造函数的参数索引 --><!-- type属性: 构造函数的参数类型--><constructor-arg name="name" index="0" type="java.lang.Integer" value="999" ></constructor-arg><constructor-arg name="car" ref="car" index="1" ></constructor-arg></bean>
1.3 p名称空间注入
<!-- p名称空间注入, 走set方法
1.导入P名称空间 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
2.使用p:属性完成注入
|-值类型: p:属性名="值"
|-对象类型: p:属性名-ref="bean名称" --><bean name="user3" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" p:name="jack" p:age="20" p:car-ref="car" ></bean>1.4 spel注入
<!--
spel注入: spring Expression Language sping表达式语言 --><bean name="user4" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ><property name="name" value="#{user.name}" ></property><property name="age" value="#{user3.age}" ></property><property name="car" ref="car" ></property></bean>2.复杂类型注入
2.1 数组
<!-- 如果数组中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可
<property name="arr" value="tom" ></property>--><!-- array注入,多个元素注入 --><property name="arr"><array><value>tom</value><value>jerry</value><ref bean="user4" /></array></property>2.2 List
<!-- 如果List中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可
<property name="list" value="jack" ></property>--><property name="list" ><list><value>jack</value><value>rose</value><ref bean="user3" /></list></property>2.3 Map
<!-- map类型注入 --><property name="map" ><map><entry key="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///crm" ></entry><entry key="user" value-ref="user4" ></entry><entry key-ref="user3" value-ref="user2" ></entry></map> </property>
2.4 Properties
<!-- prperties 类型注入 --><property name="prop" ><props><prop key="driverClass">com.jdbc.mysql.Driver</prop><prop key="userName">root</prop><prop key="password">1234</prop></props></property>
六、练习:将spring容器应用到struts-crm项目
管理Service对象以及Dao对象
1.导包(4+2),再加1
再加1指的是:spring-web-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar(因为要用到web的监听)
2.将Service对象以及Dao对象配置到spring容器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans "><!-- 配置Dao --><bean name="customerDao" class="cn.itheima.dao.impl.CustomerDaoImpl" ></bean><bean name="linkManDao" class="cn.itheima.dao.impl.LinkManDaoImpl" ></bean><bean name="userDao" class="cn.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" ></bean><!-- 配置Service --><bean name="customerService" class="cn.itheima.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl" ><property name="customerDao" ref="customerDao" ></property></bean><bean name="linkManService" class="cn.itheima.service.impl.LinkManServiceImpl" ><property name="cd" ref="customerDao" ></property><property name="lmd" ref="linkManDao" ></property></bean><bean name="userService" class="cn.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" ><property name="ud" ref="userDao" ></property></bean></beans>
3.在Action中获得容器中的Service对象
3.1 web.xml中配置容器随项目启动
<!-- 可以让spring容器随项目的启动而创建,随项目的关闭而销毁 --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 指定加载spring配置文件的位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param>
3.2 在Action中获得容器
//获得spring容器=>从Application域获得即可 //1 获得servletContext对象ServletContext sc = ServletActionContext.getServletContext();//2.从Sc中获得ac容器WebApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc);//3.从容器中获得CustomerServiceUserService us = (UserService) ac.getBean("userService");
4.管理容器在项目中的生命周期
下面错误的示范.导致每次请求都创建新的容器
//创建容器对象ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//获得cs(customerService对象)CustomerService cs = (CustomerService) ac.getBean("customerService");
위 내용은 JAVAEE에 대한 자세한 소개—스프링의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

