PHP는 무한 분류(재귀를 사용하지 않고)_php 기술을 구현합니다.
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB원래의
- 2016-05-16 20:06:141068검색
부서구조, 기사분류 등 개발에서는 무한급 분류가 자주 사용됩니다. 무한 분류의 어려움은
과 같은 "출력"과 "쿼리"에 있습니다.- 기사 분류를
- 목록 형식으로 출력합니다.
카테고리 A에서 모든 카테고리에 포함된 기사를 찾아보세요.
1. 시행원칙
몇 가지 일반적인 구현 방법이 있으며 각 방법에는 장점과 단점이 있습니다. 그 중 '개선된 선주문 순회 트리' 데이터 구조는 출력 및 쿼리에는 편리하지만 모바일 분류 및 일반적인 이해에서는 다소 복잡합니다.
2. 데이터 구조
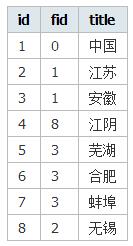
<?php
$list = array(
array('id'=>1, 'fid'=>0, 'title' => '中国'),
array('id'=>2, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '江苏'),
array('id'=>3, 'fid'=>1, 'title' => '安徽'),
array('id'=>4, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '江阴'),
array('id'=>5, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '芜湖'),
array('id'=>6, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '合肥'),
array('id'=>7, 'fid'=>3, 'title' => '蚌埠'),
array('id'=>8, 'fid'=>8, 'title' => '无锡')
);
?>
이 데이터 구조를 출력에 사용할 때 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 알고리즘은 "재귀"입니다. PHP 언어에 익숙한 친구들은 PHP가 재귀에 능숙하지 않다는 것과 재귀 횟수가 제한되어 있다는 것을 알아야 합니다(약 100회, 운영 체제 및 구성에 따라 다름)).
모든 재귀는 루프를 사용하여 구현할 수 있으므로 이 기사에서는 재귀 구현보다 효율적인 "무한 수준" 분류를 위한 함수 집합을 PHP 언어의 특성에 맞게 작성했습니다.
3. ul 목록 형식 출력
위의 데이터를 다음 HTML로 출력
<ul> <li class="first-child"> <div>江苏</div> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <div>无锡</div> <ul> <li class="first-child last-child"> <div>江阴</div> </li> </ul> </li> </ul> </li> <li class="last-child"> <div>安徽</div> <ul> <li class="first-child"><div>芜湖</div></li> <li><div>合肥</div></li> <li class="last-child"><div>蚌埠</div></li> </ul> </li> </ul>
<ul><?php echo get_tree_ul($list, 1); ?></ul>
4. 출력 옵션 목록 양식
<select> <option value="2">江苏</option> <option value="8"> 无锡</option> <option value="4"> 江阴</option> <option value="3">安徽</option> <option value="5"> 芜湖</option> <option value="6"> 合肥</option> <option value="7"> 蚌埠</option> </select>
<select>
<?php
// get_tree_option()返回数组,并为每个元素增加了“深度”(即depth)列,直接输出即可
$options = get_tree_option($list, 1);
foreach($options as $op) {
echo '<option value="' . $op['id'] .'">' . str_repeat(" ", $op['depth'] * 4) . $op['title'] . '<;/option>';
}
?>
<;/select>
5. 특정 카테고리의 모든 하위 카테고리 찾기
<?php
$children = get_tree_child($list, 0);
echo implode(',', $children); // 输出:1,3,2,7,6,5,8,4
?>
6. 특정 카테고리의 모든 상위 카테고리 찾기
<?php
$children = get_tree_parent($list, 4);
echo implode(',', $children); //8, 2, 10
?>
7. 관련 기능
<?php
function get_tree_child($data, $fid) {
$result = array();
$fids = array($fid);
do {
$cids = array();
$flag = false;
foreach($fids as $fid) {
for($i = count($data) - 1; $i >=0 ; $i--) {
$node = $data[$i];
if($node['fid'] == $fid) {
array_splice($data, $i , 1);
$result[] = $node['id'];
$cids[] = $node['id'];
$flag = true;
}
}
}
$fids = $cids;
} while($flag === true);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_parent($data, $id) {
$result = array();
$obj = array();
foreach($data as $node) {
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
while($value) {
$id = null;
foreach($data as $node) {
if($node['id'] == $value['fid']) {
$id = $node['id'];
$result[] = $node['id'];
break;
}
}
if($id === null) {
$result[] = $value['fid'];
}
$value = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
}
unset($obj);
return $result;
}
function get_tree_ul($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added_left = array();
$added_right= array();
$html_left = array();
$html_right = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
$cids = $child[$id];
$length = count($cids);
for($i = $length - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $cids[$i]);
}
$obj[$cids[$length - 1]]['isLastChild'] = true;
$obj[$cids[0]]['isFirstChild'] = true;
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_left[$id])) {
if(isset($node['isFirstChild']) && isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child last-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isFirstChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="first-child">';
} else if(isset($node['isLastChild'])) {
$html_left[] = '<li class="last-child">';
} else {
$html_left[] = '<li>';
}
$html_left[] = ($flag === true) ? "<div>{$node['title']}</div><ul>" : "<div>{$node['title']}</div>";
$added_left[$id] = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added_right[$id])) {
$html_right[] = ($flag === true) ? '</ul></li>' : '</li>';
$added_right[$id] = true;
}
if ($flag == false) {
if($node) {
$cids = $child[$node['fid']];
for ($i = count($cids) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($cids[$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
}
}
array_push($html_left, array_pop($html_right));
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $html_left;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return implode('', $html_left);
}
function get_tree_option($data, $fid) {
$stack = array($fid);
$child = array();
$added = array();
$options = array();
$obj = array();
$loop = 0;
$depth = -1;
foreach($data as $node) {
$pid = $node['fid'];
if(!isset($child[$pid])) {
$child[$pid] = array();
}
array_push($child[$pid], $node['id']);
$obj[$node['id']] = $node;
}
while (count($stack) > 0) {
$id = $stack[0];
$flag = false;
$node = isset($obj[$id]) ? $obj[$id] : null;
if (isset($child[$id])) {
for($i = count($child[$id]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
array_unshift($stack, $child[$id][$i]);
}
$flag = true;
}
if ($id != $fid && $node && !isset($added[$id])) {
$node['depth'] = $depth;
$options[] = $node;
$added[$id] = true;
}
if($flag == true){
$depth++;
} else {
if($node) {
for ($i = count($child[$node['fid']]) - 1; $i >= 0; $i--) {
if ($child[$node['fid']][$i] == $id) {
array_splice($child[$node['fid']], $i, 1);
break;
}
}
if(count($child[$node['fid']]) == 0) {
$child[$node['fid']] = null;
$depth--;
}
}
array_shift($stack);
}
$loop++;
if($loop > 5000) return $options;
}
unset($child);
unset($obj);
return $options;
}
?>
위의 소개는 재귀를 사용하지 않고 PHP에서 Infinitus 분류를 구현하는 방법에 대한 내용입니다. 모든 분들의 학습에 도움이 되기를 바랍니다.
성명:
본 글의 내용은 네티즌들의 자발적인 기여로 작성되었으며, 저작권은 원저작자에게 있습니다. 본 사이트는 이에 상응하는 법적 책임을 지지 않습니다. 표절이나 침해가 의심되는 콘텐츠를 발견한 경우 admin@php.cn으로 문의하세요.

