bitmap是很常用的数据结构,比如用于Bloom Filter中;用于无重复整数的排序等等。bitmap通常基于数组来实现,数组中每个元素可以看成是一系列二进制数,所有元素组成更大的二进制集合。对于Python来说,整数类型默认是有符号类型,所以一个整数的可用位数为31位。
bitmap实现思路
bitmap是用于对每一位进行操作。举例来说,一个Python数组包含4个32位有符号整型,则总共可用位为4 * 31 = 124位。如果要在第90个二进制位上操作,则要先获取到操作数组的第几个元素,再获取相应的位索引,然后执行操作。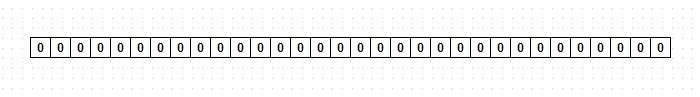
上图所示为一个32位整型,在Python中默认是有符号类型,最高位为符号位,bitmap不能使用它。左边是高位,右边是低位,最低位为第0位。
bitmap是用于对每一位进行操作。举例来说,一个Python数组包含4个32位有符号整型,则总共可用位为4 * 31 = 124位。如果要在第90个二进制位上操作,则要先获取到操作数组的第几个元素,再获取相应的位索引,然后执行操作。
初始化bitmap
首先需要初始化bitmap。拿90这个整数来说,因为单个整型只能使用31位,所以90除以31并向上取整则可得知需要几个数组元素。代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = int((max + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(90)
print '需要 %d 个元素。' % bitmap.size
$ python bitmap.py
需要 3 个元素。
计算在数组中的索引
计算在数组中的索引其实是跟之前计算数组大小是一样的。只不过之前是对最大数计算,现在换成任一需要存储的整数。但是有一点不同,计算在数组中的索引是向下取整,所以需要修改calcElemIndex方法的实现。代码改为如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(90)
print '数组需要 %d 个元素。' % bitmap.size
print '47 应存储在第 %d 个数组元素上。' % bitmap.calcElemIndex(47)
$ python bitmap.py
数组需要 3 个元素。
47 应存储在第 1 个数组元素上。
所以获取最大整数很重要,否则有可能创建的数组容纳不下某些数据。
计算在数组元素中的位索引
数组元素中的位索引可以通过取模运算来得到。令需存储的整数跟31取模即可得到位索引。代码改为如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
def calcBitIndex(self, num):
return num % 31
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(90)
print '数组需要 %d 个元素。' % bitmap.size
print '47 应存储在第 %d 个数组元素上。' % bitmap.calcElemIndex(47)
print '47 应存储在第 %d 个数组元素的第 %d 位上。' % (bitmap.calcElemIndex(47), bitmap.calcBitIndex(47),)
别忘了是从第0位算起哦。
置1操作
二进制位默认是0,将某位置1则表示在此位存储了数据。代码改为如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
def calcBitIndex(self, num):
return num % 31
def set(self, num):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(num)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(num)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem | (1
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(90)
bitmap.set(0)
print bitmap.array
因为从第0位算起,所以如需要存储0,则需要把第0位置1。
清0操作
将某位置0,也即丢弃已存储的数据。代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
def calcBitIndex(self, num):
return num % 31
def set(self, num):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(num)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(num)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem | (1
def clean(self, i):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(i)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(i)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem & (~(1
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(87)
bitmap.set(0)
bitmap.set(34)
print bitmap.array
bitmap.clean(0)
print bitmap.array
bitmap.clean(34)
print bitmap.array
清0和置1是互反操作。
测试某位是否为1
判断某位是否为1是为了取出之前所存储的数据。代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
def calcBitIndex(self, num):
return num % 31
def set(self, num):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(num)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(num)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem | (1
def clean(self, i):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(i)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(i)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem & (~(1
def test(self, i):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(i)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(i)
if self.array[elemIndex] & (1 return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
bitmap = Bitmap(90)
bitmap.set(0)
print bitmap.array
print bitmap.test(0)
bitmap.set(1)
print bitmap.test(1)
print bitmap.test(2)
bitmap.clean(1)
print bitmap.test(1)
$ python bitmap.py
[1, 0, 0]
True
True
False
False
接下来实现一个不重复数组的排序。已知一个无序非负整数数组的最大元素为879,请对其自然排序。代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf8
class Bitmap(object):
def __init__(self, max):
self.size = self.calcElemIndex(max, True)
self.array = [0 for i in range(self.size)]
def calcElemIndex(self, num, up=False):
'''up为True则为向上取整, 否则为向下取整'''
if up:
return int((num + 31 - 1) / 31) #向上取整
return num / 31
def calcBitIndex(self, num):
return num % 31
def set(self, num):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(num)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(num)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem | (1
def clean(self, i):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(i)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(i)
elem = self.array[elemIndex]
self.array[elemIndex] = elem & (~(1
def test(self, i):
elemIndex = self.calcElemIndex(i)
byteIndex = self.calcBitIndex(i)
if self.array[elemIndex] & (1 return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
MAX = 879
suffle_array = [45, 2, 78, 35, 67, 90, 879, 0, 340, 123, 46]
result = []
bitmap = Bitmap(MAX)
for num in suffle_array:
bitmap.set(num)
for i in range(MAX + 1):
if bitmap.test(i):
result.append(i)
print '原始数组为: %s' % suffle_array
print '排序后的数组为: %s' % result
bitmap实现了,则利用其进行排序就非常简单了。其它语言也同样可以实现bitmap,但对于静态类型语言来说,比如C/Golang这样的语言,因为可以直接声明无符号整型,所以可用位就变成32位,只需将上述代码中的31改成32即可,这点请大家注意。
 어레이는 파이썬으로 과학 컴퓨팅에 어떻게 사용됩니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AM
어레이는 파이썬으로 과학 컴퓨팅에 어떻게 사용됩니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AMArraysinpython, 특히 비밀 복구를위한 ArecrucialInscientificcomputing.1) theaRearedFornumericalOperations, DataAnalysis 및 MachinELearning.2) Numpy'SimplementationIncensuressuressurations thanpythonlists.3) arraysenablequick
 같은 시스템에서 다른 파이썬 버전을 어떻게 처리합니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AM
같은 시스템에서 다른 파이썬 버전을 어떻게 처리합니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AMPyenv, Venv 및 Anaconda를 사용하여 다양한 Python 버전을 관리 할 수 있습니다. 1) PYENV를 사용하여 여러 Python 버전을 관리합니다. Pyenv를 설치하고 글로벌 및 로컬 버전을 설정하십시오. 2) VENV를 사용하여 프로젝트 종속성을 분리하기 위해 가상 환경을 만듭니다. 3) Anaconda를 사용하여 데이터 과학 프로젝트에서 Python 버전을 관리하십시오. 4) 시스템 수준의 작업을 위해 시스템 파이썬을 유지하십시오. 이러한 도구와 전략을 통해 다양한 버전의 Python을 효과적으로 관리하여 프로젝트의 원활한 실행을 보장 할 수 있습니다.
 표준 파이썬 어레이를 통해 Numpy Array를 사용하면 몇 가지 장점은 무엇입니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AM
표준 파이썬 어레이를 통해 Numpy Array를 사용하면 몇 가지 장점은 무엇입니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AMNumpyarrayshaveseveraladvantagesstandardpythonarrays : 1) thearemuchfasterduetoc 기반 간증, 2) thearemorememory-refficient, 특히 withlargedatasets 및 3) wepferoptizedformationsformationstaticaloperations, 만들기, 만들기
 어레이의 균질 한 특성은 성능에 어떤 영향을 미칩니 까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:13 AM
어레이의 균질 한 특성은 성능에 어떤 영향을 미칩니 까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:13 AM어레이의 균질성이 성능에 미치는 영향은 이중입니다. 1) 균질성은 컴파일러가 메모리 액세스를 최적화하고 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 2) 그러나 유형 다양성을 제한하여 비 효율성으로 이어질 수 있습니다. 요컨대, 올바른 데이터 구조를 선택하는 것이 중요합니다.
 실행 파이썬 스크립트를 작성하기위한 모범 사례는 무엇입니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:11 AM
실행 파이썬 스크립트를 작성하기위한 모범 사례는 무엇입니까?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:11 AMtocraftexecutablepythonscripts, 다음과 같은 비스트 프랙티스를 따르십시오 : 1) 1) addashebangline (#!/usr/bin/envpython3) tomakethescriptexecutable.2) setpermissionswithchmod xyour_script.py.3) organtionewithlarstringanduseifname == "__"
 Numpy 배열은 배열 모듈을 사용하여 생성 된 배열과 어떻게 다릅니 까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:53 PM
Numpy 배열은 배열 모듈을 사용하여 생성 된 배열과 어떻게 다릅니 까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:53 PMnumpyarraysarebetterfornumericaloperations 및 multi-dimensionaldata, mumemer-efficientArrays
 Numpy Array의 사용은 Python에서 어레이 모듈 어레이를 사용하는 것과 어떻게 비교됩니까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
Numpy Array의 사용은 Python에서 어레이 모듈 어레이를 사용하는 것과 어떻게 비교됩니까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:49 PMnumpyarraysarebetterforheavynumericalcomputing, whilearraymoduleisiMoresuily-sportainedprojectswithsimpledatatypes.1) numpyarraysofferversatively 및 formanceforgedatasets 및 complexoperations.2) Thearraymoduleisweighit 및 ep
 CTYPES 모듈은 파이썬의 어레이와 어떤 관련이 있습니까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
CTYPES 모듈은 파이썬의 어레이와 어떤 관련이 있습니까?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:45 PMctypesallowscreatingandmanipulatingC-stylearraysinPython.1)UsectypestointerfacewithClibrariesforperformance.2)CreateC-stylearraysfornumericalcomputations.3)PassarraystoCfunctionsforefficientoperations.However,becautiousofmemorymanagement,performanceo


핫 AI 도구

Undresser.AI Undress
사실적인 누드 사진을 만들기 위한 AI 기반 앱

AI Clothes Remover
사진에서 옷을 제거하는 온라인 AI 도구입니다.

Undress AI Tool
무료로 이미지를 벗다

Clothoff.io
AI 옷 제거제

Video Face Swap
완전히 무료인 AI 얼굴 교환 도구를 사용하여 모든 비디오의 얼굴을 쉽게 바꾸세요!

인기 기사

뜨거운 도구

안전한 시험 브라우저
안전한 시험 브라우저는 온라인 시험을 안전하게 치르기 위한 보안 브라우저 환경입니다. 이 소프트웨어는 모든 컴퓨터를 안전한 워크스테이션으로 바꿔줍니다. 이는 모든 유틸리티에 대한 액세스를 제어하고 학생들이 승인되지 않은 리소스를 사용하는 것을 방지합니다.

PhpStorm 맥 버전
최신(2018.2.1) 전문 PHP 통합 개발 도구

MinGW - Windows용 미니멀리스트 GNU
이 프로젝트는 osdn.net/projects/mingw로 마이그레이션되는 중입니다. 계속해서 그곳에서 우리를 팔로우할 수 있습니다. MinGW: GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)의 기본 Windows 포트로, 기본 Windows 애플리케이션을 구축하기 위한 무료 배포 가능 가져오기 라이브러리 및 헤더 파일로 C99 기능을 지원하는 MSVC 런타임에 대한 확장이 포함되어 있습니다. 모든 MinGW 소프트웨어는 64비트 Windows 플랫폼에서 실행될 수 있습니다.

맨티스BT
Mantis는 제품 결함 추적을 돕기 위해 설계된 배포하기 쉬운 웹 기반 결함 추적 도구입니다. PHP, MySQL 및 웹 서버가 필요합니다. 데모 및 호스팅 서비스를 확인해 보세요.

VSCode Windows 64비트 다운로드
Microsoft에서 출시한 강력한 무료 IDE 편집기






