.NET프레임워크의 LinkList는 이중 연결 목록을 구현합니다. 구현 소스 코드를 요약해 보겠습니다.
먼저 LinkedList에서 제공하는 공용 속성 및 메서드 맵을 살펴보세요.
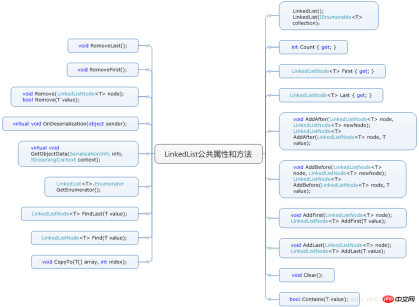
1 LinkedList에 의해 구현된 인터페이스:
public class LinkedList<T> : ICollection<T>, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback
2 LinkedList의 전역 변수에는
head가 포함됩니다. 은 캡슐화된 클래스의 헤드 노드입니다.
// This LinkedList is a doubly-Linked circular list.
internal LinkedListNode<T> head;
internal int count;
internal int version;
private object _syncRoot;
//A temporary variable which we need during deserialization.
private SerializationInfo _siInfo;
// names for serialization
private const string VersionName = "Version";
private const string CountName = "Count";
private const string ValuesName = "Data";캡슐화된 각 노드의 데이터 구조는 다음과 같습니다.
public sealed class LinkedListNode<T>
{ public LinkedListNode(T value);
//获取LinkedListNode所属的LinkedList
public LinkedList<T> List { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Next { get; }
public LinkedListNode<T> Previous { get; }
//获取节点中包含的值。
public T Value { get; set; }
}3 생성자 :
public LinkedList() //默认的构造函数
{
} //带有参数的
public LinkedList(IEnumerable<T> collection)
{ if (collection == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(collection));
} foreach (T item in collection)
{
AddLast(item);
}
}는 IEnumerable 유형의 컬렉션을 구성할 때 AddLast(T) 메서드를 사용합니다. 여기에는 오버로드도 포함됩니다.
public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
}
public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this; //结合LinkedListNode看
}위 내용은 다음과 같습니다. 2가지 방법에서 의미론은 노드를 삽입하는 것입니다.
빈 목록에 새 노드를 삽입하고 InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList
비어 있지 않은 목록인 InternalInsertNodeBefore에 새 노드를 삽입하고 newNode가 삽입되기 전에 노드를 제공합니다. 또한 새로 삽입된 노드는 유효한 새 노드가 아니라고 판단합니다.
internal void ValidateNewNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != null)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.LinkedListNodeIsAttached);
}
}동시에 노드가 유효한 노드인지 확인하는 방법도 제공합니다.
internal void ValidateNode(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{ if (node == null)
{ throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(node));
} if (node.list != this)
{ throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.ExternalLinkedListNode);
}
}이것은 이중 연결 목록의 중요한 내부 방법입니다
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList의 구현 세부 사항:
private void InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
Debug.Assert(head == null && count == 0, "LinkedList must be empty when this method is called!");
newNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}InternalInsertNodeBefore 구현 세부 사항:
private void InternalInsertNodeBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
newNode.next = node;
newNode.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = newNode;
node.prev = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}4 연결된 목록은 노드를 삽입하는 공용 메서드
public LinkedListNode<T> AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, result); return result;
} public void AddAfter(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node.next, newNode);
newNode.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, T value)
{
ValidateNode(node);
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(node.list, value);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, result); if (node == head)
{
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
ValidateNode(node);
ValidateNewNode(newNode);
InternalInsertNodeBefore(node, newNode);
newNode.list = this; if (node == head)
{
head = newNode;
}
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddFirst(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
head = result;
} return result;
} public void AddFirst(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
head = node;
}
node.list = this;
} public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
} return result;
} public void AddLast(LinkedListNode<T> node)
{
ValidateNewNode(node); if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(node);
} else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, node);
}
node.list = this;
}5와 자연스럽게 분리될 수 없습니다. 다시 보면 연결리스트에 있는 모든 노드를 삭제하고, 여기에서는 모든 노드가 메모리 힙을 가리키지 않도록 설정한 다음 GC 재활용을 기다리는 것인데,
public void Clear()
{
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
while (current != null)
{
LinkedListNode<T> temp = current;
current = current.Next;
// use Next the instead of "next", otherwise it will loop forever
temp.Invalidate();
}
head = null;
count = 0;
version++;
}6에 해당하는 것은 a만 제거하는 것입니다. 추가와 유사하며 자세히 설명하지 않을 특정 노드의 일련의 인터페이스
Clear는 Invalidate()를 호출하고 구현은 매우 간단합니다.
internal void Invalidate()
{
list = null;
next = null;
prev = null;
}7 결정하려면 노드 값이 값으로 존재하면 Find 메서드,
public bool Contains(T value)
{ return Find(value) != null;
}Find 메서드 구현 세부 정보를 호출합니다. API 및 FindLast와 유사합니다. 연결 목록 방식이므로 끝에서 연결 목록을 순회하세요.
public LinkedListNode<T> Find(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
//调用默认相等比较器
EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default;
if (node != null)//链表为null
{
if (value != null)
{
do
{
if (c.Equals(node.item, value)) //Equals:某个节点node的item与value相等
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
else
{
do
{
if (node.item == null)
{
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
} return null; //链表为null,直接返回null
}8 배열 구현에 대한 또 다른 데이터 복사본을 살펴보겠습니다.
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int index)
{
if (array == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(array));
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNum);
}
if (index > array.Length)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index), index, SR.ArgumentOutOfRange_BiggerThanCollection);
}
if (array.Length - index < Count)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Arg_InsufficientSpace);
}
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
if (node != null)
{
do
{
array[index++] = node.item;
node = node.next;
} while (node != head); //双向链表,再次遍历到头结点时
}
}위 내용은 .NET Framework-이중 연결 목록(LinkedList) 코드 분석(그림)의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
 C# .NET로 개발 : 실용적인 가이드 및 예제May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
C# .NET로 개발 : 실용적인 가이드 및 예제May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMC# 및 .NET은 강력한 기능과 효율적인 개발 환경을 제공합니다. 1) C#은 C의 힘과 Java의 단순성을 결합한 최신 객체 지향 프로그래밍 언어입니다. 2) .NET 프레임 워크는 여러 프로그래밍 언어를 지원하는 응용 프로그램을 구축하고 실행하는 플랫폼입니다. 3) C#의 클래스와 객체는 객체 지향 프로그래밍의 핵심입니다. 클래스는 데이터와 동작을 정의하고 객체는 클래스의 사례입니다. 4) .NET의 쓰레기 수집 메커니즘은 자동으로 메모리를 관리하여 개발자의 작업을 단순화합니다. 5) C# 및 .NET은 강력한 파일 작업 기능을 제공하여 동기 및 비동기 프로그래밍을 지원합니다. 6) 디버거, 로깅 및 예외 처리를 통해 일반적인 오류를 해결할 수 있습니다. 7) 성능 최적화 및 모범 사례에는 StringBuild 사용이 포함됩니다
 C# .NET : Microsoft .NET 프레임 워크 이해May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM
C# .NET : Microsoft .NET 프레임 워크 이해May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM.NETFRAMEWORK는 일관된 프로그래밍 모델과 강력한 런타임 환경을 제공하는 교차 문자 크로스 플랫폼 개발 플랫폼입니다. 1) CLR 및 FCL로 구성되어 메모리와 스레드를 관리하고 FCL은 사전 제작 된 기능을 제공합니다. 2) 사용의 예로는 파일 읽기 및 LINQ 쿼리가 포함됩니다. 3) 일반적인 오류에는 처리되지 않은 예외와 메모리 누출이 포함되며 디버깅 도구를 사용하여 해결해야합니다. 4) 비동기 프로그래밍 및 캐싱을 통해 성능 최적화를 달성 할 수 있으며 코드 가독성 및 유지 관리 가능성을 유지하는 것이 중요합니다.
 C# .net의 수명 : 지속적인 인기에 대한 이유May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AM
C# .net의 수명 : 지속적인 인기에 대한 이유May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AMC#.NET이 지속적으로 매력적으로 유지되는 이유는 우수한 성능, 풍부한 생태계, 강력한 지역 사회 지원 및 크로스 플랫폼 개발 기능을 포함합니다. 1) 탁월한 성능과 엔터프라이즈 수준의 응용 프로그램 및 게임 개발에 적합합니다. 2) .NET 프레임 워크는 다양한 개발 분야를 지원하기위한 광범위한 클래스 라이브러리 및 도구를 제공합니다. 3) 활발한 개발자 커뮤니티와 풍부한 학습 리소스가 있습니다. 4) .netCore는 크로스 플랫폼 개발을 실현하고 응용 프로그램 시나리오를 확장합니다.
 C# .NET 디자인 패턴 마스터 링 : 싱글 톤에서 종속성 주입까지May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
C# .NET 디자인 패턴 마스터 링 : 싱글 톤에서 종속성 주입까지May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AMC#.NET의 설계 패턴에는 싱글 톤 패턴 및 종속성 주입이 포함됩니다. 1. Singleton Mode는 클래스의 인스턴스가 하나 뿐이며 글로벌 액세스 포인트가 필요한 시나리오에 적합하지만 스레드 안전 및 남용 문제에주의를 기울여야합니다. 2. 종속성 주입은 종속성을 주입하여 코드 유연성과 테스트 가능성을 향상시킵니다. 그것은 종종 생성자 주입에 사용되지만 복잡성을 증가시키기 위해 과도한 사용을 피해야합니다.
 현대 세계의 C# .net : 응용 및 산업May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AM
현대 세계의 C# .net : 응용 및 산업May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AMC#.net은 현대 세계에서 게임 개발, 금융 서비스, 사물 인터넷 및 클라우드 컴퓨팅 분야에서 널리 사용됩니다. 1) 게임 개발에서 C#을 사용하여 Unity 엔진을 통해 프로그래밍하십시오. 2) 금융 서비스 분야에서 C#.NET은 고성능 거래 시스템 및 데이터 분석 도구를 개발하는 데 사용됩니다. 3) IoT 및 클라우드 컴퓨팅 측면에서 C#.NET은 Azure 서비스를 통해 지원을 제공하여 장치 제어 로직 및 데이터 처리를 개발합니다.
 C# .NET 프레임 워크 대 .NET Core/5/6 : 차이점은 무엇입니까?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C# .NET 프레임 워크 대 .NET Core/5/6 : 차이점은 무엇입니까?May 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM.NETFRAMEWORKISWINDOWS 중심, while.netCore/5/6 SupportScross-PlatformDevelopment.1) .NETFramework, 2002 년 이후, isidealforwindowsapplicationsButlimitedIncross-platformcapabilities.2) .netcore, 2016, anditsevolutions (.net5/6).
 C# .NET 개발자 커뮤니티 : 리소스 및 지원May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C# .NET 개발자 커뮤니티 : 리소스 및 지원May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AMC#.NET 개발자 커뮤니티는 다음을 포함하여 풍부한 리소스와 지원을 제공합니다. 1. Microsoft의 공식 문서, 2. StackoverFlow 및 Reddit과 같은 커뮤니티 포럼, 3. GitHub의 오픈 소스 프로젝트. 이러한 리소스는 개발자가 기본 학습에서 고급 응용 프로그램에 이르기까지 프로그래밍 기술을 향상시키는 데 도움이됩니다.
 C# .NET 장점 : 기능, 이점 및 사용 사례May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C# .NET 장점 : 기능, 이점 및 사용 사례May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AMC#.net의 장점은 다음과 같습니다. 1) 비동기 프로그래밍과 같은 언어 기능은 개발을 단순화합니다. 2) JIT 컴파일 및 쓰레기 수집 메커니즘을 통한 효율성 향상, 성능 및 신뢰성; 3) 크로스 플랫폼 지원, .netcore는 응용 프로그램 시나리오를 확장합니다. 4) 웹에서 데스크탑 및 게임 개발에 이르기까지 뛰어난 성능을 가진 광범위한 실제 응용 프로그램.


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

SublimeText3 Mac 버전
신 수준의 코드 편집 소프트웨어(SublimeText3)

맨티스BT
Mantis는 제품 결함 추적을 돕기 위해 설계된 배포하기 쉬운 웹 기반 결함 추적 도구입니다. PHP, MySQL 및 웹 서버가 필요합니다. 데모 및 호스팅 서비스를 확인해 보세요.

드림위버 CS6
시각적 웹 개발 도구

ZendStudio 13.5.1 맥
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.





