물체 운동의 원리: 물체의 위치를 바꾸면 움직임이 변합니다. 모든 움직임은 물리학의 움직임 공식처럼 상대적입니다: s(달성됨) = s0(현재 스타일 값) vt.
방법:
1. 움직이는 물체에는 절대 위치 지정을 사용합니다
2. 위치가 지정된 개체의 속성(왼쪽, 오른쪽, 위쪽, 아래쪽)을 변경하여 개체를 이동합니다. 예를 들어 오른쪽이나 왼쪽으로 이동하려면 offsetLeft(offsetRight)를 사용하여 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 이동을 제어할 수 있습니다.
단계:
1. 이동을 시작하기 전, 기존 타이머를 클리어 해주세요. (왜냐면: 버튼을 연속해서 클릭하면 물체가 점점 더 빠르게 이동하여 이동 혼란을 야기하기 때문입니다.)
2. 타이머를 켜고 속도를 계산해보세요
3. 이동과 정지(if/else)를 분리하여 정지 조건을 판단하고 이동을 실행합니다
핵심사항:
1. 다중 개체
물체에 타이머를 부착하세요
2. 체인 모션
루프에서 타이머 호출: fnEnd 함수에서 다른 타이머 시작
3. 다중 가치 스포츠
루프 속성 값 배열: 타이머 시간, 여러 속성 값 변경 실행
이동이 끝났고 모든 속성이 미리 결정된 값에 도달했는지 확인합니다. 시작 부분에 부울 플래그를 추가합니다. var bStop=true; //가정: 루프 중에 모든 값이 도착했습니다. if(cur! =json[ attr]) bStop=false;
1. 타이머
자바스크립트에는 타이머 전용 함수가 두 개 있습니다.
1. 카운트다운 타이머: timename=setTimeout("function();",delaytime);
2. 루프 타이머: timename=setInterval("function();",delaytime)
Function()은 타이머가 실행될 때 실행되는 이벤트 함수입니다. 하나의 함수일 수도 있고, 여러 함수일 수도 있고, ";delaytime"으로만 구분하면 됩니다. 간격(밀리초)입니다.
카운트다운 타이머는 지정된 시간 후에 이벤트를 트리거하는 반면, 루프 타이머는 간격이 도래할 때 이벤트를 반복적으로 트리거하는 반면, 전자는 한 번만 작동하고 후자는 지속적으로 작동한다는 점입니다.
카운트다운 타이머는 일반적으로 페이지가 한 번만 실행되어야 하는 상황에서 사용됩니다. 예를 들어 특정 버튼을 클릭하면 일정 시간이 지나면 페이지가 해당 사이트로 이동하는지 여부를 결정하는 데에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 방문자는 귀하의 사이트에 있는 "오래된 방문자"입니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 5초 또는 10초 후에 해당 사이트로 점프한 다음 특정 버튼을 눌러 빠르게 들어갈 수 있다고 알려주세요. 나중에 다시 옵니다.
루프 타이머는 일반적으로 JavaScript 스크롤 막대나 상태 표시줄과 같이 사이트에서 반복적으로 실행되어야 하는 효과에 사용됩니다. 또한 날아다니는 눈 그림으로 페이지 배경을 나타내는 데에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 이벤트는 간격을 두고 실행되어야 합니다.
때로는 추가된 일부 타이머를 제거하고 싶을 때도 있습니다. 이 경우에는clearTimeout(timename)을 사용하여 카운트다운 타이머를 끄고,clearInterval(timename)을 사용하여 루프 타이머를 끌 수 있습니다.
2. 운동 연구
1. 운동 : 등속운동(물체를 움직이게 하는 것)
타이머 사용
DIV에 절대 위치 지정 추가
오프셋왼쪽
문제: 특정 위치에 정지 문자가 도달했습니다
해결책: 판단하고 조건이 충족되면 타이머를 끄세요(타이머 저장)
속도가 느려집니다 (보통 시간은 변하지 않지만 숫자 속도는 변합니다)
변수를 사용하여 속도 저장
문제: 7을 취하고 offsetLeft가 300이 아닌 경우 div를 중지할 수 없습니다.
해결책:>=300 //301에서 중지
문제: 300에 도달한 후에도 버튼을 클릭하면 계속 진행됩니다
이유: 버튼을 클릭하고 기능을 실행한 후 타이머를 시작합니다(현재 기능을 한 번 이상 실행)
해결책: else 추가(대상에 도달하기 전에 실행)
문제: 계속 클릭하면 속도가 빨라집니다
이유: 클릭할 때마다 타이머가 시작됩니다. 여러 번 클릭하면 여러 타이머가 동시에 작동합니다.
해결 방법: 한 번에 하나의 타이머만 작동하도록 하려면 먼저 간격()
예 1, 공유 대상:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>分享到</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:150px; height:200px; background:green; position:absolute; left:-150px;}
#div1 span {position:absolute; width:20px; height:60px; line-height:20px; background:blue; right:-20px; top:70px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(0);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(-150);
};
};
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft>iTarget)
{
speed=-10;
}
else
{
speed=10;
}
if(oDiv.offsetLeft==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<span>分享到</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
효과는 다음과 같습니다.

예 2, 페이드 인 및 페이드 아웃:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>淡入淡出</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:200px; height:200px; background:red; filter:alpha(opacity:30); opacity:0.3;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv.onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(100);
};
oDiv.onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(30);
};
};
var alpha=30;
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(alpha<iTarget)
{
speed=10;
}
else
{
speed=-10;
}
if(alpha==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(timer);
}
else
{
alpha+=speed;
oDiv.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+alpha+')';
oDiv.style.opacity=alpha/100;
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1"></div>
</body>
</html>
효과는 다음과 같습니다.
등속 운동을 위한 정지 조건
충분히 가까워요
예제 3, 등속 운동 정지 조건:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>匀速运动的停止条件</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
#div3 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:100px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
var timer=null;
function startMove(iTarget)
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
clearInterval(timer);
timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=0;
if(oDiv.offsetLeft<iTarget)
{
speed=7;
}
else
{
speed=-7;
}
if(Math.abs(iTarget-oDiv.offsetLeft)<=7)
{
clearInterval(timer);
oDiv.style.left=iTarget+'px';
}
else
{
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="到100" onclick="startMove(100)" />
<input type="button" value="到300" onclick="startMove(300)" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
<div id="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
2.变速运动(缓冲运动)
逐渐变慢,最后停止
距离越远速度越大
速度有距离决定
速度=(目标值-当前值)/缩放系数
如果没有缩放系数t速度太大,瞬间到达终点.没有过程
问题:并没有真正到达300
原因:速度只剩0.9 //像素是屏幕能够显示的最/J库位,并不会四舍五入掉
Math.ceil ()向上取整
Math.floor ()向下取整
问题:向左走,又差一块--Math.floor ()
判断:三目 speed=speed>0 ? Math.ceil ( speed ): Math.floor ( speed )
示例,缓冲运动:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>缓冲运动</title>
<style>
#div1 {width:100px; height:100px; background:red; position:absolute; left:600px; top:50px;}
#div2 {width:1px; height:300px; position:absolute; left:300px; top:0; background:black;}
</style>
<script>
function startMove()
{
var oDiv=document.getElementById('div1');
setInterval(function (){
var speed=(300-oDiv.offsetLeft)/10;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
oDiv.style.left=oDiv.offsetLeft+speed+'px';
document.title=oDiv.offsetLeft+','+speed;
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="开始运动" onclick="startMove()" />
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:

3.多物体运动
多个div ,鼠标移入变宽
运动框架传参obj,知道让哪个物体动起来
用到缓冲一定要取整
问题:div没运动回去 //清除前一个定时器
原因:只有一个定时器
解决:加物体上的定时器,使每个物体都有一个定时器。定时器作为物体属性
多个div淡入淡出
首先关闭物体上的定时器
经验:多物体运动框架所有东西都不能共用
问题:不是因为定时器,而是因为alpha
解决:作为属性附加到物体上 /不以变量形式存在
offset 的 bug
加border变宽
offsetWith并不是真正的width ,它获取的是盒模型尺寸
解决:躲着 宽度扔到行间,parselnt ( oDiv.style.width )
进一步解决: getStyle ( obj, name ) currentStyle , getComputedStyle
加border ,只要offset就有问题 去掉offset
示例,多物体运动:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:100px; height:50px; background:red; margin:10px; border:10px solid black;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var aDiv=document.getElementsByTagName('div');
for(var i=0;i<aDiv.length;i++)
{
aDiv[i].timer=null;
aDiv[i].onmouseover=function ()
{
startMove(this, 400);
};
aDiv[i].onmouseout=function ()
{
startMove(this, 100);
};
}
};
function startMove(obj, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var speed=(iTarget-obj.offsetWidth)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(obj.offsetWidth==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style.width=obj.offsetWidth+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
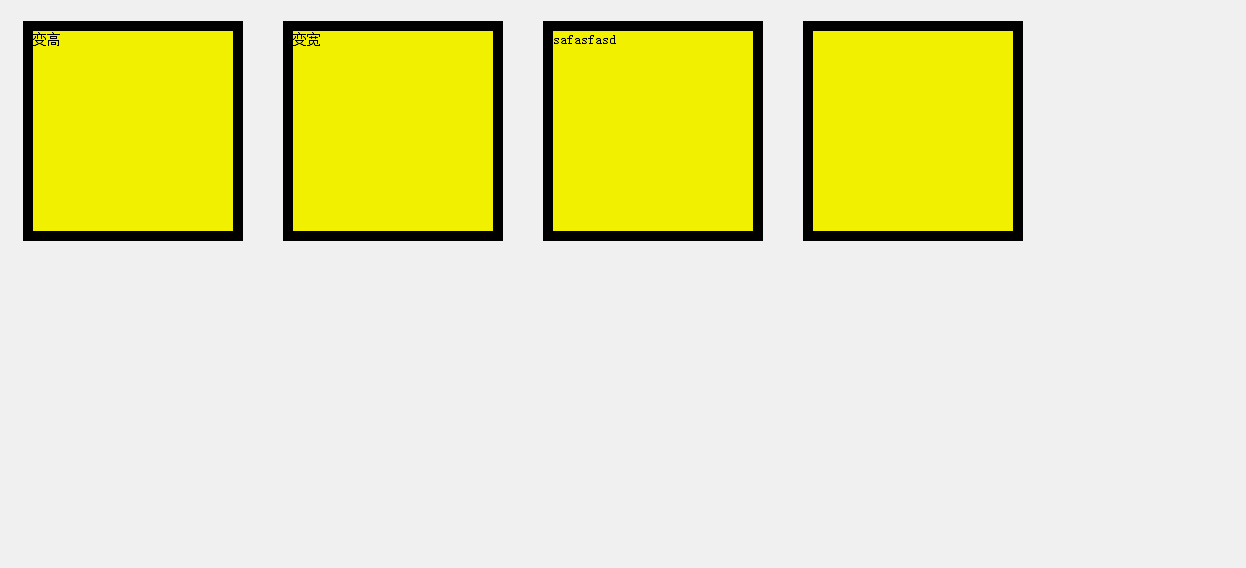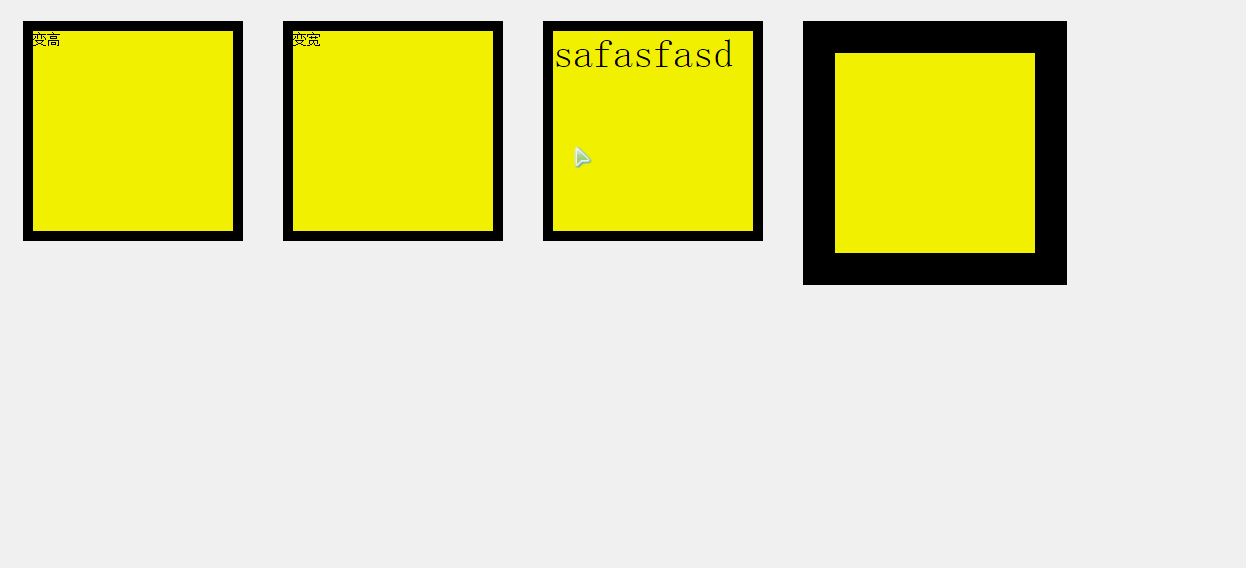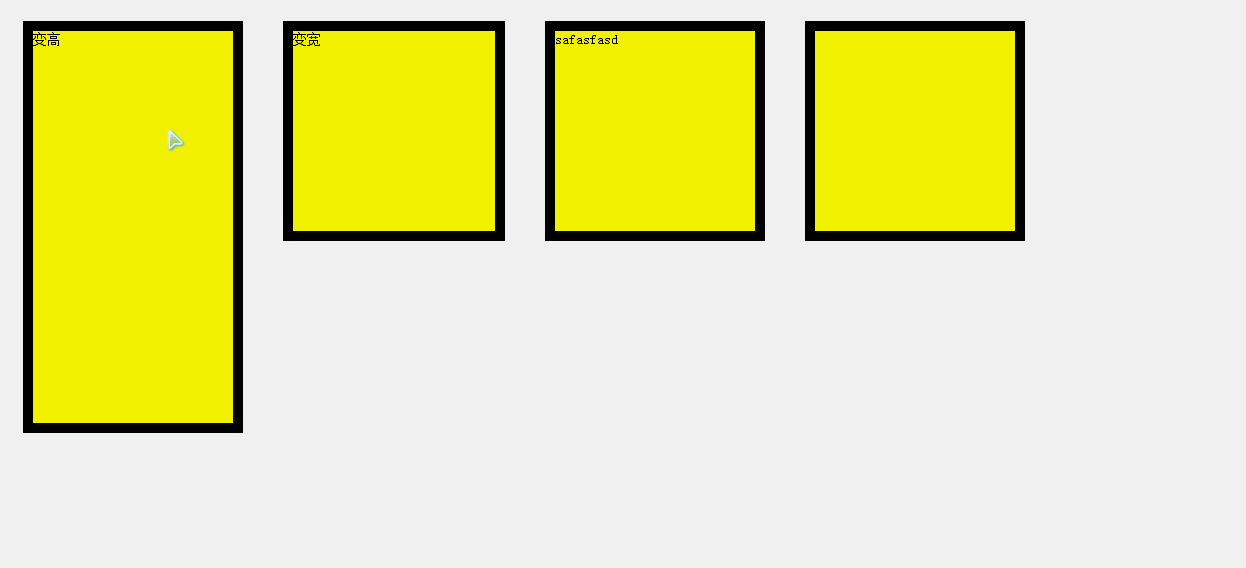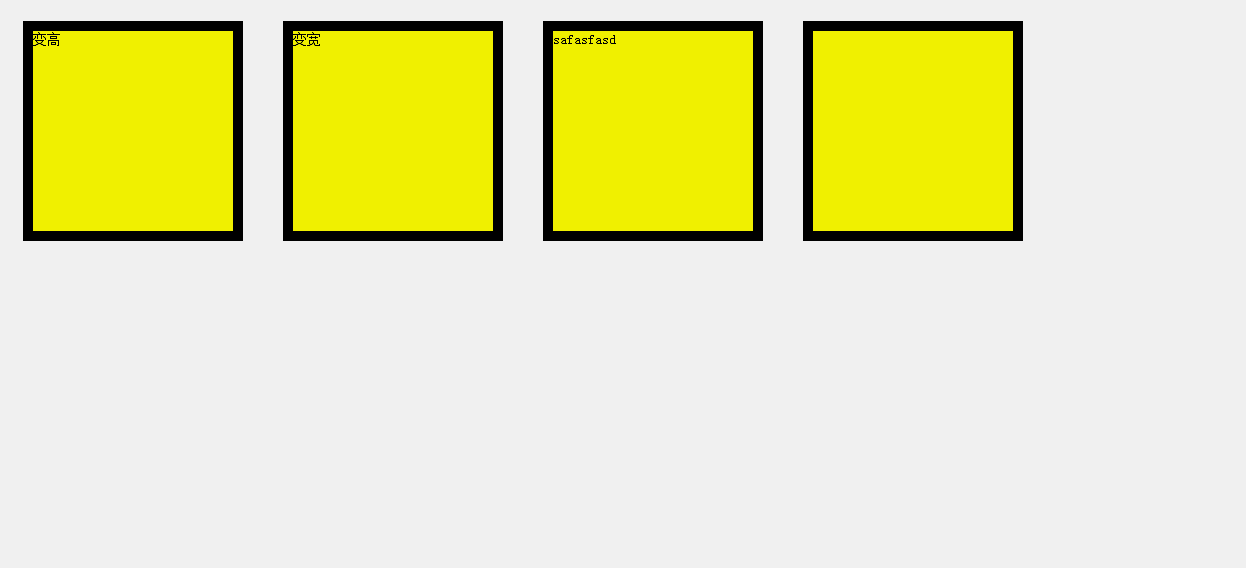
4.任意值运动
任意值运动的单位分为透明度和px。
px单位的任意值
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:200px; height:200px; margin:20px; float:left; background:yellow; border:10px solid black; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv1=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv1.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 400);};
oDiv1.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 200);};
var oDiv2=document.getElementById('div2');
oDiv2.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 400);};
oDiv2.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 200);};
var oDiv3=document.getElementById('div3');
oDiv3.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 50);};
oDiv3.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 14);};
var oDiv4=document.getElementById('div4');
oDiv4.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 100);};
oDiv4.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 10);};
};
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle){return obj.currentStyle[name];}
else{return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];}
}
function startMove(obj, attr, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
var speed=(iTarget-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">变高</div>
<div id="div2">变宽</div>
<div id="div3">safasfasd</div>
<div id="div4"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
div {width:200px; height:200px; margin:20px; float:left; background:yellow; border:10px solid black; font-size:14px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload=function ()
{
var oDiv1=document.getElementById('div1');
oDiv1.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 400);};
oDiv1.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'height', 200);};
var oDiv2=document.getElementById('div2');
oDiv2.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 400);};
oDiv2.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'width', 200);};
var oDiv3=document.getElementById('div3');
oDiv3.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 50);};
oDiv3.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'fontSize', 14);};
var oDiv4=document.getElementById('div4');
oDiv4.onmouseover=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 100);};
oDiv4.onmouseout=function (){startMove(this, 'borderWidth', 10);};
};
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle){return obj.currentStyle[name];}
else{return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];}
}
function startMove(obj, attr, iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
var speed=(iTarget-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur==iTarget)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}, 30);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">变高</div>
<div id="div2">变宽</div>
<div id="div3">safasfasd</div>
<div id="div4"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
透明度的任意值,需要做判断:
判断
var cur=0
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
cur=parseFloat ( getStyle ( obj, attr)) *100
}else{
}
设置样式判断
if ( attr== 'opacity '){
obj.style.fiIter = 'alpha ( opacity: '( cur+speed ) + ')'
obj.style.opacity= ( cur+speed ) /100
}else{
}
5.链式运动
多出来的一个参数,只有传进去的时候才调用
鼠标移入变宽,结束之后弹出abc
先横向展开.再以向展开
鼠标移出,先变回不透明,变矮,变窄
三.封装运动框架
基于以上的分析与总结,封装运动框架move.js如下:
function getStyle(obj, name)
{
if(obj.currentStyle)
{
return obj.currentStyle[name];
}
else
{
return getComputedStyle(obj, false)[name];
}
}
function startMove(obj, json, fnEnd)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
obj.timer=setInterval(function (){
var bStop=true; //假设:所有值都已经到了
for(var attr in json)
{
var cur=0;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
cur=Math.round(parseFloat(getStyle(obj, attr))*100);
}
else
{
cur=parseInt(getStyle(obj, attr));
}
var speed=(json[attr]-cur)/6;
speed=speed>0?Math.ceil(speed):Math.floor(speed);
if(cur!=json[attr])
bStop=false;
if(attr=='opacity')
{
obj.style.filter='alpha(opacity:'+(cur+speed)+')';
obj.style.opacity=(cur+speed)/100;
}
else
{
obj.style[attr]=cur+speed+'px';
}
}
if(bStop)
{
clearInterval(obj.timer);
if(fnEnd)fnEnd();
}
}, 30);
}
move.js运动框架基本满足现在网页上所有动画的需求(不包括css3)。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。
 JavaScript가 C로 작성 되었습니까? 증거를 검토합니다Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
JavaScript가 C로 작성 되었습니까? 증거를 검토합니다Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM예, JavaScript의 엔진 코어는 C로 작성되었습니다. 1) C 언어는 효율적인 성능과 기본 제어를 제공하며, 이는 JavaScript 엔진 개발에 적합합니다. 2) V8 엔진을 예를 들어, 핵심은 C로 작성되며 C의 효율성 및 객체 지향적 특성을 결합하여 C로 작성됩니다.
 JavaScript의 역할 : 웹 대화식 및 역동적 인 웹Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript의 역할 : 웹 대화식 및 역동적 인 웹Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript는 웹 페이지의 상호 작용과 역학을 향상시키기 때문에 현대 웹 사이트의 핵심입니다. 1) 페이지를 새로 고치지 않고 콘텐츠를 변경할 수 있습니다. 2) Domapi를 통해 웹 페이지 조작, 3) 애니메이션 및 드래그 앤 드롭과 같은 복잡한 대화식 효과를 지원합니다. 4) 성능 및 모범 사례를 최적화하여 사용자 경험을 향상시킵니다.
 C 및 JavaScript : 연결이 설명되었습니다Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C 및 JavaScript : 연결이 설명되었습니다Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC 및 JavaScript는 WebAssembly를 통한 상호 운용성을 달성합니다. 1) C 코드는 WebAssembly 모듈로 컴파일되어 컴퓨팅 전력을 향상시키기 위해 JavaScript 환경에 도입됩니다. 2) 게임 개발에서 C는 물리 엔진 및 그래픽 렌더링을 처리하며 JavaScript는 게임 로직 및 사용자 인터페이스를 담당합니다.
 웹 사이트에서 앱으로 : 다양한 JavaScript 애플리케이션Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
웹 사이트에서 앱으로 : 다양한 JavaScript 애플리케이션Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript는 웹 사이트, 모바일 응용 프로그램, 데스크탑 응용 프로그램 및 서버 측 프로그래밍에서 널리 사용됩니다. 1) 웹 사이트 개발에서 JavaScript는 HTML 및 CSS와 함께 DOM을 운영하여 동적 효과를 달성하고 jQuery 및 React와 같은 프레임 워크를 지원합니다. 2) 반응 및 이온 성을 통해 JavaScript는 크로스 플랫폼 모바일 애플리케이션을 개발하는 데 사용됩니다. 3) 전자 프레임 워크를 사용하면 JavaScript가 데스크탑 애플리케이션을 구축 할 수 있습니다. 4) node.js는 JavaScript가 서버 측에서 실행되도록하고 동시 요청이 높은 높은 요청을 지원합니다.
 Python vs. JavaScript : 사용 사례 및 응용 프로그램 비교Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript : 사용 사례 및 응용 프로그램 비교Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython은 데이터 과학 및 자동화에 더 적합한 반면 JavaScript는 프론트 엔드 및 풀 스택 개발에 더 적합합니다. 1. Python은 데이터 처리 및 모델링을 위해 Numpy 및 Pandas와 같은 라이브러리를 사용하여 데이터 과학 및 기계 학습에서 잘 수행됩니다. 2. 파이썬은 간결하고 자동화 및 스크립팅이 효율적입니다. 3. JavaScript는 프론트 엔드 개발에 없어서는 안될 것이며 동적 웹 페이지 및 단일 페이지 응용 프로그램을 구축하는 데 사용됩니다. 4. JavaScript는 Node.js를 통해 백엔드 개발에 역할을하며 전체 스택 개발을 지원합니다.
 JavaScript 통역사 및 컴파일러에서 C/C의 역할Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript 통역사 및 컴파일러에서 C/C의 역할Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC와 C는 주로 통역사와 JIT 컴파일러를 구현하는 데 사용되는 JavaScript 엔진에서 중요한 역할을합니다. 1) C는 JavaScript 소스 코드를 구문 분석하고 추상 구문 트리를 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. 2) C는 바이트 코드 생성 및 실행을 담당합니다. 3) C는 JIT 컴파일러를 구현하고 런타임에 핫스팟 코드를 최적화하고 컴파일하며 JavaScript의 실행 효율을 크게 향상시킵니다.
 자바 스크립트 행동 : 실제 예제 및 프로젝트Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
자바 스크립트 행동 : 실제 예제 및 프로젝트Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM실제 세계에서 JavaScript의 응용 프로그램에는 프론트 엔드 및 백엔드 개발이 포함됩니다. 1) DOM 운영 및 이벤트 처리와 관련된 TODO 목록 응용 프로그램을 구축하여 프론트 엔드 애플리케이션을 표시합니다. 2) Node.js를 통해 RESTFULAPI를 구축하고 Express를 통해 백엔드 응용 프로그램을 시연하십시오.
 JavaScript 및 웹 : 핵심 기능 및 사용 사례Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript 및 웹 : 핵심 기능 및 사용 사례Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM웹 개발에서 JavaScript의 주요 용도에는 클라이언트 상호 작용, 양식 검증 및 비동기 통신이 포함됩니다. 1) DOM 운영을 통한 동적 컨텐츠 업데이트 및 사용자 상호 작용; 2) 사용자가 사용자 경험을 향상시키기 위해 데이터를 제출하기 전에 클라이언트 확인이 수행됩니다. 3) 서버와의 진실한 통신은 Ajax 기술을 통해 달성됩니다.


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

SublimeText3 영어 버전
권장 사항: Win 버전, 코드 프롬프트 지원!

ZendStudio 13.5.1 맥
강력한 PHP 통합 개발 환경

MinGW - Windows용 미니멀리스트 GNU
이 프로젝트는 osdn.net/projects/mingw로 마이그레이션되는 중입니다. 계속해서 그곳에서 우리를 팔로우할 수 있습니다. MinGW: GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)의 기본 Windows 포트로, 기본 Windows 애플리케이션을 구축하기 위한 무료 배포 가능 가져오기 라이브러리 및 헤더 파일로 C99 기능을 지원하는 MSVC 런타임에 대한 확장이 포함되어 있습니다. 모든 MinGW 소프트웨어는 64비트 Windows 플랫폼에서 실행될 수 있습니다.

Eclipse용 SAP NetWeaver 서버 어댑터
Eclipse를 SAP NetWeaver 애플리케이션 서버와 통합합니다.

Atom Editor Mac 버전 다운로드
가장 인기 있는 오픈 소스 편집기






