1. 도커 설치
실제로 시작하기 전에 Linux 시스템에 Docker가 설치되어 있는지 확인해야 합니다. 우리가 사용하는 호스트는 CentOS 7이므로 다음 명령을 사용하여 yum 관리자를 사용하여 docker를 설치합니다.
# yum install docker
# systemctl restart docker.service
2. 워드프레스 Dockerfile 생성
wordpress와 필수 구성 요소를 자동으로 설치하려면 Dockerfile을 만들어야 합니다. 이 Dockerfile은 WordPress 설치 이미지를 빌드하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 WordPress Dockerfile은 Docker Registry Hub에서 CentOS 7 이미지를 가져오고 사용 가능한 최신 업데이트로 시스템을 업그레이드합니다. 그런 다음 Nginx 웹 서버, PHP, MariaDB, Open SSH 서버 및 Docker 컨테이너의 올바른 작동에 필수적인 기타 구성 요소와 같은 필수 소프트웨어를 설치합니다. 마지막으로 WordPress 설치를 초기화하는 스크립트를 실행합니다.
# nano Dockerfile
그런 다음 Dockerfile에 다음 구성 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
FROM centos:centos7 MAINTAINER The CentOS Project <cloud-ops@centos.org> RUN yum -y update; yum clean all RUN yum -y install epel-release; yum clean all RUN yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server mariadb-client nginx php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-magickwand php-magpierss php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mssql php-shout php-snmp php-soap php-tidy php-apc pwgen python-setuptools curl git tar; yum clean all ADD ./start.sh /start.sh ADD ./nginx-site.conf /nginx.conf RUN mv /nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf RUN rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/* RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor-stdout ADD ./supervisord.conf /etc/supervisord.conf RUN echo %sudo ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL >> /etc/sudoers ADD http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz /wordpress.tar.gz RUN tar xvzf /wordpress.tar.gz RUN mv /wordpress/* /usr/share/nginx/html/. RUN chown -R apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/ RUN chmod 755 /start.sh RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd EXPOSE 80 EXPOSE 22 CMD ["/bin/bash", "/start.sh"]
3. 시작 스크립트 생성
Dockerfile을 생성한 후 WordPress 설치를 실행하고 구성하는 데 사용할 start.sh라는 스크립트를 생성해야 합니다. WordPress용 데이터베이스와 비밀번호를 생성하고 구성합니다. 즐겨 사용하는 텍스트 편집기로 start.sh를 엽니다.
# nano start.sh
start.sh를 연 후 파일에 다음 구성 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
#!/bin/bash
__check() {
if [ -f /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php ]; then
exit
fi
}
__create_user() {
# 创建用于 SSH 登录的用户
SSH_USERPASS=`pwgen -c -n -1 8`
useradd -G wheel user
echo user:$SSH_USERPASS | chpasswd
echo ssh user password: $SSH_USERPASS
}
__mysql_config() {
# 启用并运行 MySQL
yum -y erase mariadb mariadb-server
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/ /etc/my.cnf
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
mysql_install_db
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
/usr/bin/mysqld_safe &
sleep 10
}
__handle_passwords() {
# 在这里我们生成随机密码(多亏了 pwgen)。前面两个用于 mysql 用户,最后一个用于 wp-config.php 的随机密钥。
WORDPRESS_DB="wordpress"
MYSQL_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
WORDPRESS_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
# 这是在日志中显示的密码。
echo mysql root password: $MYSQL_PASSWORD
echo wordpress password: $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD
echo $MYSQL_PASSWORD > /mysql-root-pw.txt
echo $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD > /wordpress-db-pw.txt
# 这里原来是一个包括 sed、cat、pipe 和 stuff 的很长的行,但多亏了
# @djfiander 的 https://gist.github.com/djfiander/6141138
# 现在没有了
sed -e "s/database_name_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/username_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/password_here/$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD/
/'AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/" /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config-sample.php > /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__httpd_perms() {
chown apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__start_mysql() {
# systemctl 启动 mysqld 服务
mysqladmin -u root password $MYSQL_PASSWORD
mysql -uroot -p$MYSQL_PASSWORD -e "CREATE DATABASE wordpress; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wordpress'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
killall mysqld
sleep 10
}
__run_supervisor() {
supervisord -n
}
# 调用所有函数
__check
__create_user
__mysql_config
__handle_passwords
__httpd_perms
__start_mysql
__run_supervisor
위 구성을 추가한 후 파일을 저장하고 닫습니다.
4. 구성 파일 생성
이제 nginx-site.conf라는 Nginx 웹 서버용 구성 파일을 생성해야 합니다.
# nano nginx-site.conf
그런 다음 구성 파일에 다음 구성 정보를 추가합니다.
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}

이제 supervisor.conf 파일을 생성하고 다음 줄을 추가합니다.
# nano supervisord.conf
그런 다음 다음 줄을 추가하세요.
[unix_http_server] file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; (the path to the socket file) [supervisord] logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; (main log file;default $CWD/supervisord.log) logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (max main logfile bytes b4 rotation;default 50MB) logfile_backups=10 ; (num of main logfile rotation backups;default 10) loglevel=info ; (log level;default info; others: debug,warn,trace) pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord pidfile;default supervisord.pid) nodaemon=false ; (start in foreground if true;default false) minfds=1024 ; (min. avail startup file descriptors;default 1024) minprocs=200 ; (min. avail process descriptors;default 200) ; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC ; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be ; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections [rpcinterface:supervisor] supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface [supervisorctl] serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket [program:php-fpm] command=/usr/sbin/php-fpm -c /etc/php/fpm stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:php-fpm-log] command=tail -f /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm.log stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:mysql] command=/usr/bin/mysql --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/lib/mysql/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/var/log/mysql/error.log --pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid --socket=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock --port=3306 stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:nginx] command=/usr/sbin/nginx stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [eventlistener:stdout] command = supervisor_stdout buffer_size = 100 events = PROCESS_LOG result_handler = supervisor_stdout:event_handler
추가 후 파일을 저장하고 닫습니다.
5. WordPress 컨테이너 구축
이제 구성 파일과 스크립트 생성을 완료한 후 마침내 Dockerfile을 사용하여 최신 WordPress CMS(번역자 주: 콘텐츠 관리 시스템, 콘텐츠 관리 시스템)를 설치하는 데 필요한 컨테이너를 만들고 다음 지침에 따라 구성해야 합니다. 구성 파일 . 이를 위해서는 해당 디렉터리에서 다음 명령을 실행해야 합니다.
# docker build --rm -t wordpress:centos7 .
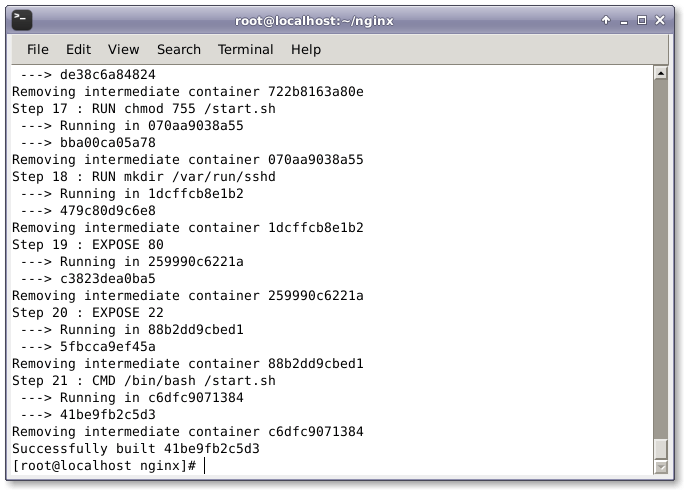
6. WordPress 컨테이너 실행
이제 다음 명령을 실행하여 새로 빌드된 컨테이너를 실행하고 Nginx 웹 서버 및 SSH 액세스를 위해 해당 포트 88 및 22를 엽니다.
# CID=$(docker run -d -p 80:80 wordpress:centos7)

다음 명령어를 실행하면 컨테이너 내부에서 실행되는 프로세스와 명령어를 확인할 수 있습니다.
# echo "$(docker logs $CID )"
다음 명령을 실행하여 포트 매핑이 올바른지 확인하세요.
# docker ps
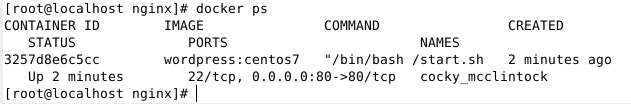
7. 웹 인터페이스
마지막으로 모든 것이 순조롭게 진행되면 브라우저로 http://ip-address/ 또는 http://mywebsite.com/을 열면 WordPress 환영 인터페이스가 표시됩니다.
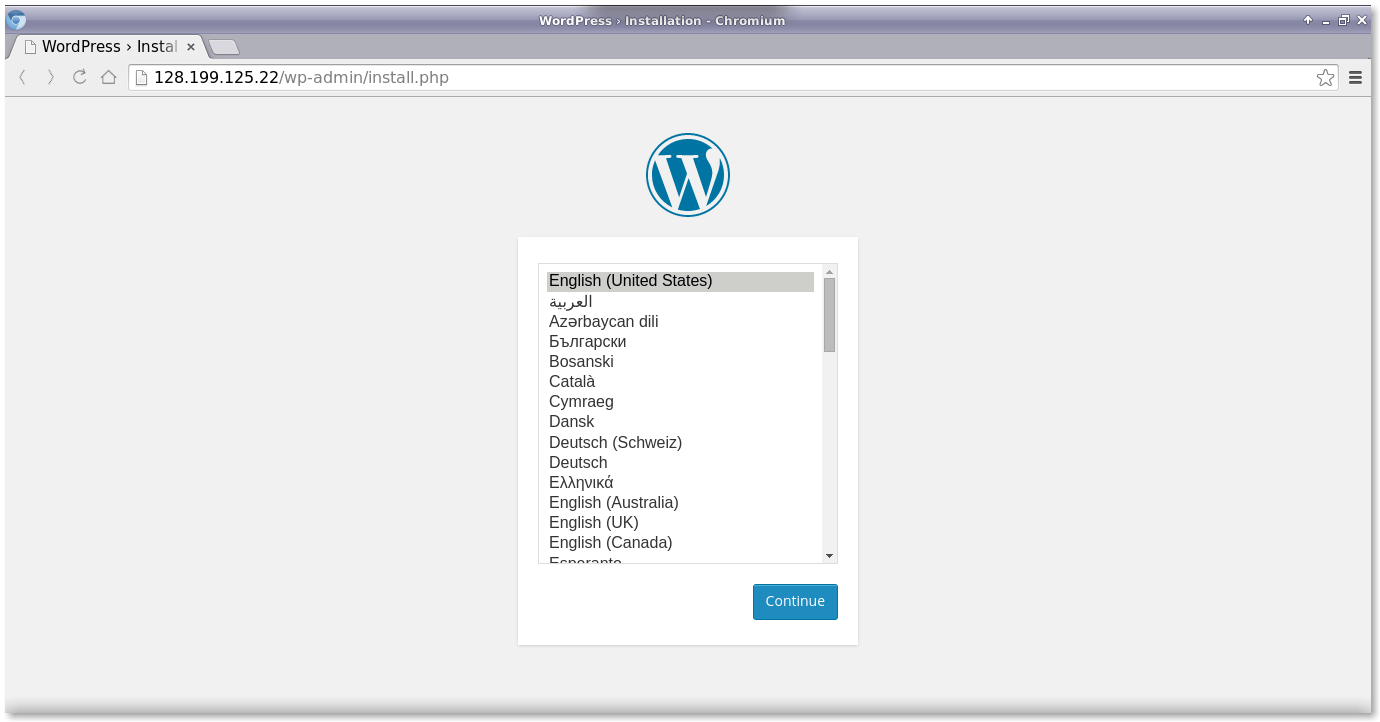
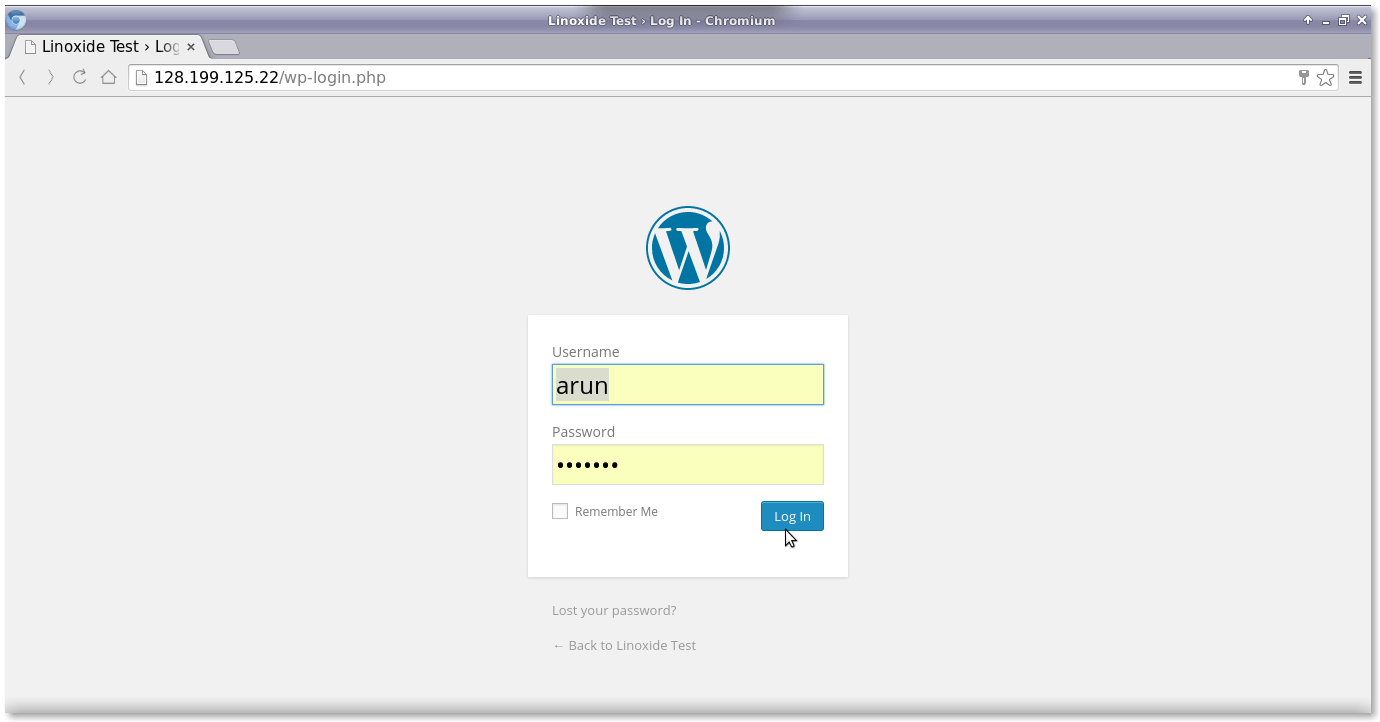
이제 웹 인터페이스를 통해 WordPress 패널의 WordPress 구성, 사용자 이름 및 비밀번호를 설정하겠습니다.
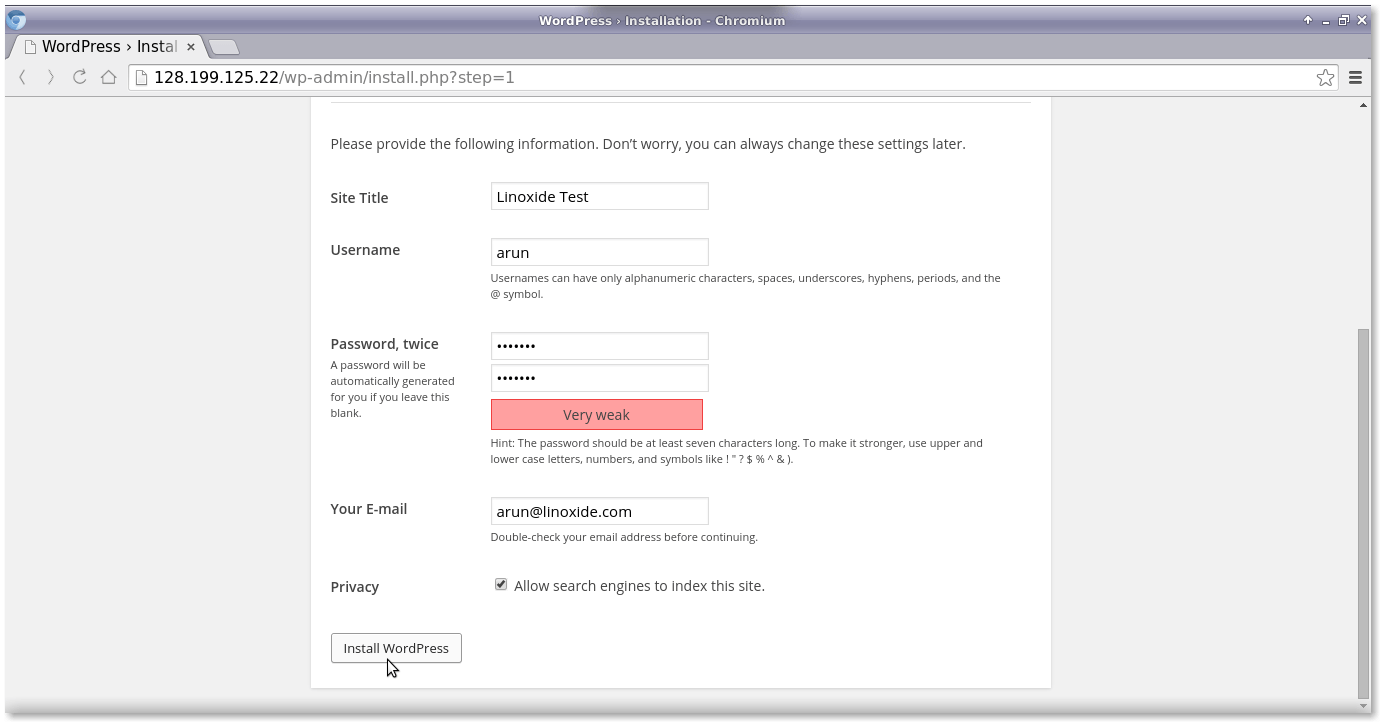
그런 다음 위의 사용자 이름과 비밀번호를 WordPress 로그인 인터페이스에 입력하세요.
요약
CentOS 7을 docker OS로 사용하여 LEMP 스택에서 WordPress CMS를 성공적으로 구축하고 실행했습니다. 보안 관점에서 볼 때 컨테이너에서 WordPress를 실행하는 것이 호스트 시스템에 대해 더 안전하고 안정적입니다. 이 게시물은 Docker 컨테이너에서 실행되는 Nginx 웹 서버에서 WordPress를 사용하기 위한 전체 구성을 다룹니다. 질문, 제안, 피드백이 있는 경우 아래 댓글 상자에 적어주시면 콘텐츠를 개선하고 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 매우 감사합니다! 즐겨보세요 :-)
 세션을 저장하기 위해 데이터베이스를 사용하면 어떤 장점이 있습니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:16 AM
세션을 저장하기 위해 데이터베이스를 사용하면 어떤 장점이 있습니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:16 AM데이터베이스 스토리지 세션 사용의 주요 장점에는 지속성, 확장 성 및 보안이 포함됩니다. 1. 지속성 : 서버가 다시 시작 되더라도 세션 데이터는 변경되지 않아도됩니다. 2. 확장 성 : 분산 시스템에 적용하여 세션 데이터가 여러 서버간에 동기화되도록합니다. 3. 보안 : 데이터베이스는 민감한 정보를 보호하기 위해 암호화 된 스토리지를 제공합니다.
 PHP에서 사용자 정의 세션 처리를 어떻게 구현합니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP에서 사용자 정의 세션 처리를 어떻게 구현합니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:16 AMSessionHandlerInterface 인터페이스를 구현하여 PHP에서 사용자 정의 세션 처리 구현을 수행 할 수 있습니다. 특정 단계에는 다음이 포함됩니다. 1) CustomsessionHandler와 같은 SessionHandlerInterface를 구현하는 클래스 만들기; 2) 인터페이스의 방법 (예 : Open, Close, Read, Write, Despare, GC)의 수명주기 및 세션 데이터의 저장 방법을 정의하기 위해 방법을 다시 작성합니다. 3) PHP 스크립트에 사용자 정의 세션 프로세서를 등록하고 세션을 시작하십시오. 이를 통해 MySQL 및 Redis와 같은 미디어에 데이터를 저장하여 성능, 보안 및 확장 성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 세션 ID 란 무엇입니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:13 AM
세션 ID 란 무엇입니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:13 AMSessionId는 웹 애플리케이션에 사용되는 메커니즘으로 사용자 세션 상태를 추적합니다. 1. 사용자와 서버 간의 여러 상호 작용 중에 사용자의 신원 정보를 유지하는 데 사용되는 무작위로 생성 된 문자열입니다. 2. 서버는 쿠키 또는 URL 매개 변수를 통해 클라이언트로 생성하여 보낸다. 3. 생성은 일반적으로 임의의 알고리즘을 사용하여 독창성과 예측 불가능 성을 보장합니다. 4. 실제 개발에서 Redis와 같은 메모리 내 데이터베이스를 사용하여 세션 데이터를 저장하여 성능 및 보안을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 무국적 환경 (예 : API)에서 세션을 어떻게 처리합니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
무국적 환경 (예 : API)에서 세션을 어떻게 처리합니까?Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJWT 또는 쿠키를 사용하여 API와 같은 무국적 환경에서 세션을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 1. JWT는 무국적자 및 확장 성에 적합하지만 빅 데이터와 관련하여 크기가 크다. 2. 쿠키는보다 전통적이고 구현하기 쉽지만 보안을 보장하기 위해주의해서 구성해야합니다.
 세션과 관련된 크로스 사이트 스크립팅 (XSS) 공격으로부터 어떻게 보호 할 수 있습니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:16 AM
세션과 관련된 크로스 사이트 스크립팅 (XSS) 공격으로부터 어떻게 보호 할 수 있습니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:16 AM세션 관련 XSS 공격으로부터 응용 프로그램을 보호하려면 다음 조치가 필요합니다. 1. 세션 쿠키를 보호하기 위해 Httponly 및 Secure 플래그를 설정하십시오. 2. 모든 사용자 입력에 대한 내보내기 코드. 3. 스크립트 소스를 제한하기 위해 컨텐츠 보안 정책 (CSP)을 구현하십시오. 이러한 정책을 통해 세션 관련 XSS 공격을 효과적으로 보호 할 수 있으며 사용자 데이터가 보장 될 수 있습니다.
 PHP 세션 성능을 어떻게 최적화 할 수 있습니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP 세션 성능을 어떻게 최적화 할 수 있습니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:13 AMPHP 세션 성능을 최적화하는 방법 : 1. 지연 세션 시작, 2. 데이터베이스를 사용하여 세션을 저장, 3. 세션 데이터 압축, 4. 세션 수명주기 관리 및 5. 세션 공유 구현. 이러한 전략은 높은 동시성 환경에서 응용의 효율성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
 SESSION.GC_MAXLIFETIME 구성 설정은 무엇입니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:10 AM
SESSION.GC_MAXLIFETIME 구성 설정은 무엇입니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:10 AMTHESESSION.GC_MAXLIFETIMESETTINGINSTTINGTINGSTINGTERMINESTERMINESTERSTINGSESSIONDATA, SETINSECONDS.1) IT'SCONFIGUDEDINPHP.INIORVIAINI_SET ()
 PHP에서 세션 이름을 어떻게 구성합니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP에서 세션 이름을 어떻게 구성합니까?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:08 AMPHP에서는 Session_Name () 함수를 사용하여 세션 이름을 구성 할 수 있습니다. 특정 단계는 다음과 같습니다. 1. Session_Name () 함수를 사용하여 Session_Name ( "my_session")과 같은 세션 이름을 설정하십시오. 2. 세션 이름을 설정 한 후 세션을 시작하여 세션을 시작하십시오. 세션 이름을 구성하면 여러 응용 프로그램 간의 세션 데이터 충돌을 피하고 보안을 향상시킬 수 있지만 세션 이름의 독창성, 보안, 길이 및 설정 타이밍에주의를 기울일 수 있습니다.


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

SublimeText3 중국어 버전
중국어 버전, 사용하기 매우 쉽습니다.

SublimeText3 영어 버전
권장 사항: Win 버전, 코드 프롬프트 지원!

SublimeText3 Linux 새 버전
SublimeText3 Linux 최신 버전

WebStorm Mac 버전
유용한 JavaScript 개발 도구

mPDF
mPDF는 UTF-8로 인코딩된 HTML에서 PDF 파일을 생성할 수 있는 PHP 라이브러리입니다. 원저자인 Ian Back은 자신의 웹 사이트에서 "즉시" PDF 파일을 출력하고 다양한 언어를 처리하기 위해 mPDF를 작성했습니다. HTML2FPDF와 같은 원본 스크립트보다 유니코드 글꼴을 사용할 때 속도가 느리고 더 큰 파일을 생성하지만 CSS 스타일 등을 지원하고 많은 개선 사항이 있습니다. RTL(아랍어, 히브리어), CJK(중국어, 일본어, 한국어)를 포함한 거의 모든 언어를 지원합니다. 중첩된 블록 수준 요소(예: P, DIV)를 지원합니다.






