JPA를 통한 Java 데이터베이스 작업의 예에 대한 자세한 설명
- Y2J원래의
- 2017-05-06 13:19:153114검색
오늘은 SpringBoot에서 Mysql 데이터베이스에 접속하는 방법과 JPA를 이용해 데이터베이스 관련 작업을 수행하는 방법을 소개하겠습니다.
오늘은 SpringBoot에서 Mysql 데이터베이스에 접속하는 방법과 JPA를 이용해 데이터베이스 관련 작업을 수행하는 방법을 소개하겠습니다.
1단계: pom.xml 파일에 관련 Jar 패키지 종속성을 추가합니다. 구체적인 추가 위치는 다음과 같습니다. .
<!--数据库相关配置-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.11</version>
</dependency>2단계: application.properties 구성 파일에 해당 데이터베이스 구성을 추가합니다. 구성 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/webtest spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = 220316 spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # Specify the DBMS spring.jpa.database = MYSQL # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update # Naming strategy spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy # stripped before adding them to the entity manager) spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
설명은 다음과 같습니다. webtest는 데이터베이스 이름을 나타내고, root는 사용자 이름, 220316은 비밀번호입니다.
3단계: 데이터베이스 작업 의 엔터티 클래스, 엔터티 클래스의 구체적인 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
package example.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
@Column(name = "name", nullable = true, length = 30)
private String name;
@Column(name = "height", nullable = true, length = 10)
private int height;
@Column(name = "sex", nullable = true, length = 2)
private char sex;
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
private Date birthday;
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date sendtime; // 日期类型,格式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
@Column(name = "price", nullable = true, length = 10)
private BigDecimal price;
@Column(name = "floatprice", nullable = true, length = 10)
private float floatprice;
@Column(name = "doubleprice", nullable = true, length = 10)
private double doubleprice;
public Date getSendtime() {
return sendtime;
}
public void setSendtime(Date sendtime) {
this.sendtime = sendtime;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public float getFloatprice() {
return floatprice;
}
public void setFloatprice(float floatprice) {
this.floatprice = floatprice;
}
public double getDoubleprice() {
return doubleprice;
}
public void setDoubleprice(double doubleprice) {
this.doubleprice = doubleprice;
}
public User() { }
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
}여기서 모두가 주목해야 할 것은 클래스 이름과 필드 속성 엔터티 클래스의 필드는 데이터베이스의 테이블과 일치해야 합니다. 필드는 서로 일치합니다. 다음은 MYSQL-JAVA의 다양한 속성에 대한 대응도이다.
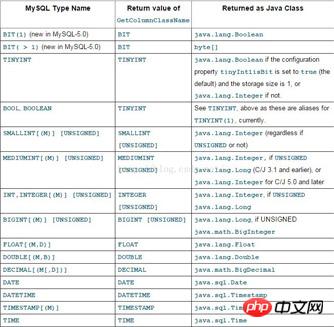
4단계: dao 레이어의 데이터 연산 클래스, dao 데이터 쓰기 오퍼레이션 클래스는 다음과 같습니다:
package example.dao;
import example.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Transactional
public interface UserDao extends CrudRepository<User, Integer> {
public List<User> findByName(String name);
public List<User> findBySex(char sex);
public List<User> findByBirthday(Date birthday);
public List<User> findBySendtime(Date sendtime);
public List<User> findByPrice(BigDecimal price);
public List<User> findByFloatprice(float floatprice);
public List<User> findByDoubleprice(double doubleprice);
}여기서 질문이 있을 수 있습니다. CrudRepository0e4b54218c9a07445335f10bb61dc1ba를 상속해야 하는 이유와 구체적인 역할은 무엇입니까?
여기에서는 JPA의 몇 가지 일반적인 사용 및 사용 지침에 대해 간략하게 소개하겠습니다.
1. two 두 매개변수의 구체적인 의미는 첫 번째 매개변수는 운용되는 엔터티 클래스의 이름을 나타내고, 두 번째 매개변수는 엔터티 클래스의 기본키 유형을 나타낸다.
2. 상속 후 상위 클래스에서 상속된 일부 메소드를 사용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 위와 같이 findBy+ "필드 이름을 쿼리하고 싶습니다. >", 이를 통해 SQL 쿼리의 기능을 쉽게 구현할 수 있는 방법이다.
5단계: 컨트롤 클래스 컨트롤러를 작성합니다. 컨트롤 클래스의 구체적인 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
package example.controller;
import example.dao.UserDao;
import example.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@RequestMapping("/getName")
@ResponseBody
public String getByName(String name) {
List<User> userList = userDao.findByName(name);
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + name + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getSex")
@ResponseBody
public String getBySex(char sex) {
List<User> userList = userDao.findBySex(sex);
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + sex + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getBirthday")
@ResponseBody
public String findByBirthday(String birthday) {
System.out.println("birthday:"+birthday);
SimpleDateFormat formate=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
List<User> userList = null;
try {
userList = userDao.findByBirthday(formate.parse(birthday));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + birthday + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getSendtime")
@ResponseBody
public String findBySendtime(String sendtime) {
System.out.println("sendtime:"+sendtime);
SimpleDateFormat formate=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
List<User> userList = null;
try {
userList = userDao.findBySendtime(formate.parse(sendtime));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + sendtime + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getPrice")
@ResponseBody
public String findByPrice(BigDecimal price) {
List<User> userList = null;
userList = userDao.findByPrice(price);
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + price + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getFloatprice")
@ResponseBody
public String findFloatprice(float floatprice) {
List<User> userList = null;
userList = userDao.findByFloatprice(floatprice);
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + floatprice + " is not exist.";
}
@RequestMapping("/getDoubleprice")
@ResponseBody
public String findByPrice(double doubleprice) {
List<User> userList = null;
userList = userDao.findByDoubleprice(doubleprice);
if (userList != null && userList.size()!=0) {
return "The user length is: " + userList.size();
}
return "user " + doubleprice + " is not exist.";
}
}여기서 큰 질문이 있을 수 있습니다. 나는 또한 처음에 이 문제를 깊이 무시했습니다. 즉, 왜 userDao를 인스턴스화하지 않고 직접 사용할 수 있습니까? . userDao 위에 @Autowired 속성만 추가하면 인터페이스를 자동으로 인스턴스화할 수 있으므로 이전처럼 userDaoImp와 같은 구현 클래스를 작성할 필요가 없습니다. 이를 통해 코드의 단순성과 개발 속도를 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
6단계: 데이터베이스의 테이블 이름과 필드 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
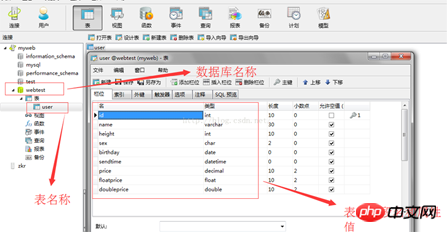
위 내용은 JPA를 통한 Java 데이터베이스 작업의 예에 대한 자세한 설명의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!

