Python을 사용하여 간단한 포트 스캐너를 구현하는 방법 소개
- 高洛峰원래의
- 2017-03-15 13:37:421494검색
Python소켓프로그래밍실습이라고 생각되는 인터넷상의 일부 정보를 바탕으로 새로운 내용을 추가했습니다.
#coding=utf-8
import socket
import time
import sys
import struct
import threading
from threading import Thread,activeCount
results=[]
def portScanner(ip,port):
server = (ip,port)
sockfd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sockfd.settimeout(0.1) #设置阻塞模式下socket的超时时间
ret = sockfd.connect_ex(server) #成功返回0,失败返回error的值。
if not ret:
sockfd.close()
results.append([ip,port])
#print '%s:%s is opened...' % (ip,port)
else:
sockfd.close()
pass
return ''
def ip2num(ip): #将ip地址转换成数字
lp = [int(x) for x in ip.split('.')]
return lp[0] << 24 | lp[1] << 16 | lp[2] << 8 |lp[3]
def num2ip(num):
ip = ['','','','']
ip[3] = (num & 0xff)
ip[2] = (num & 0xff00) >> 8
ip[1] = (num & 0xff0000) >> 16
ip[0] = (num & 0xff000000) >> 24
return '%s.%s.%s.%s' % (ip[0],ip[1],ip[2],ip[3])
def iprange(ip1,ip2):
num1 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip1)))[0])
num2 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip2)))[0])
tmp = num2 - num1
if tmp < 0:
return None
else:
return num1,num2,tmp
if name == 'main':
if((len(sys.argv)!= 4)&(len(sys.argv)!= 2)): #用法说明
print 'Usage:\n\tscanner.py startip endip port'
print '\tscanner.py ip'
sys.exit()
if len(sys.argv)==4: #对某一IP段的扫描
time_start=time.time() #起始时间
startip = sys.argv[1] #起始IP
endip = sys.argv[2] #结束IP
port = int(sys.argv[3]) #端口号
res = iprange(startip,endip)
if not res:
print 'endip must be bigger than startone'
sys.exit()
elif res[2] == 0:
portScanner(startip,port)
else:
for x in xrange(int(res[2])+1): #IP地址依次递增
startipnum = ip2num(startip)
startipnum = startipnum + x
if activeCount() <=1000:
Thread(target=portScanner,args=(num2ip(startipnum),port)).start()
print "There are %d hosts." %len(results)
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start #用时
print 'use time : %s' % times
if len(sys.argv)==2:
time_start=time.time()
port=0
ip=sys.argv[1]
while(port<2000):
if activeCount() <= 40: #设置40线程扫描
Thread(target = portScanner, args = (ip, port)).start()
port=port+1
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start
print 'use time : %s' % times
효과는 다음과 같습니다.
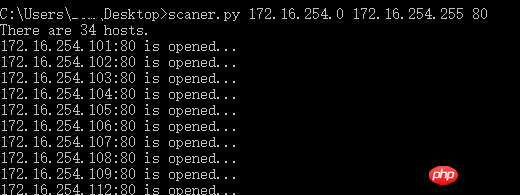

위 내용은 Python을 사용하여 간단한 포트 스캐너를 구현하는 방법 소개의 상세 내용입니다. 자세한 내용은 PHP 중국어 웹사이트의 기타 관련 기사를 참조하세요!
성명:
본 글의 내용은 네티즌들의 자발적인 기여로 작성되었으며, 저작권은 원저작자에게 있습니다. 본 사이트는 이에 상응하는 법적 책임을 지지 않습니다. 표절이나 침해가 의심되는 콘텐츠를 발견한 경우 admin@php.cn으로 문의하세요.
이전 기사:python-csv 사용 소개다음 기사:python-csv 사용 소개

